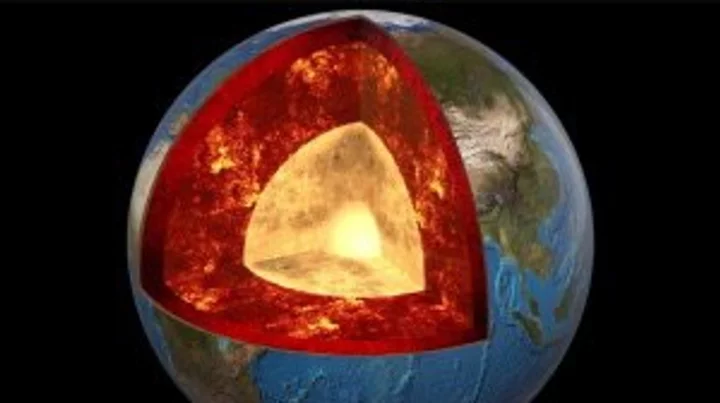
Two giant structures deep within the Earth could be the remains of an ancient planet
Many of us look to the stars for answers to life’s most complex questions. But actually, some of the greatest mysteries lie beneath our very feet. One might think we’d know the Earth pretty well by now but, in fact, our planet’s core remains shrouded in enigma. Indeed, there are two gigantic blobs located beneath Africa and the Pacific Ocean that occupy around six per cent of the world’s entire volume. And yet, we’re still not entirely sure what they’re made of or where they came from. There are a number of hypotheses, including that they are piles of oceanic crust that have accumulated over billions of years. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter But a more interesting theory is that they are huge chunks of an ancient planet that hit the Earth around 4.5 billion years ago. To give an indication of just how massive these things are, the structure under Africa – an area known as Tuzo – is thought to be around 800km (497 miles) tall – the equivalent of some 90 Mount Everests stacked on top of one another, as IFLScience notes. The problem with determining the origin of these monster formations is that there are no direct ways of observing the Earth’s core. The deepest hole humans have ever dug – branded the "entrance to hell" – reached a pretty staggering 12,263m (40,230ft), but that doesn’t even come close to breaking through the crust to the layers beneath. Our most effective tool for analysing what lies beneath the ground is a technique called seismic tomography, which looks at how waves of energy travel when earthquakes occur. Since rocks and liquids have different densities, the waves move through them at different speeds. By measuring the tremors from different points on the surface, geologists can determine what kind of material the waves are travelling through and, in so doing, map out the Earth’s interior. It was by using this technique that the two unusual structures – known as large low shear velocity provinces (LLSVPs) – were found. Waves travel more slowly in these areas – fondly known as “blobs” – than through the surrounding lower mantle, indicating that they’re made of something different. We can’t tell what this material is based on seismic tomography data alone, but some scientists like to believe that they are the remnants of an ancient planet called Theia – an idea known as the “giant impact hypothesis”. According to this hypothesis, around 4.5 billion years ago, a Mars-sized object collided with the Earth. This impact not only created the planet we call home today, but also threw off enough rock to form the moon that lights up our night skies. Some scientists suggest that some of Theia’s leftovers also sunk to the bottom of the planet, probably settling somewhere above the core – thereby forming at least one of the two LLSVPs. More Updates About Strange Blob Structures Inside Planet Earth youtu.be Experts have been investigating the area for decades but there’s still no way of knowing for sure just what these two giant blobs are. Still, studies into Theia have offered important insights into how the possible collision might have kickstarted key plate tectonic and mantle motion inside our planet – crucial processes for establishing the world on which we live. It’s also a useful reminder that we still have so much to learn about our planet and where we came from. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Silvio Berlusconi obituary: Italy's flamboyant bounce-back politician
A media mogul who went into politics, he survived several corruption allegations.
1970-01-01 08:00

Nomura to Scale Back Loss-Making Brokerage Venture With Line
Nomura Holdings Inc. plans to scale back a brokerage venture with messaging app operator Line Group amid a
1970-01-01 08:00

STI cases at record highs: 6 things everyone needs to know about sexually transmitted infections
Cases of gonorrhoea in England have reached record highs, while syphilis cases are at the highest level since just after the Second World War, according to the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA). Gonorrhoea diagnoses rose to 82,592 in 2022, an increase of 50.3% compared to 2021, while infectious syphilis cases increased to 8,692 in 2022, the largest annual number since 1948. As well as gonorrhoea and syphilis, it’s important to be aware of the risk around all sexually transmitted infections (STIs) including chlamydia, genital herpes, genital warts and HIV. As Dr Hamish Mohammed, consultant epidemiologist at UKHSA, pointed out: “STIs aren’t just an inconvenience – they can have a major impact on your health and that of any sexual partners.” Here, sexual health experts talk through what you need to know about STI prevention, testing and treatment… 1. Anyone can potentially get an STI “Don’t think that because you haven’t caught one in the past – or because you only sleep with people that you don’t think have STIs – that you are immune, because the truth is that no one is,” Sarah Mulindwa, a specialist sexual health nurse who is working with Lovehoney, told PA Media. Regardless of gender, sexual orientation, whether you have lots of partners or you’re in a monogamous relationship, anyone can potentially get an STI. And they affect all age groups, too. “There’s no upper age limit on getting an STI,” Julie Bowring, consultant gynaecologist in sexual and reproductive health at London Gynaecology, added. The number of common STIs caught among the over 65s in the UK increased by 20% from 2017 to 2019, according to the Local Government Association. This may in part be due to differences in health awareness. “When that generation of patients were at school, they didn’t get quite as good and comprehensive sexual health education as we get now,” Bowring said. “And if you look at all the media campaigns for sexual health infections, it’s usually targeted at a younger demographic.” 2. Not all contraceptives protect against all STIs “It’s a common myth that when you’re on regular contraception, you might have protection against STIs,” said Bowring. “I think that can sometimes be missing in information that’s given to patients when they start contraception.” While birth control methods such as the pill, coil or IUD will protect against unintended pregnancy, they won’t protect against STIs. “Condoms [or dental dams] are the only effective method of protecting against STIs if you are sexually active,” said Mulindwa. “And even then, only when you use them correctly: wearing one to cover the whole length of the penis, and using from start to finish of sex, including during oral, anal, or vaginal penetration.” 3. Symptoms can vary greatly With a wide range of symptoms that vary in severity, STIs can sometimes be difficult to spot. “Certain STIs, such as chlamydia for example, might not even present any symptoms in the person that has it,” Mulindwa explained. “If you are experiencing any form of discomfort in and around your genitals, then it is imperative that you get tested right away.” Other signs may include an unusual discharge from the vagina, penis or anus; pain when peeing; lumps or skin growths around the genitals or anus; a rash; unusual vaginal bleeding; itchy genitals or anus; and blisters, sores or warts around these areas. “It can be quite difficult for women to sometimes know when a symptom might be STI related,” added Bowring. “It could be their periods, it could be something non-STI related. If there is a risk of infection and you have noticed a change in either your discharge or your pain, then it is worth getting checked out.” 4. Routine testing is a good idea Because some infections don’t result in any symptoms, routine testing is important. “If you’ve changed partner then it’s a good idea, if you haven’t had STI screening, to attend your local service to get that done,” Bowring advised. Home testing kits are also available with swabs and finger-prick blood tests. “It’s recommended that you screen at least every six months for the most common infections – chlamydia and gonorrhoea – and yearly for blood tests to screen for HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis C,” Mulindwa added. “Depending on your risk factors, you may need to screen more frequently.” 5. Treatments are available STIs are extremely common and there’s no need to feel embarrassed or ashamed if you do catch one, and treatments are available. “The majority of STIs are curable, and even those that aren’t – for example, herpes – have treatments available to manage outbreaks,” said Mulindwa. “Some STIs like chlamydia are treatable with a course of antibiotics, and others require creams and ointments.” 6. Options for people with HIV have come a long way Thanks to scientific breakthroughs, providing they have access to treatment, most people with HIV will not develop any AIDS-related illnesses and can live full lives. “There are now options available that can stop HIV reproducing in the body and prevent you from passing it on, as well as drugs designed to prevent infection if you have been exposed,” said Mulindwa. “People who are HIV positive and are undetectable (which means the level of the virus is very low) are unable to pass it on even when they have unprotected sex.” A relatively new drug called Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) – designed to reduce the chance of contracting HIV – can be helpful for people who may be at increased risk. Health professionals at NHS sexual health clinics can talk you through the options for preventing and managing HIV. Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live What’s wrong with my roses? Men’s Health Week: How to talk about sensitive or ’embarrassing’ health issues Prince William responds after three guardsman collapse during UK heatwave
1970-01-01 08:00

Credit Suisse's Exit From Stock Benchmark Shows Fading Heft of Swiss Financials
Credit Suisse Group AG’s imminent exit from the Swiss Market Index is symbolic of the decreasing importance of
1970-01-01 08:00

Sam Bankman-Fried’s Risky Japan Trade Seeded a Crypto Empire
Fresh out of college, Sam Bankman-Fried had a trading job at Jane Street Group in New York. As
1970-01-01 08:00
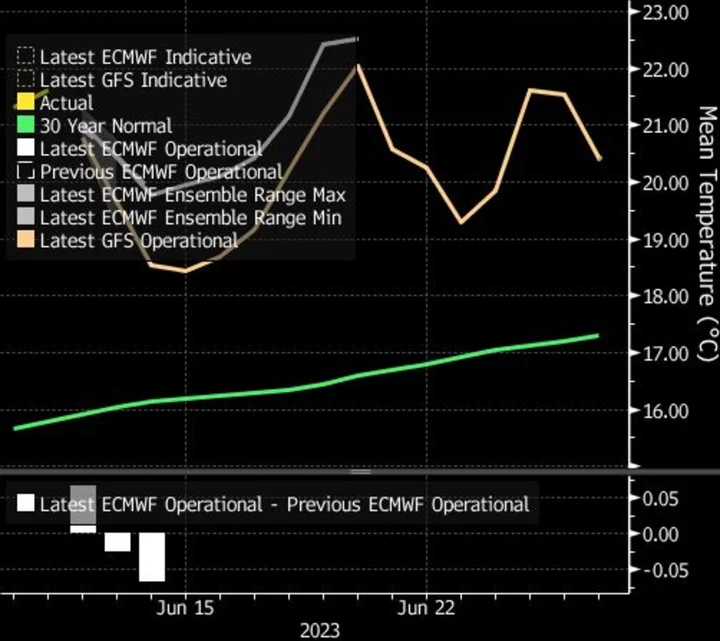
London to Be Hotter Than Madrid as Warm Spell Continues
Heat will persist across the UK and northern Europe this week, potentially boosting demand for energy to keep
1970-01-01 08:00
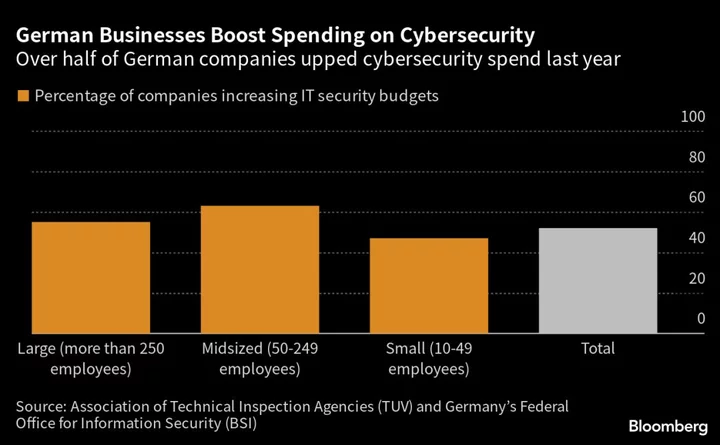
War in Ukraine Prompts Increased Cyberattacks on German Businesses
More than one in 10 German companies were the victim of a cyberattack last year, according to a
1970-01-01 08:00

Glencore Offers to Buy Teck’s Coal Business
Glencore Plc is in talks with Teck Resources Ltd. after making an offer to buy the Canadian miner’s
1970-01-01 08:00

Josh Hartnett hails 'genius filmmaker' Christopher Nolan
Josh Hartnett has loved working with Christopher Nolan on 'Oppenheimer'.
1970-01-01 08:00

Directing Flamin' Hot was super empowering, says Eva Longoria
Eva Longoria has revealed that she relished the experience of directing 'Flamin' Hot'.
1970-01-01 08:00
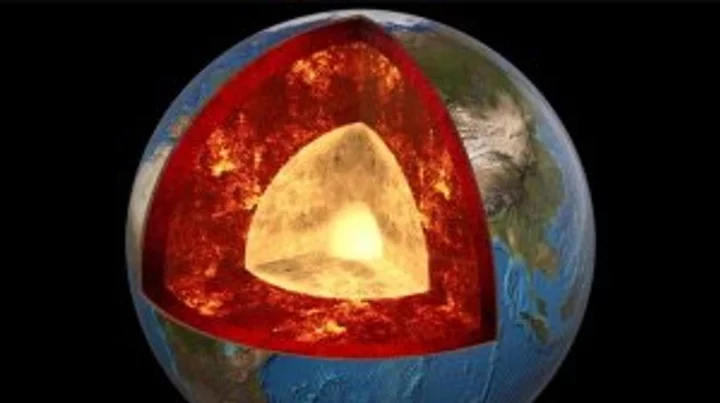
Ancient formation discovered wrapped around Earth's core
The structure of the Earth beneath our feet has been fascinating to members of the scientific community recently, and it turns out it’s far more complex than people initially thought. First, we learned of the news that there’s a massive ocean beneath the Earth’s crust which contains more water than all of the seas on the surface. Now, another study has been published which has taken an in-depth look at the geology beneath the southern hemisphere. The new research, published in Science Advances, has found evidence that an entire ocean floor actually runs the length around the core. Sign up to our new free Indy100 weekly newsletter This is a relatively thin layer that sits on the core-mantle boundary around 1,800 miles beneath the surface of the Earth. It's an ancient formation that could provide more insight into the structure of the planet beneath our feet. Geologist Samantha Hansen and her colleagues from the University of Alabama led the research. They observed the structure by using 15 monitoring stations under the ice of Antarctica, mapping the waves from earthquakes. Doing this allowed them to analyse the structure of the Earth below the surface, including the ultra-low velocity zones where waves moved much slower. "Seismic investigations, such as ours, provide the highest resolution imaging of the interior structure of our planet, and we are finding that this structure is vastly more complicated than once thought," Hansen said. "Analyzing [thousands] of seismic recordings from Antarctica, our high-definition imaging method found thin anomalous zones of material at the CMB everywhere we probed," geophysicist Edward Garnero from Arizona State University also said. "The material's thickness varies from a few kilometers to [tens] of kilometers. This suggests we are seeing mountains on the core, in some places up to five times taller than Mt. Everest." "Our research provides important connections between shallow and deep Earth structure and the overall processes driving our planet," Hansen added. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
