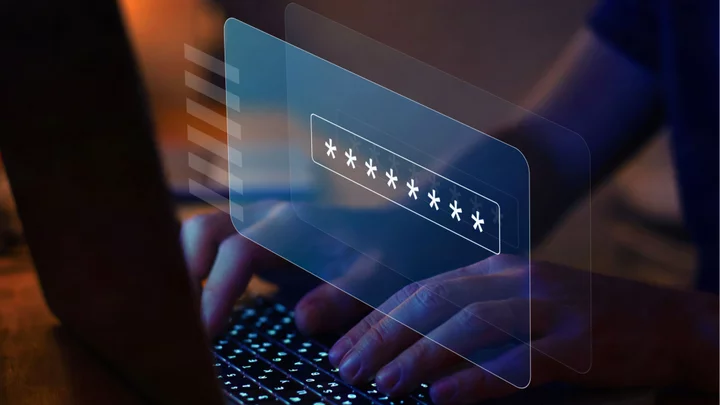
We've long been told to craft long, hard-to-guess passwords for our online accounts, but lengthy codes are not enough to protect your data, according to new research
As TechRadar reports, Specops Software finds that even passwords topping 15 characters can be circumvented by attackers. While longer passwords are often more difficult to guess and crack through brute force and hybrid dictionary attacks, the longer length doesn’t protect the passwords from phishing attacks or password-reuse issues. Those 15-character passwords came in eighth in the company’s list of common lengths for compromised passwords.
That’s not to say you should return to the days of short passwords. On average, Specops finds that 85% of compromised passwords are 12 characters in length or less, so that 15-character password still puts you in a decent spot, comparatively.
“Longer passwords are better,” says Darren James, Senior Product Manager at Specops Software. “And I don’t think that’s news to most IT teams. However, it’s important to understand that equipping users with strong, lengthy passwords isn’t a foolproof way to avoid compromised credentials. Attackers can still find workarounds, and user behavior can undo a good password policy.”
The most common length for compromised passwords is eight characters, likely because that’s the default password in the Active Directory and the requirement for many sites. The most commonly compromised passwords were “password” unsurprisingly, along with “research” and “GGGGGGGG.”
When it comes to those 15-character passwords, two of the three most commonly compromised passwords include the phrase “new hire” suggesting that IT departments should consider doing things a little differently for their newest employees. The company also suggests making sure passwords are not reused across different sites, an issue that can potentially be solved by using password managers.
This comes as many companies are embracing passkeys. Here's what you need to know about this passwordless authentication.