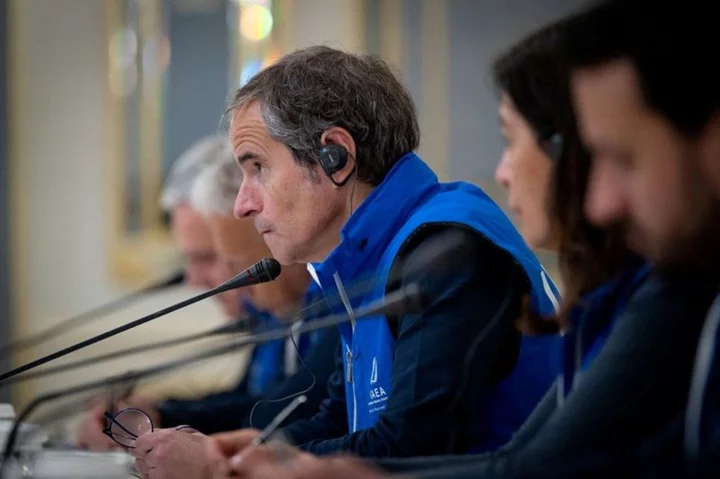

U.N. nuclear chief delays Ukraine nuclear plant visit over security
By Pavel Polityuk KYIV (Reuters) -U.N. nuclear chief Rafael Grossi delayed a trip to the Russian-held Zaporizhzhia nuclear power station
2023-06-14 23:22
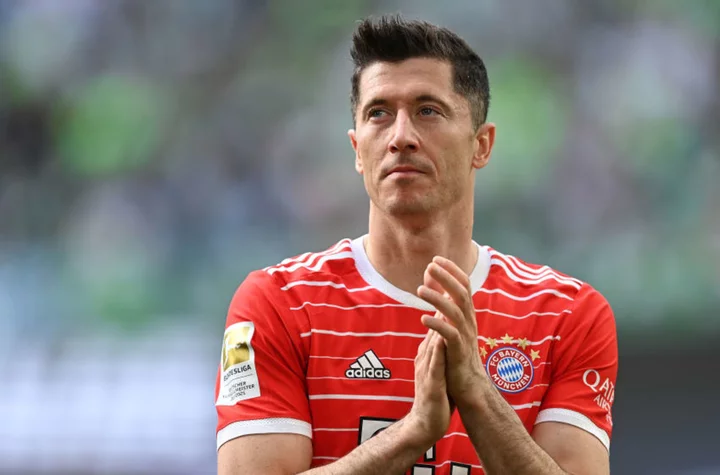

The 15 best goal-scoring seasons in Bundesliga history
Robert Lewandowski is no longer in the Bundesliga as he now plays for Barcelona but it would take some doing for any player to replicate his remarkable goal-scoring exploits. Here are the 15 best goal-scoring seasons in Bundesliga history.
2023-10-07 00:05

Critics lambast Lily-Rose Depp starrer 'The Idol' for 'graphic' sex scenes and too much nudity
A critics called 'The Idol' 'more regressive than transgressive' while slamming HBO for marketing the show
2023-05-23 23:30

Zac Efron was jealous of Leonardo DiCaprio's success before star advised him how to handle his own fame
'I look at young Zac Efron and think 'Go get it pal, leave me in peace, I was never happy with the teen idol tag at all,' said Leonardo DiCaprio
2023-06-17 16:09

Hong Kong’s Regulator Buys 12 Floors From Swire Properties
Hong Kong’s market regulator bought 12 floors in its current office building from Swire Properties Ltd. for HK$5.4
2023-11-17 17:50
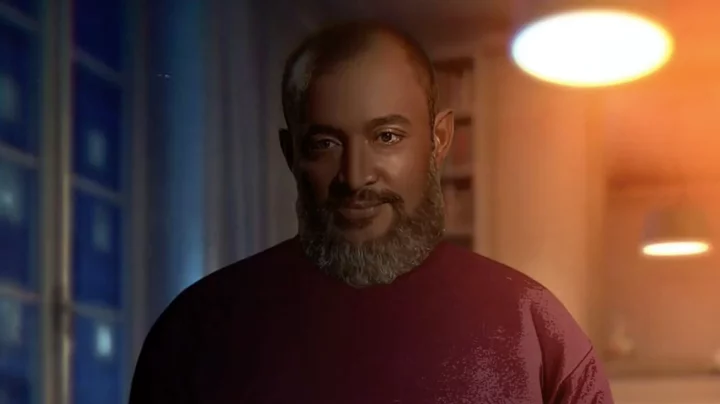

Saudi club's latest transfer announcement video called 'terrifying'
Saudi Arabia have been spending an awful lot in the transfer window already this year, but they’ll have to up their transfer announcement video game if they want to become a real force in the world of football social media. Fans are reacting with bewilderment after Saudi Pro League club Al Ittihad released an incredibly strange clip confirming the signing of Celtic winger Jota. They’ve already signed Karim Benzema and N'Golo Kante, and now they decided that they’d push the boat out with the new announcement. Jota, who cost £25 million from the Scottish club, appears in the new clip, which stars a very CGI-looking version of manager Nuno Espirito Santo. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The clip, which has racked up millions of views, sees this uncanny-looking version of Santo watching Joto play on TV leaving many unnerved. Then, an android-looking version of the coach puts on a suit and drives to a shop. When he’s there, he is dealt a pack of cards that all feature Celtic players. After choosing Jota, he puts them in a fresh pack alongside Benzema and Kante, before saying: "We want to rule the world." Football writer Si Lloyd wrote: “Don’t think I’ve ever been quite so terrified of football.” A fan added: “Babe wake up the most unhinged new signing announcement video of all time just dropped.” Another commented: "Nah cause why are the graphics so scary, like it’s a trailer for a horror film." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-04 18:30

PwC Barred From All New RBA Contracts Until Scandal Clears
Reserve Bank of Australia Governor Philip Lowe said he’s “appalled” by the tax scandal that’s engulfed PricewaterhouseCoopers and
2023-05-31 08:34

A look inside Donald Trump's deposition: Defiance, deflection and the 'hottest brand in the world'
In newly public testimony, Donald Trump boasts about building a multibillion-dollar brand and saving “millions of lives” as president
2023-09-01 07:23
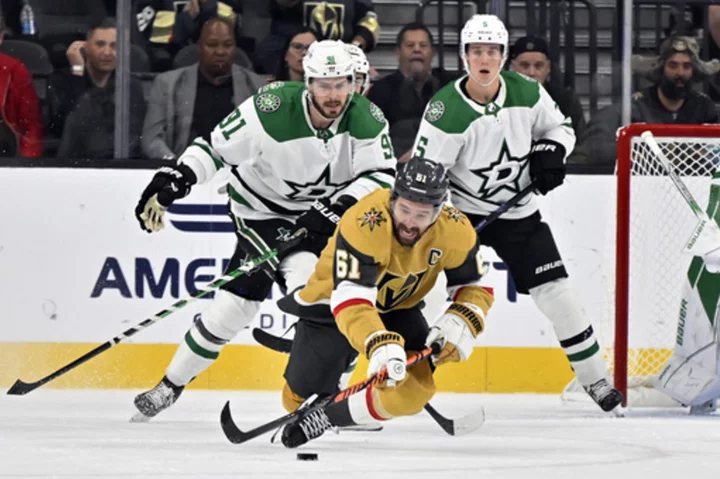

Marchessault breaks tie in shootout, unbeaten Golden Knights beat Stars 3-2
Jonathan Marchessault broke a shootout tie in the Vegas Golden Knights’ 3-2 victory over the Dallas Stars on Tuesday night in a Western Conference final rematch
2023-10-18 13:42
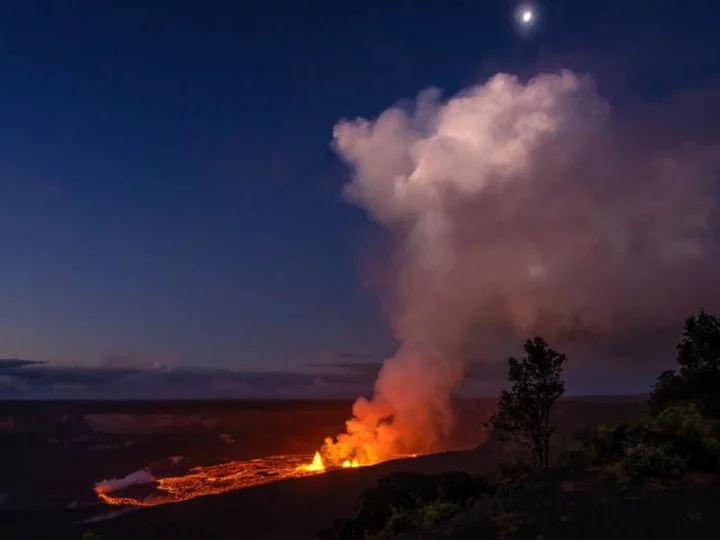

Alert level lowered for Hawaii's erupting Kilauea volcano as thousands watch the dazzling display
US officials lowered the warning level for Hawaii's erupting Kīlauea volcano on Thursday, saying the burst of lava spewing from within one of its craters has lowered.
2023-06-09 07:07

Schott to Hold IPO of Medical Glassware Unit in September
Schott AG plans to list its specialty medical-glassware division as soon as September, according to people familiar with
2023-06-22 13:30
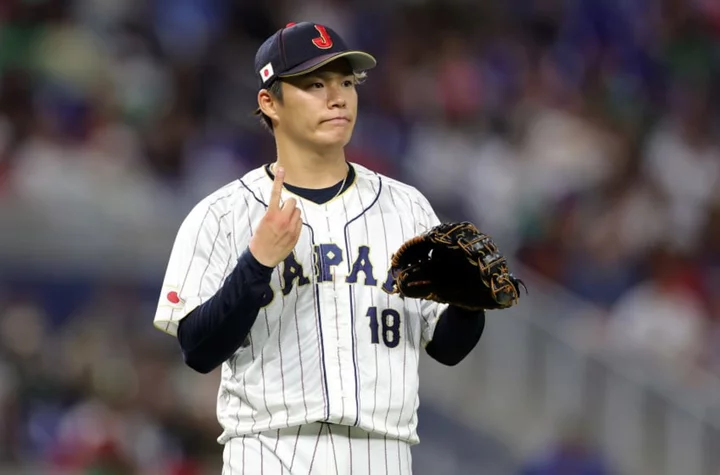

MLB Rumors: 5 Yoshinobu Yamamoto free agency fits after Japanese star’s no-hitter
Yoshinobu Yamamoto will have a plethora of suitors as he's set to hit free agency. His stock only increased after his no-hitter.
2023-09-10 07:37
You Might Like...

CSquared delivers high-speed connectivity to Togo with Adtran open optical solution

Cheika -- behind the quips, a shrewd rugby brain
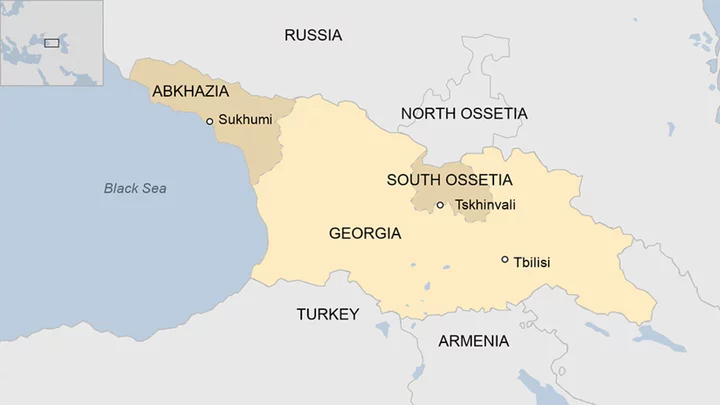
South Ossetia profile
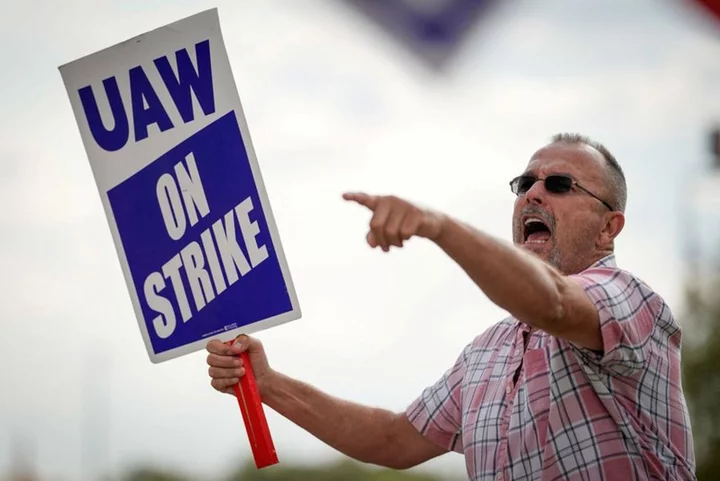

As UAW strike looms, Biden admin considers aid for small suppliers -source

Elon Musk called out by Princess Bride actor after quoting beloved movie
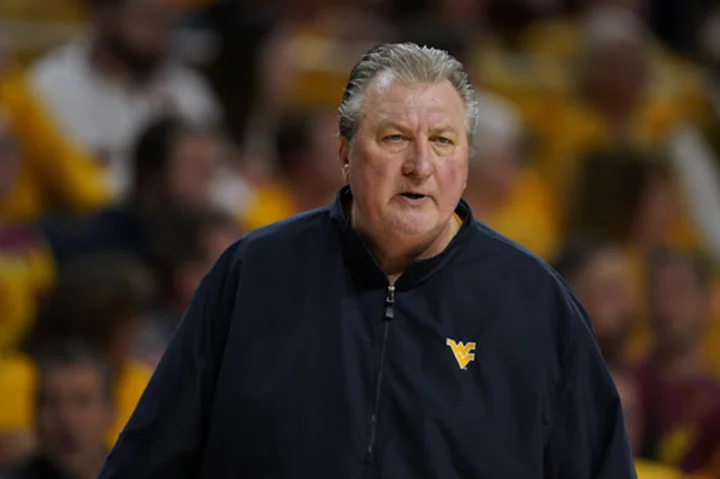

West Virginia basketball coach Bob Huggins resigns hours after drunken driving arrest

Microsoft-backed AI4Bharat set to raise $12 million funding from Peak XV, Lightspeed - sources
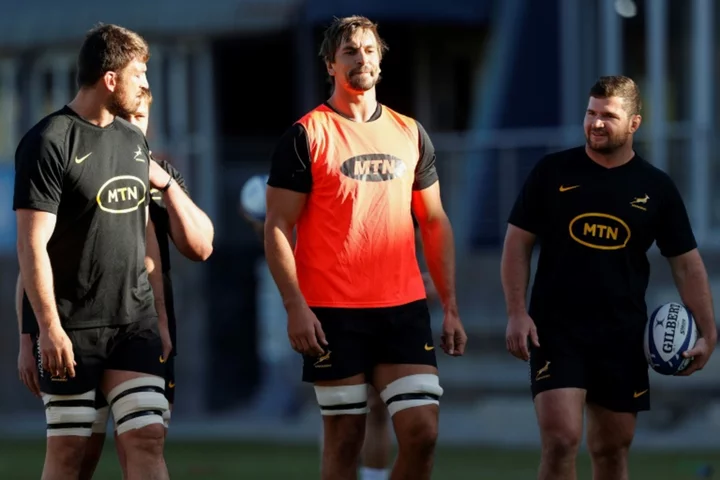

Etzebeth returns to captain reshuffled Springboks against All Blacks
