
European shares inch lower ahead of ECB meet
European shares opened lower on Thursday, as the European Central Bank (ECB) was expected to raise borrowing costs
2023-06-15 15:27

Antonio Alvarez: Phoenix Police launches search for missing man with dementia
Antonio Alvarez is a 60-year-old man, standing 5 feet 8 inches tall and weighing approximately 180 pounds
2023-11-26 19:27

Best Monday Night Football Fantasy Picks for Broncos vs. Bills
Find out our best fantasy football picks for Broncos vs. Bills on Monday Night Football and how you can utilize Sleeper Picks' 100% deposit match for the game!
2023-11-14 01:24

Is Luke Bryan OK? 'American Idol' judge cancels third show in three days, fans ask him to get some rest
Luke Bryan was slated to perform at the Watershed Festival on Sunday, August 6, in George, Washington
2023-08-08 17:54

Does Pokimane want to have a baby? Twitch queen reacts to Mizkif's reservations about having children as a streamer
The Twitch personalities discussed their future in live streaming, with Mizkif expressing his firm stance of never having children
2023-07-06 18:48
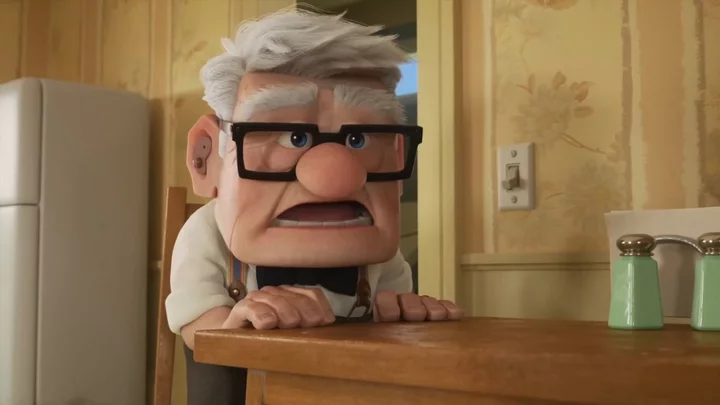

Carl from 'Up' is back in a new short film and everyone is crying again
Carl from Pixar's hit movie 'Up' is back, and everyone is preparing to be in tears all over again. The sweet old man is reappearing in a new short film that sees him finally go on a date following the death of his wife, which was explored in the original movie. Of course, Doug the dog will be there for the ride too, advising Carl on whether the chocolates he bought for his date are good enough. Carl's date is released on 16 June. Sign up to our new free Indy100 weekly newsletter
2023-06-14 23:58
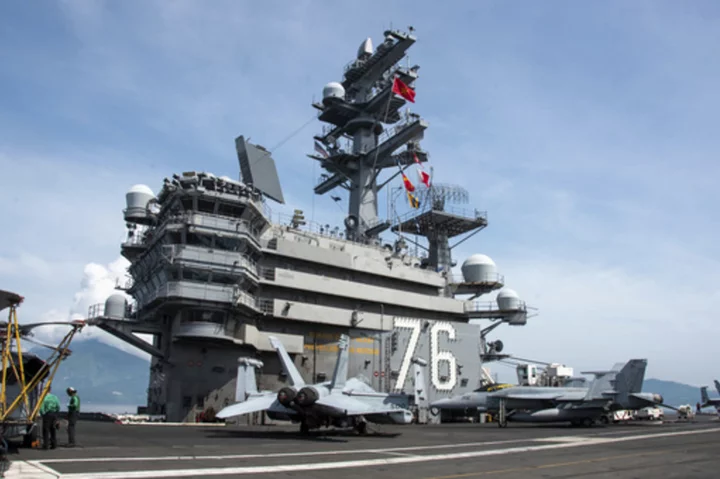

US aircraft carrier makes Da Nang port call as America looks to strengthen ties with Vietnam
A U.S. aircraft carrier and two guided missile cruisers are visiting Vietnam in a rare port call that comes as the United States and China increasingly vie for influence in Southeast Asia
2023-06-26 13:31
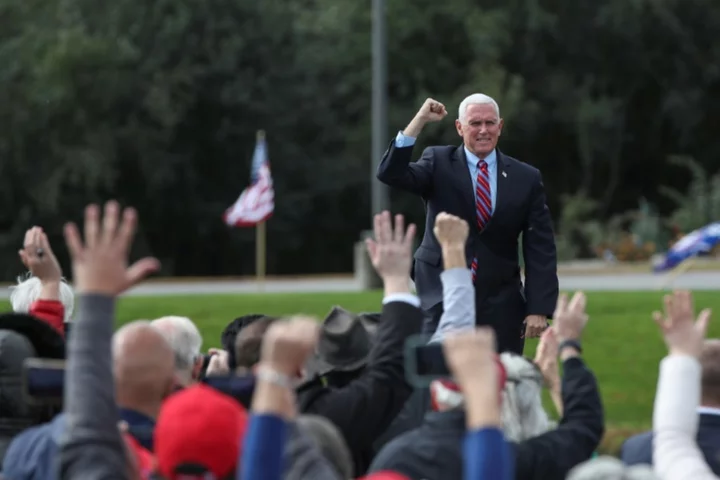

Ex-VP Pence jumps into 2024 White House race
Republican former vice president Mike Pence launched Monday his hotly-anticipated challenge to one-time boss Donald Trump for the party's 2024 White House nomination, setting up the unusual scenario...
2023-06-06 00:44

BlackRock Backs Fewer Climate, Social Shareholder Proposals
BlackRock Inc. backed fewer shareholder proposals on environmental and social issues over the past year as it stressed
2023-08-23 19:00
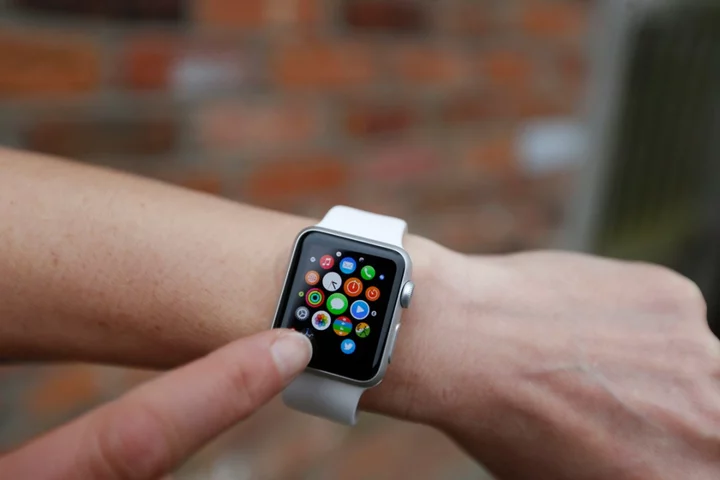

Watch X: Apple working on dramatic redesign for its wearable, report claims
Apple is working on a “Watch X”, bring a major redesign and new features to its wearable, according to a new report. The new version will be thinner, bring new health features such as a blood pressure sensor and change the technology powering the screen, according to a new report from Bloomberg’s Mark Gurman. But the new version of the Watch might not arrive until next year, or even the year after that, he reported. As such, the new design would mark the 10th anniversary of the Watch, which went on sale in April 2015. Apple undertook a similar significant redesign for the 10th version of the iPhone, with the iPhone X. That also brought a new look, with a slimmer design and a display that wrapped all the way to the edge of the phone, and new technologies such as facial recognition. This year’s Apple Watch is expected to bring a new processor, which would be the first since 2020’s Series 6. Otherwise, it is expected to stay largely the same on the outside. That might give Apple more time to work on that rumoured “Apple Watch X”, for the years that would follow. As well as the new redesign and features, it might rely on a microLED screen that has not yet been seen in the Apple Watch. Apple has long been rumoured to be working on such screen technology for the Watch, to bring the brighter and more colourful screen technology to the small display. Rumours have suggested however that the company has struggled with the new technology, and hit problems with shrinking it down to the size of the Watch and allowing it to stay affordable. The other major feature update is said to be a blood pressure built into the Watch itself. Chief executive Tim Cook has repeatedly said that health is one of the big focuses of Apple’s work, and has been rumoured to be working on new sensors including blood glucose and blood pressure, presumably for its wearables. The redesign could have some drawbacks. The redesign will bring with it a new, magnetic way of attaching watchbands – which would presumably mean that existing Watch straps will not work with the Watch X. Until now, all versions of the Watch have been compatible with all of Apple’s straps, as long as they are the correct one of two sizes. Mr Gurman did suggest on Twitter that Apple or third-party manufacturers could create adapters to allow old straps to work on new Watches. Read More Apple Watch 7 pre-order: How to buy the new smartwatch in the UK Apple introduces new version of Watch with complete redesign iPhone 13 - live: UK contract deals and prices for Apple, EE and O2
2023-08-15 01:06
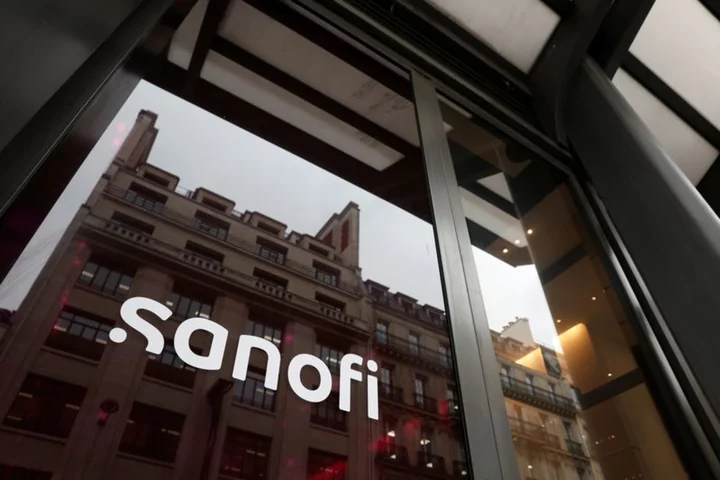

US CDC panel recommends Sanofi-AstraZeneca's preventive RSV therapy for babies
(Reuters) -The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) said its advisory panel on Thursday recommended use of Sanofi
2023-08-04 07:12
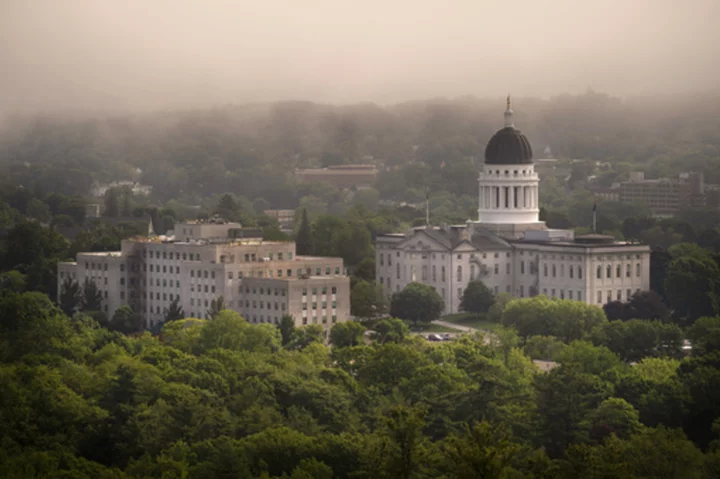

Maine governor expected to sign bill easing restrictions on abortions later in pregnancy
The Maine Senate has given final approval to a bill that would expand access to abortions later in pregnancy, sending the proposal to the governor for her signature
2023-07-07 07:24
You Might Like...
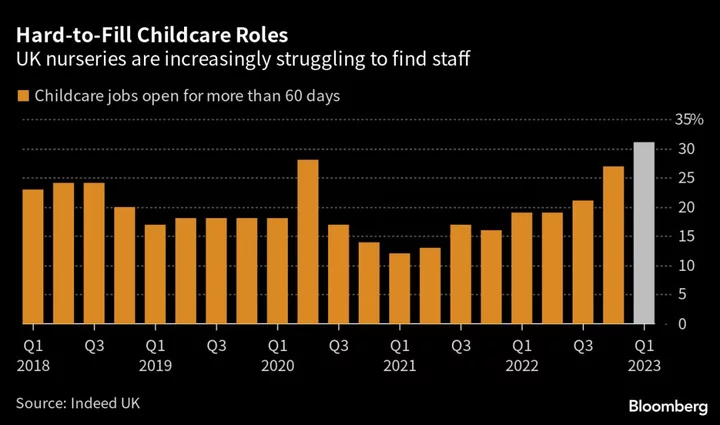
UK Government Killed Au Pair Industry, Leaving British Parents Desperate

Western Australia to overturn 2021 Aboriginal heritage protection laws

Raiders on the cusp of making an irredeemable mistake with Davante Adams

Ederson ready to bet Champions League glory on continuing to ‘play with personality’

The danger of America’s aging politicians

How to Apply for Fortnite FTC Refund

Euro slips as Germany enters recession, dollar hits 2-month peak
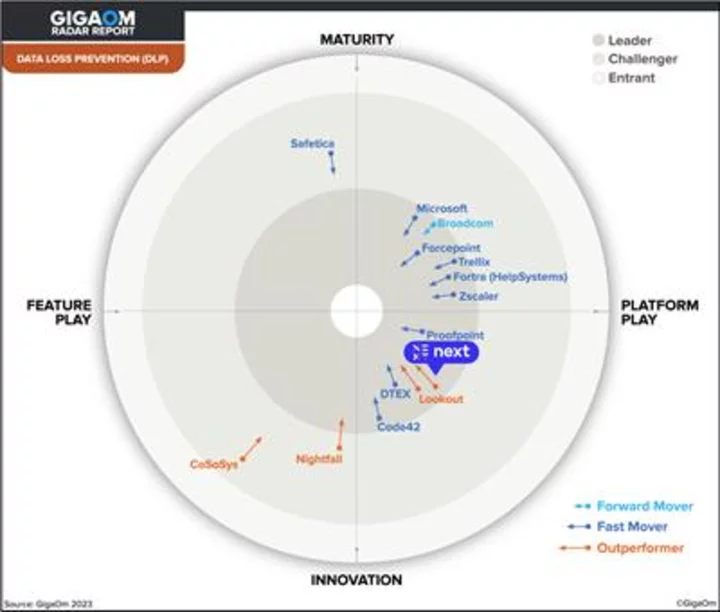
Next Named a “Leader” in GigaOm Radar for Data Loss Prevention
