
'GMA' host Michael Strahan's daughter Sophia stuns in black as she shares snaps of Thanksgiving with sister and father's girlfriend
Sophia celebrated Thanksgiving with her sister, her father Michael Strahan and his girlfriend Kayla Quick
2023-11-24 16:43
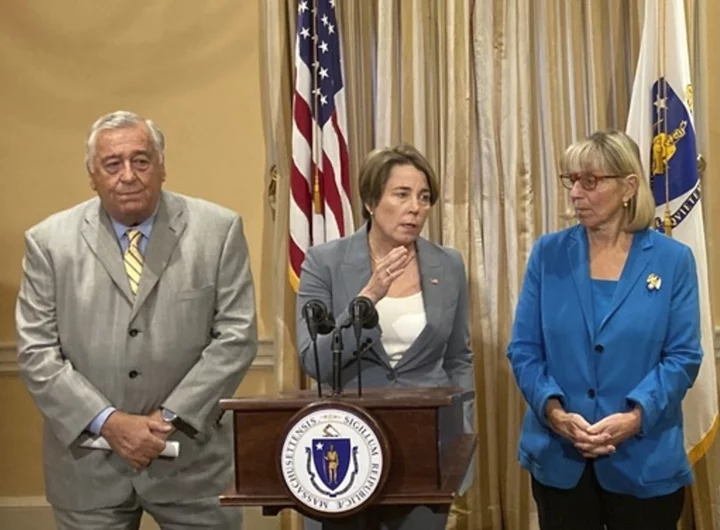

Massachusetts to begin denying shelter beds to homeless families, putting names on a waitlist
The number of homeless families seeking emergency shelter in Massachusetts is nearing a 7,500-family threshold, past which Democratic Gov. Maura Healey says the state can no longer guarantee shelter
2023-11-09 04:33
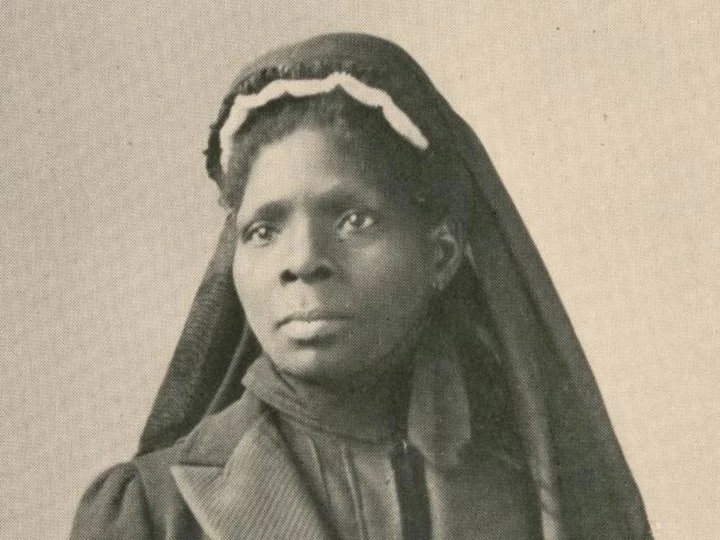

Savannah renames historic square after Black woman who taught emancipated slaves to read and write
The city council of Savannah, Georgia, voted Thursday to rename a downtown square after Susie King Taylor, a Black woman who once taught slaves to read and write.
2023-08-26 06:00
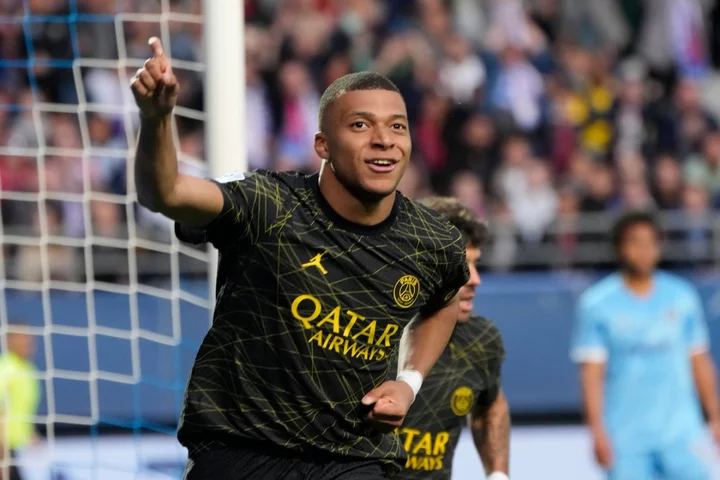

Kylian Mbappe alerts Premier League clubs with surprise announcement about his future
Kylian Mbappe has told Paris Saint-Germain he will not take up the option of a one-year extension in his contract when it expires next June, according to reports from L’Equipe. Mbappe, a World Cup winner with France in 2018, confirmed his decision in a letter to the club and could even be sold this summer as PSG will seek to avoid losing him for free, according to the report. The forward would be free to negotiate and sign a pre-contract agreement with a new club from January should he decide to see out the remaining year of his deal at PSG. The French club, owned by Qatar Sports Investments, have already lost Lionel Messi on a free transfer after the Argentina forward left at the end of his two-year contract to join Major League Soccer’s Inter Miami. PSG have not responded to a request for comment. Mbappe was widely tipped to join Real Madrid last season but rejected a move to Spain to sign a contract extension with PSG. The 24-year-old has long been admired by Real, who had a bid reported to be as high as €200m turned down in 2021. Real, who have already agreed a deal to sign England midfielder Jude Bellingham from Borussia Dortmund, could step up their interest in Mbappe following striker Karim Benzema’s move to Al-Ittihad in Saudi Arabia. However, Premier League clubs such as Manchester United and Man City will also likely assess their options and see if they can bring in one of the best players in the world. Mbappe, one of the game’s finest talents who burst onto the scene as a teenager, has won five Ligue 1 titles with PSG but the Champions League trophy has remained out of reach. PSG signed Mbappe from AS Monaco in 2017 in a deal reported to be around €180m, making him the world’s second-most expensive signing after Neymar, who joined them from Barcelona for €222m. Mbappe became PSG’s all-time top scorer after netting 41 goals in 43 games in all competitions and helped the capital club win a record 11th French title. He was named France captain after leading them to a second straight World Cup final in December, where he netted a hat-trick against Argentina before losing on penalties. Reuters Read More Lionel Messi to Inter Miami: Apple deal, MLS contract, salary, debut and everything we know How Jude Bellingham can become the anti-Haaland for Real Madrid Vinicius Jr needs protecting — or racism will drive him from La Liga
2023-06-13 14:45

5 Arch Manning transfer destinations if Quinn Ewers returns to Texas
Find out where Arch Manning could transfer and shake up the college football landscape.
2023-11-15 09:28
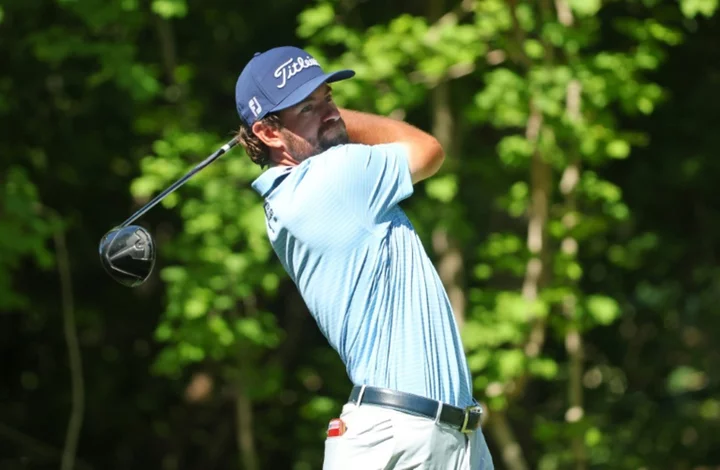

Young seizes two-stroke lead at PGA John Deere Classic
Cameron Young, last year's British Open runner-up, fired a seven-under par 64 to grab a two-stroke lead after Friday's second round of...
2023-07-08 08:21
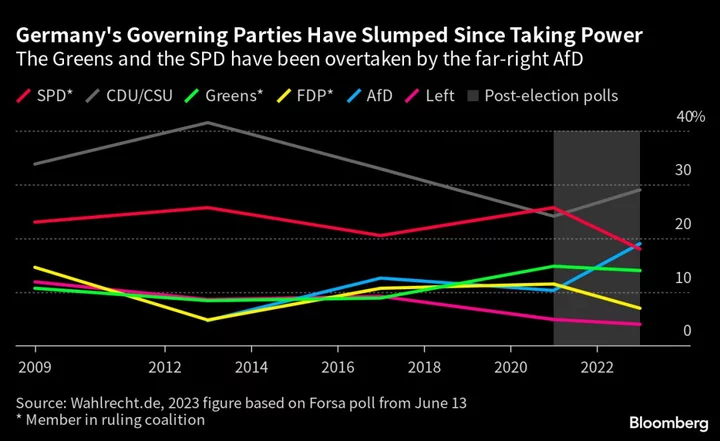
German Greens Are in Crisis Like the Rest of Scholz’s Coalition
Germany’s Greens attacked their highest-ranking cabinet ministers at a party convention near Frankfurt this weekend. Nominally, the subject
2023-06-19 12:00
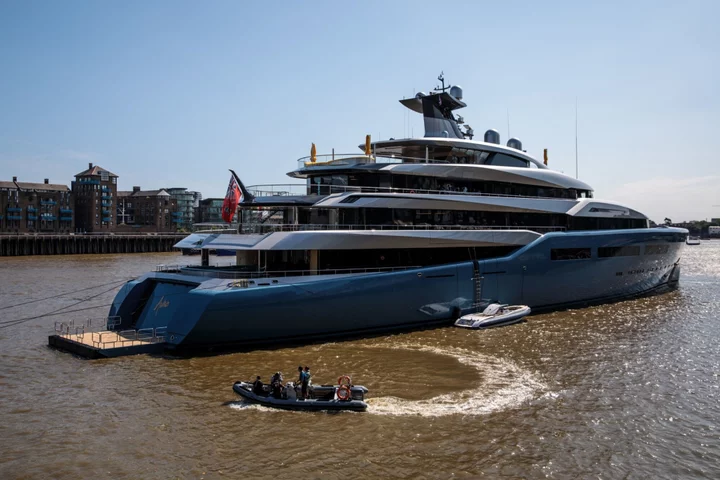

Superyacht Dinners and Alleged Insider Tips Ensnare Billionaire
On a September night in California aboard the superyacht “Aviva,” one of the UK’s richest men sat down
2023-07-28 14:00

YouTube prankster Mizzy challenges IShowSpeed to boxing match: 'Fight of the year'
Previously, Mizzy shared a picture of himself being handcuffed and escorted by the police, which quickly went viral on social media
2023-06-14 12:39
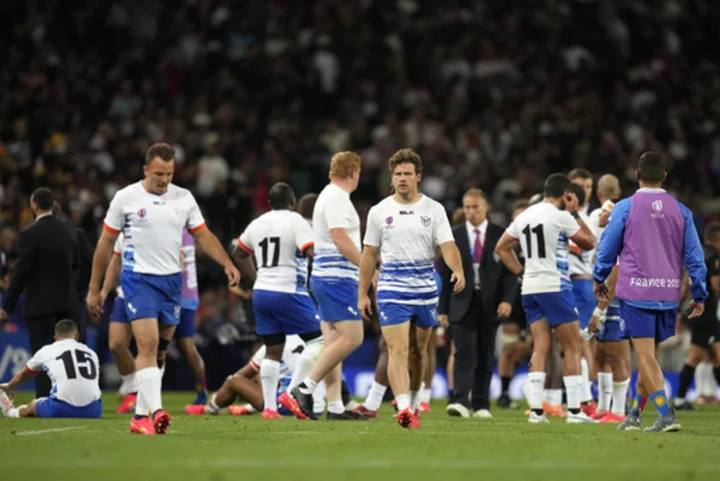

Baille and Danty return to France team for 3rd RWC pool game against Namibia
Prop Cyril Baille has recovered from a calf injury and returns to the France team along with center Jonathan Danty for the team’s third Rugby World Cup pool game against Namibia on Thursday
2023-09-19 22:17

India's Modi breaks silence over Manipur ethnic violence after viral video shows mob molesting women
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has broken his public silence over deadly ethnic clashes in India’s northeast after a video went viral showing two women being assaulted by a mob
2023-07-20 15:20
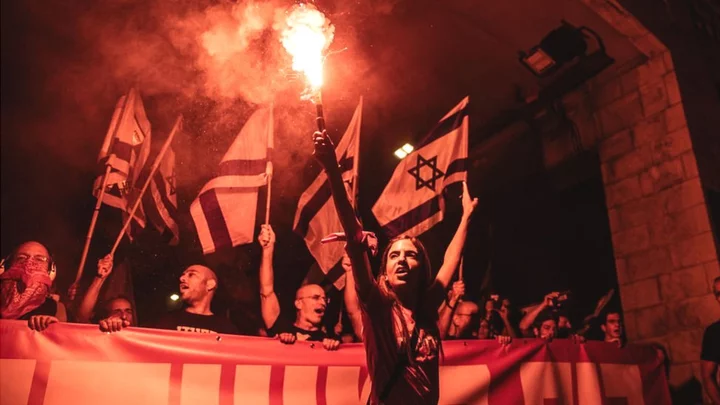

Israel Supreme Court showdown over controversial judicial reform
For the first time ever, all 15 judges convene to consider blocking a new controversial law.
2023-09-12 14:15
You Might Like...

St. Kitts and Nevis Player Takes Wicked Shot to the Groin in Loss to USMNT

India thwarts young Wellalage to beat Sri Lanka and reach Asia Cup final

Work or play with a new-to-you MacBook Air for 68% off

'It's a repeat': 'The View' fans furious over show's 'disappointing' schedule modification

Krafton gets approval to resume battle-royale game in India
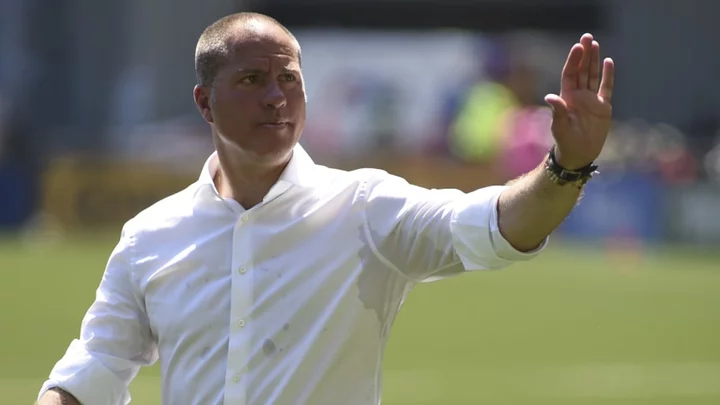

Portland Timbers part ways with head coach Giovanni Savarese
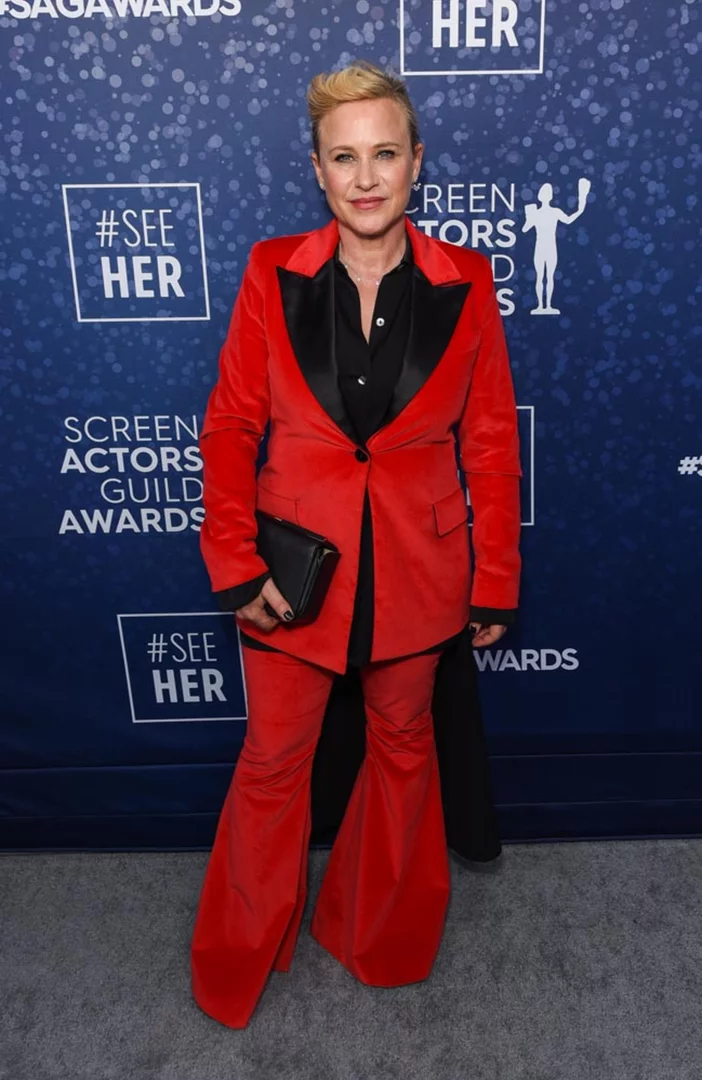

Patricia Arquette used Gonzo Girl to explore addiction and co-dependency
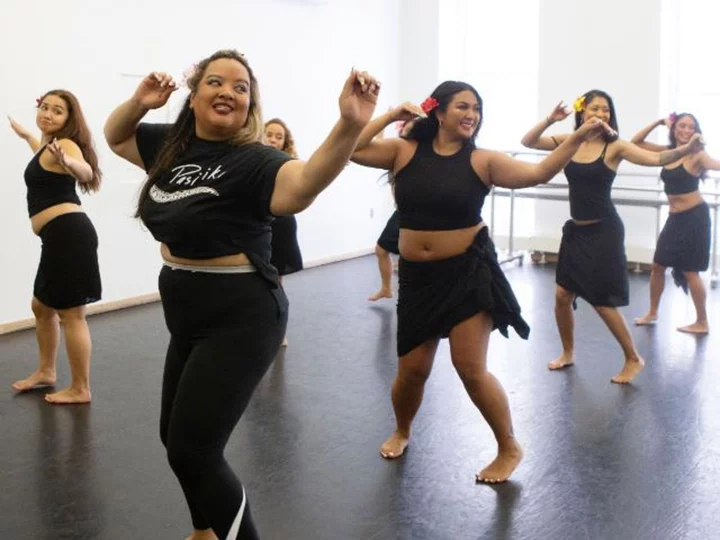

How Pacific Islanders in the US are keeping their culture alive through dance
