Hezbollah, Israel’s enemy on the northern front, is probably stronger than it’s ever been – which means it also has more to lose.
That’s one reason why the Lebanese militant group wants to avoid getting drawn into a full-blown war with Israel, a reluctance shared by its patron Iran.
Such calculations may decide how the latest war in the Middle East unfolds. Hezbollah and the Israeli military have exchanged almost daily fire since Hamas attacked Israel on Oct. 7.
But those clashes across the Lebanese border have been relatively restrained, even as Israeli troops push into Gaza and casualties soar. A wider regional conflict -– which could upend oil markets and jolt the global economy — has been averted so far.
Hezbollah and Hamas are both designated by the US as terrorist organizations. They both help Iran to deter its enemies and expand its influence. But the Lebanese group is more important, according to Joseph Daher, author of “Hezbollah: The Political Economy of Lebanon’s Party of God.”
‘Crown Jewel’
“Iran wouldn’t want to see its crown jewel get weakened,” says Daher. Iran’s geopolitical goal is not to liberate the Palestinians but to use such groups as leverage, especially in its relations with the US, he says.
Hezbollah, founded four decades ago to defend Lebanon after Israel invaded, has its own agenda too: “We shouldn’t just look at it as a simple instrument of Iran.”
Read more: Why Hezbollah Is a Wild Card in New Mideast Fighting: QuickTake
The Shiite group has more firepower than Hamas. Hezbollah says it has 100,000 fighters, and analysts estimate its missile stockpile at between 130,000 and 150,000. For the past five weeks, it’s been using the latter to strike Israeli army outposts along the 120-kilometer border.
In his most recent televised speech on Nov. 11, Hezbollah’s chief Hassan Nasrallah said the group has started deploying more potent weaponry, including spy drones and bombs that weigh as much as half a ton.
Nasrallah said it himself: the group aims to maintain Israel’s northern front as a pressure point. “That is the general course of action,”’ Nasrallah, who lives in hiding, said in a video address.
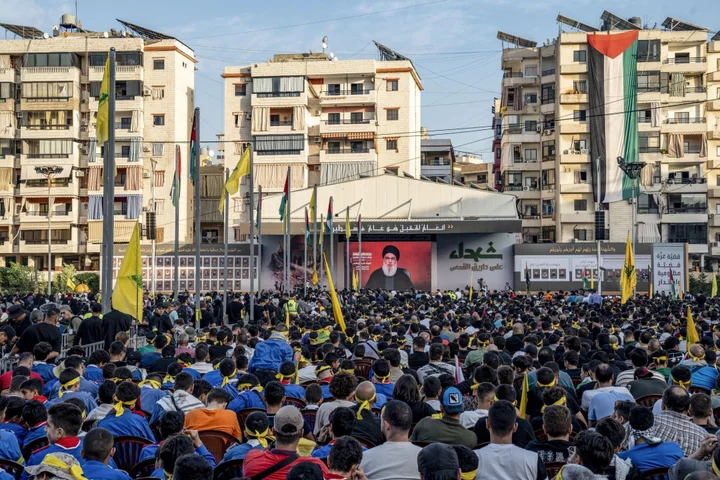
Thousands gathered in Beirut’s southern suburbs, and elsewhere in the country, to hear him speak on giant screens. That’s not an unusual scene: Nasrallah has celebrity status. Followers debate the nuances of his demeanor — what color cloak he wears, how he wags his finger when he threatens Israel.
What is unusual is the series of funerals held in Lebanese villages for men killed since Oct. 8. There haven’t been this many since Hezbollah intervened in the Syrian war a decade ago. The group has lost at least 70 fighters to Israeli strikes, and Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu warned Hezbollah that it’s “playing with fire.”
‘A Single Mishap’
Still, clashes have remained broadly within their so-called rules of engagement — which limits fighting to Lebanese areas that Hezbollah considers occupied, and to military targets.
The big risk is that the restraint won’t last.
Israel says its war aim is to eliminate Hamas, which killed some 1,200 Israelis and abducted more than 200 hostages in last month’s attack.
“Neither Iran nor Hezbollah want a regional conflagration that’s bound to be highly costly for them,” says Ali Vaez, director of the Iran project at the International Crisis Group. “But there’s also a cost associated with letting a member of their alliance be completely destroyed.”
“The way they seem to be squaring the circle is through calibrated and incremental escalation,” he says. “This strategy is at the mercy of a single mishap or miscalculation.”
One example: Last week Israel said it struck a target 40 kilometers inside Lebanon, well beyond what the usual rules involve.
‘People Are Scared’
There are signs that the US is warning both sides against escalation. Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin expressed concern to his Israeli counterpart last weekend about Israel’s role in stoking tensions on the Lebanese border, Axios reported. US Special Envoy Amos Hochstein met with Hezbollah allies in Beirut, urging calm.
There’s a domestic risk for Hezbollah too, because Lebanon has been in dire straits since a financial meltdown in 2019. The currency has lost almost all its value, inflation is running above 200%, almost three-quarters of the population lives in poverty, and the banking system collapsed.
Hezbollah has a hard core of support, but it’s also made many enemies inside Lebanon – and it could alienate even more people if it’s seen as dragging the country into someone else’s war.
“Were Hezbollah to start all-out war with Israel, the cost of domestic alienation for Hezbollah would be higher than any gain in popularity it could have in the rest of the Arab world,” says Lina Khatib, director of the Middle East Institute at the School of Oriental and African Studies in London.
Read More: With Bread and Oil, Hezbollah Tightens Grip on Sinking Lebanon
The fear is apparent in southern Lebanon, where many residents have fled their village homes near the border, while others make preparations to do so in case Israel decides it’s had enough.
“Hezbollah knows that people, its people, are scared,” says Ibrahim Bayram, a Beirut-based writer with a focus on Hezbollah.
‘Long Gone’
There was a time when Hezbollah enjoyed broader backing in the country and region. Pictures of Nasrallah were displayed on the streets of Egypt, Bahrain and Syria in 2006 after the group fought and survived a 33-day war with Israel, winning admirers across the Islamic world.
But things changed in the following decade when Hezbollah fought alongside Syrian President Bashar al-Assad -– and Iran and Russia — to crush what was seen by many Arabs as a legitimate uprising against a brutal regime.
In that conflict, Shiite Muslim Hezbollah and Sunni Hamas backed opposite sides. They’ve since reconciled. Hezbollah also helped restore ties between Hamas and Assad, and it’s reportedly trained Houthi rebels who are fighting against a Saudi-backed government in Yemen.
Read More: Who Are Yemen’s Houthis? Can They Strike Israel?
Hezbollah’s strategy in the Gaza war is to be a “support front” for Hamas, according to Bayram — letting the Palestinian group lead what’s seen by many in the region as a fight for the Palestinian cause.
That serves another purpose for Hezbollah too, Bayram says: “It embarrasses the rest of the Arab world, who might have thought that the Arab-Israel conflict is long gone.”
--With assistance from Julius Domoney.