Spiraling prices of tomato, onion and pulses are emerging as new risks for India’s retail inflation, reaffirming expectations of a hawkish hold from the central bank for the rest of the year.
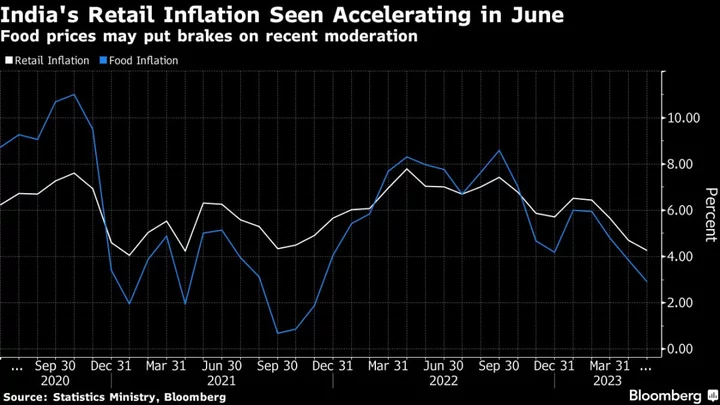
After moderating for four months, consumer price inflation probably accelerated to 4.6% in June, according to a Bloomberg survey of economists. That compares with a 25-month low reading of 4.25% in May. Official data is due 5:30 p.m. local time Wednesday.
The gains are broadly in line with the Reserve Bank of India’s projections, but an impact on supply chains and crops due to an erratic weather may fan the prices further.
That means the central bank will take longer to reach the mid-point of its 2%-6% target, delaying a pivot to rate cut to support growth. It left the rates unchanged in the last two meetings to see the impact of past hikes on inflation.
High borrowing costs may further dent demand in Asia’s third-largest economy where growth has lost pace tracking a global slowdown. It may also pause the rally in India’s stocks which have touched record highs, according to some market watchers.
Economists are crunching numbers to gauge the impact of the sharp acceleration in food prices on headline inflation in the coming months. A jump of more than 400% in the prices of tomato since the start of the year will likely push up inflation beyond the RBI’s target ceiling in the July reading due next month.
“The weather-related price disruption has also been seen in other vegetables and most notably in onion prices,” said Anubhuti Sahay, an economist with Standard Chartered Bank. She sees the risk of inflation touching 6% in July if the increase in food prices is sustained.
What Bloomberg Economics Says ...
“We estimate CPI gains quickened in June after a four-month slowdown. This could mark the start of a sustained pickup, propelled by food prices. We see the central bank maintaining a hawkish hold through December.”
— Abhishek Gupta, India economist
Read the full report here.
Prices of tomato, onion and potato — key ingredients in an Indian meal — are major contributors to volatility in retail inflation, even if they make up a small portion of the index, according to a study by the RBI.
Weaker monsoon in some parts of the country and floods in other areas is contributing to soaring prices of vegetables and pulses. After months of blistering heat, northern India is seeing deluge that has led to a widespread damage.
Read: Delhi Sees Wettest July Day in Decades as Rains Lash India
Besides food, “rentals and housing prices have been firming up in urban areas and demand for contact-intensive services has seen an increase during the holiday season,” said Rupa Rege Nitsure, an economist with L&T Finance Holdings Ltd.
The central bank will carefully parse through the data before its Aug. 10 decision. In the June meeting, the rate setters said they would keep a close vigil on upside risks to inflation, including the spread of the monsoons and geopolitical tensions.
“Much of the increase in food inflation is led by perishable items,” said Upasna Bhardwaj, an economist with Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd. “We continue to monitor the spatial distribution of rains in next few weeks to determine the likelihood of persistence of adverse impact on cereals and pulses.”
--With assistance from Tomoko Sato and Atul Prakash.