
Consistent lack of sleep may increase risk of future depressive symptoms – study
Consistently sleeping less than five hours a night could increase the risk of depression, research suggests. Poor sleep has been considered a side-effect of mental ill health in the past, but the new study found that the link between sleep and mental illness is more complex. People with a stronger genetic predisposition to short sleep – less than five hours in a given night – were more likely to develop depressive symptoms over four to 12 years, the study led by UCL researchers found. But those with a greater genetic predisposition to depression were not more likely to have short sleep. Using genetic susceptibility to disease, we determined that sleep likely precedes depressive symptoms, rather than the inverse Lead author Odessa Hamilton The experts also found that the link was not exclusive to those who were genetically inclined towards sleeping for shorter periods, and people who regularly dozed for five hours or less – without the genetic association – were also more likely to have depression. Lead author Odessa Hamilton, UCL Institute of Epidemiology and Health Care, said: “We have this chicken or egg scenario between suboptimal sleep duration and depression, they frequently co-occur, but which comes first is largely unresolved. “Using genetic susceptibility to disease, we determined that sleep likely precedes depressive symptoms, rather than the inverse.” Researchers used genetic and health data from 7,146 people recruited by the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (ELSA), with an average age of 65. Short and long sleep durations, along with depression, are major contributors to (the) public health burden that are highly heritable Senior author Dr Olesya Ajnakina Analysis of genetic and health data suggested that short sleep was associated with the start of depressive symptoms, like feeling sad or lonely. Senior author Dr Olesya Ajnakina, UCL Institute of Epidemiology and Health Care and the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience at King’s College London, said: “Short and long sleep durations, along with depression, are major contributors to (the) public health burden that are highly heritable. “Polygenic scores, indices of an individual’s genetic propensity for a trait, are thought to be key in beginning to understand the nature of sleep duration and depressive symptoms.” When looking at non-genetic associations between depressive symptoms and sleep duration, the researchers also found that people sleeping five hours or less were 2.5 times more likely to develop depressive symptoms. And people with signs of depression were a third more likely to suffer from short sleep. Suboptimal sleep and depression increase with age, and with the worldwide phenomenon of population ageing there is a growing need to better understand the mechanism connecting depression and a lack of sleep Professor Andrew Steptoe The study, published in Nature, Translational Psychiatry, also revealed a link between sleeping long and developing depressive symptoms. According to the findings, people who slept for more than nine hours were 1.5 times more likely to develop depressive symptoms than those who sleep an average of seven hours. However, depressive symptoms were not associated with sleeping longer four to 12 years later, which corresponded to the genetic findings. Professor Andrew Steptoe, head of Behavioural Science and Health, UCL Institute of Epidemiology and Health Care, said: “Suboptimal sleep and depression increase with age, and with the worldwide phenomenon of population ageing there is a growing need to better understand the mechanism connecting depression and a lack of sleep. “This study lays important groundwork for future investigations on the intersection of genetics, sleep, and depressive symptoms.” People enrolled in the study had an average of seven hours’ sleep a night. More than 10% slept for less than five hours a night at the start of the study period, rising to more than 15% at the end of the study. The proportion of people classed as having depressive symptoms increased by about three percentage points, from 8.75% to 11.47%. In the study, data on sleep and depressive symptoms were combined from two Elsa surveys conducted two years apart, as sleep duration and depression are known to fluctuate over time. Sleep duration and depression are both partly inherited from one generation to the next. Earlier studies have suggested depression is about 35% heritable, and that genetic differences account for 40% of the variance in sleep duration. Read More World Osteoporosis Day: The risk factors and early warning signs everyone needs to know about How to support a child with a stammer From colourful gowns to drones, these wedding trends are set take over 2024 Call The Midwife ‘should come with a health warning’ Halloween: 10 wicked ways to kit out your haunted house Black magic: Go back to black this season with the catwalk-inspired trend
1970-01-01 08:00

World Osteoporosis Day: The risk factors and early warning signs everyone needs to know about
October 20 marks World Osteoporosis Day – but despite being a relatively common condition, many people are unaware they’re at risk. According to Age UK, osteoporosis – which is associated with weakened bones and often referred to as a ‘silent disease’, as symptoms can creep up on people – affects approximately three million people in the UK. Yet, many only find out they have it when they break a bone. “[Osteoporosis] is a condition characterised by weakened bones, making them more prone to fractures,” explains Dr Zulqarnain Shah, a medical director at SSP Health. “It occurs when the body loses too much bone or makes too little bone, or both. Diagnosis of osteoporosis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specialised tests, such as bone mineral density scans,” Shah adds. Could I be at risk of osteoporosis? According to Age UK, around half of women over 50, and around one in nine men in the same age group, will experience a fracture due to osteoporosis. However, several risk factors contribute to the development of the condition, meaning some people may be more likely to get it. “These include menopause, low calcium and vitamin D intake during younger years, family history, a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medications,” explains Shah. “While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of osteoporosis, adopting a healthy lifestyle with regular weight-bearing exercise, a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol intake can help reduce the risk.” Being aware of osteoporosis can be particularly important if you have a family history. “A family history of osteoporosis or fragility fractures can indicate an increased risk,” explains Dr Elise Dallas, GP at The London General Practice. Other things that increase risk include having a history of “rheumatoid arthritis, low levels of oestrogen due to early menopause, anorexia nervosa or Turner’s syndrome, hyperthyroidism, parathyroid disease, Crohn’s and coeliac disease, and conditions that cause long periods of immobility”, adds Dallas. What are the symptoms of osteoporosis? When you have osteoporosis, you may suffer from “increased fracture risk, height loss, and chronic pain”, says Shah. “Fractures associated with osteoporosis are known as ‘fragility fractures’, which can occur with minimal impact. Fractures commonly occur in the spine, hip, and wrist, and can lead to significant pain, disability, and reduced quality of life,” he explains. Are there any early warning signs? Shah says: “Early signs of osteoporosis may not be apparent until a fracture occurs. However, a precursor condition called osteopenia may be detected through scans before the onset of full-blown osteoporosis.” Osteopenia is where the density of the bones decreases, but not thoroughly enough to be classed as osteoporosis. There are no real symptoms however, so it can only be detected with scans. The good news is, lifestyle measures and sometimes treatment can help prevent it getting worse. How is osteoporosis treated? Treatment for osteoporosis is mostly aimed at “strengthening bones and preventing fractures”, says Shah. “This typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, such as exercise and dietary changes, along with medication. “Medications may include calcium, vitamin D and bisphosphonates, hormone therapy for postmenopausal women, selective oestrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), and other options. “SERMS help manage the way oestrogen interacts with your body and has a similar impact on osteoporosis as hormone replacement therapy, to help mitigate the impacts of hormones on osteoporosis,” Shah explains. “Regular monitoring and adherence to treatment plans can help slow down or stop the progression of osteoporosis. A bone density scan – also known as a DEXA scan – can help monitor the progress of a condition and may be done at three to five-year intervals to assess progress. “Once a patient has been on bisphosphonates for five years, they may go on a ‘pill holiday’ for a couple of years, though the benefits of taking bisphosphonates continue long after the medication is stopped.” Getting support and advice to manage any pain and mobility challenges and reduce the risk of falls and injuries can also be very important for people living with osteoporosis, along with finding ways to stay active. If you are worried about your bones and osteoporosis risk you can reach out to charities like the Royal Osteoporosis Society and find out about your risk level. Read More How to support a child with a stammer From colourful gowns to drones, these wedding trends are set take over 2024 Call The Midwife ‘should come with a health warning’ Halloween: 10 wicked ways to kit out your haunted house Black magic: Go back to black this season with the catwalk-inspired trend How to prep your home for when the clocks go back
1970-01-01 08:00

Hitting snooze button can actually benefit brain sometimes, study suggests
Hitting the snooze button on the alarm clock once in a while might actually support the brain’s process of waking from deep sleep, according to a new study. People sometimes want to go right back to sleep even after the alarm goes off in the morning, using the snooze button in clocks and cell phones. Decades of previous research suggested that hitting snooze can have negative effects, both on sleep and the brain’s ability to wake up, but until now there hasn’t been any direct evidence of this, say scientists. The new study, published in the Journal of Sleep Research, assessed how common snoozing is and what effects this behaviour has on sleep, sleepiness, mood, and the brain’s cognitive abilities. Researchers found that those who snooze on an average sleep slightly shorter and feel more drowsy in the morning compared to those who never snooze. But they also saw that there were no negative effects of snoozing on the release of the stress hormone cortisol, mood, or sleep quality throughout the night. In the study, 1732 individuals answered questions about their morning habits, including how often they hit the snooze button with many – especially young adults – reporting that they use the alarm feature regularly. The most common reason for snoozing, according to participants, is feeling too tired to get out of bed when the alarm goes off. In another small follow-up experiment, 31 regular snoozers spent two nights in a sleep lab in order to measure their sleep in more detail. On one of the mornings, they were allowed to snooze for 30 minutes, and on the other, they had to get up right when the alarm went off. While in the first case, participants’ sleep was disturbed during the half hour of snoozing, most of them still got more than 20 minutes of sleep – meaning that their total night’s sleep was not affected much. In the snooze condition, no one had to wake up suddenly from deep sleep, and the snoozers performed a bit better on cognitive tests right upon waking. There were also no clear effects of snoozing on mood, sleepiness, or the amount of cortisol in the saliva. The results hint that half an hour of snoozing may not have negative effects on night sleep and could have some positive effects like a decreased likelihood of waking from deep sleep. However, researchers caution that the second experiment was small and only included people who are regular snoozers who find it easy to go back to sleep after each alarm. They say snoozing is most likely not for everyone. Jennifer Kanaan from the University of Connecticut in the US, who is another sleep scientist unrelated to the study, said the latest findings should be interpreted with caution as it could send the wrong message to people. “If you’re coming in and out of sleep for 30 minutes, after the alarm goes off the first time, you’re costing yourself 30 minutes of uninterrupted, quality, restorative sleep,” Dr Kanaan said in a statement. Instead of trying to figure out how to manipulate our alarm clocks, she says people should make a consistent good night’s sleep a greater priority and be less reliant on snooze buttons. “Simply put, instead of hitting the snooze button they should get more sleep,” Dr Kanaan said. Read More Study reveals why millions of women wake up at 3.29am Consistent lack of sleep may increase risk of future depressive symptoms – study Breakthrough study allows scientists to communicate with people as they sleep How to support a child with a stammer ‘I lost nearly a stone on Ozempic, but now it’s run out what am I to do?’ Miriam Margolyes now has part of a cow’s heart as she opens up about health
1970-01-01 08:00

How to support a child with a stammer
For people with a stammer, it can be hard to deal with, but it’s made worse by the fact that understanding of the condition amongst the general public is low. The speech problem usually starts in childhood, between the ages of around two and five years old, affecting around 8% of children and 2% of adults – that’s more than 1.3 million people in the UK. International Stammering Awareness Day (October 22) aims to destigmatise stammering and promote understanding and support for people who do have it, including advice for parents about how they can help affected children. “There’s a lot of stigma around stammering in society – even from an early age, children may be teased or bullied, and adults may tell them to speak properly,” says Catherine Woolley, children and families programme lead at STAMMA (the British Stammering Association). “Children who stammer sometimes feel embarrassed or worried about their speech and try to hide it. They might start to speak less or change words they want to say to ones which are easier to produce. “How you respond to your child can affect how they feel about their talking. It’s common for parents to worry about stammering, and if this is you, you can seek support to help you feel comfortable around your child’s stammering.” Woolley points out that, contrary to popular belief, stammering isn’t caused by anxiety or stress, and there’s no evidence that people who stammer are less intelligent than fluent speakers. “Research suggests stammering is neurological, which means there are subtle differences in the way the brains of people who stammer work,” she explains. “This means it belongs to the same group of neurodiverse conditions as ADHD, autism and dyslexia.” The condition is often hereditary, with about 60% of people who stammer having another family member who stammers, and while there’s no specific cure, Woolley says there are many different techniques and approaches that can increase people’s fluency in certain situations, although they may not work for everyone. “There isn’t one treatment which can miraculously make all people stop stammering,” she stresses. “Everyone’s stammer is unique, as is the way they want to manage their speech.” But there’s no doubt, she says, that parents can help their children deal with stammering, and make them feel more comfortable. 1. Value your child’s stammered voice “It’s simply the way they talk,” says Woolley. “What’s important is what they say and not the way they say it.” 2. Be patient Although it can obviously take more time for a child who stammers to say something, it’s important for parents and the rest of the family not to rush them. “Give them time to say what they want, and model this to their siblings and other family members,” she adds. 3. Don’t finish their words or sentences Woolley says that while it can be tempting to finish your child’s words or sentences for them, especially if you can see them struggling, it’s important to resist this urge to help. “It can be disempowering and embarrassing if you speak over them,” explains Woolley, “not to mention frustrating if your guess is wrong and they have to start all over again.” 4, Slow down yourself Rather than telling your child to speed up, slow down your own speech to reduce any time pressure they may feel. 5. Don’t show your own anxietyEven if you feel anxious when your child is stammering, try not to show it, advises Woolley, who suggests maintaining natural eye contact and remaining calm. “It can be uncomfortable listening to someone who stammers, but think how they feel. Try and maintain eye contact even if you feel awkward, as looking away can make them feel awkward too, or think you’ve lost interest in what they’re saying. Keep looking at them and give the occasional encouraging head nod to show you’re interested.” 6. Try not to be negative Woolley says it can be important to describe stammering using neutral language instead of negative references. So, for example, say, ‘He’s stammered more this week’, rather than, ‘His speech has been bad’. 7. Seek help Parents who are worried about their child’s talking or would like some help should contact their local NHS speech and language therapy department to talk through their concerns. In addition, STAMMA offers free Parent2Parent peer support groups run by parents of children who stammer, and workshops for such parents, plus a helpline (0808 802 0002) and a webchat service. Read More From colourful gowns to drones, these wedding trends are set take over 2024 Call The Midwife ‘should come with a health warning’ Halloween: 10 wicked ways to kit out your haunted house Black magic: Go back to black this season with the catwalk-inspired trend How to prep your home for when the clocks go back Menopause campaigner Mariella Frostrup: ‘I look forward to a future where women gradually stop feeling so ashamed’
1970-01-01 08:00
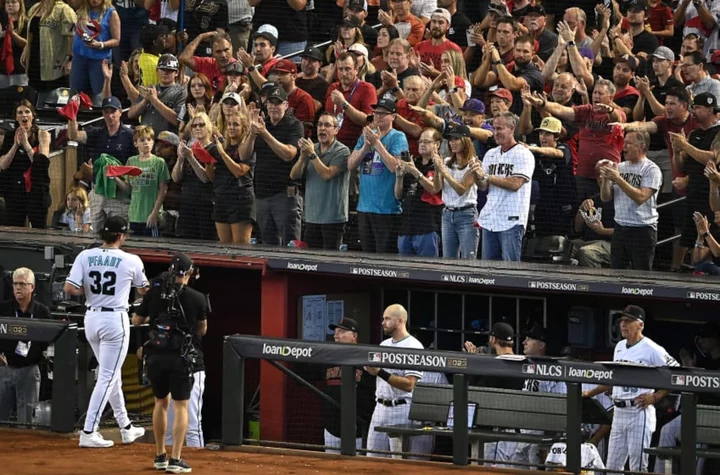
Clubhouse quotes and insights to how Brandon Pfaadt, Diamondbacks defeated Phillies in Game 3
With their backs against the wall, the Diamondbacks pulled out an impressive 2-1 win against the Phillies in the NLCS. Here's how they did it.
1970-01-01 08:00

3 Phillies to blame for lifeless NLCS Game 3 defeat
The D-Backs are making this a series, after all. The Phillies lost Game 3 of the NLCS, and here are the players to point the finger at.
1970-01-01 08:00

Ump show: Phillies, Diamondbacks are in for rough night thanks to umpire disaster
Game 3 of the NLCS could get ugly depending on the officiating crew's decisions. Apologies in advance to Phillies and Diamondbacks fans.
1970-01-01 08:00

Phillies already have psychological edge on Brandon Pfaadt thanks to unlikely source
Arizona Diamondbacks right-hander Brandon Pfaadt was compared to Charlie Morton, and that could play into the Phillies' hand ahead of Game 3.
1970-01-01 08:00
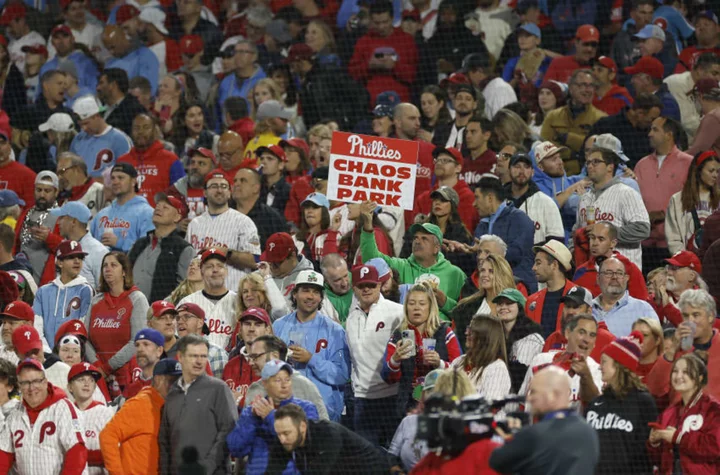
Psychological fanfare: Phillies fans ensure empty Chase Field by any means necessary
Philadelphia Phillies fans are going the extra mile to defeat the Arizona Diamondbacks, including buying empty seats at Chase Field.
1970-01-01 08:00
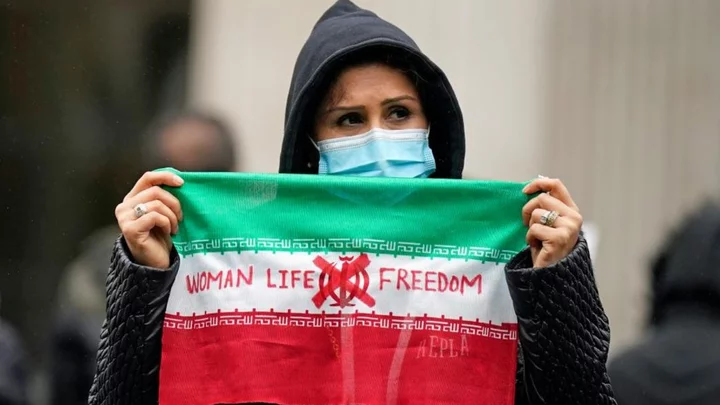

Mahsa Amini awarded EU's Sakharov human rights prize
The 22-year-old died in custody after allegedly violating Iran's strict dress code, sparking mass protests.
1970-01-01 08:00
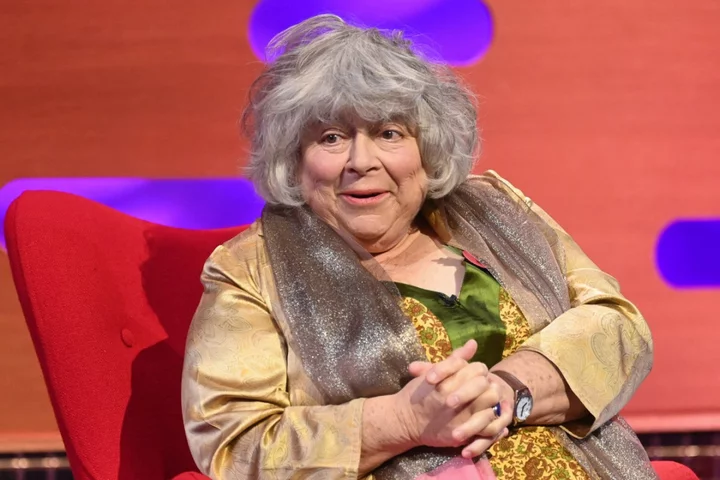

Miriam Margolyes now has part of a cow’s heart as she opens up about health after surgery
Miriam Margolyes has shared a health update after heart surgery, revealing that she now has part of a cow’s heart. Back in May, the Harry Potter actor underwent a minimally invasive procedure called a Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) to replace a narrow aortic valve after it fails to open properly. Appearing on the Table Manners podcast, Margolyes, 82, discussed the heart operation with hosts Jessie Ware and her mother, Lennie. “I’ve got a cow’s heart,” Margolyes revealed. “Well, not the whole heart. I’ve had an aortic valve replaced by a cow’s aortic valve.” Jessie asked if that was “common”, with Margolyes joking: “I think it’s rather refined, actually… I don’t know how common it is, I’d never heard of that operation. But it saves you from having open heart surgery, which would be infinitely more invasive.” Further discussing the surgery, Margolyes explained: “They made two little holes in your groin, one in each groin. and then they shoved this thing through. And I don’t know how they pull it up but they sort of pull it up with strings, into your heart. “And then when it comes to the point when it’s in your heart, they pull a little string and it goes pow! And lo and behold, your artery or your aortic valve is shoved unceremoniously to the side, and the cow’s aortic valve says, ‘Moo, I’m here.’ It’s rather amazing.” Margolyes also shared that she would “probably” use a wheelchair soon due to her bad back, but had “just sort of accepted” that it was going to be necessary. On her new fandom and being seen as a “national treasure”, thanks to her outspoken nature, she added: “It’s lovely to hear that you like me and you approve of me. But I truly am a little old lady. Trying to make a living. Trying to keep going.” Last month, the actor released her new memoir, titled Oh Miriam: Stories from an Extraordinary Life. In the book, which was full to the brim with revelations, Margolyes wrote that her current state of disability meant that she now is mostly unable to perform on the theatre. Describing herself as “semi-crippled”, she wrote that “usually that means you have to stop”. “I don’t think I can do theatre again unless I’m playing a character similarly disabled,” she said. “I know Maggie [Smith] and Eileen [Atkins] and Judi [Dench] and Vanessa [Redgrave] still tread the boards, and they’re older than me – but they’re fitter, b***** it, and good luck to them!” Read More Tilda Swinton, Steve Coogan and Miriam Margolyes among 2,000 artists calling for Gaza ceasefire 11 biggest revelations from Miriam Margolyes’ hilarious new memoir Miriam Margolyes says Steve Martin was ‘horrid’ on film set: ‘Perhaps he was method acting’ Call The Midwife ‘should come with a health warning’ My kids don’t have sushi in their packed lunches – does it make me a bad mum? Adele reveals she’s three months sober after being ‘borderline alcoholic’ in her 20s
1970-01-01 08:00
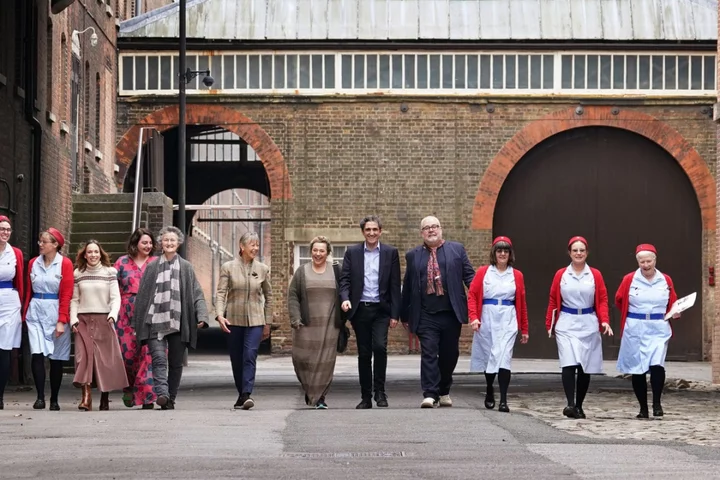

Call The Midwife ‘should come with a health warning’
Popular TV show Call the Midwife needs a health warning, academics have said. Experts from King’s College London and the University of Liverpool said television programmes showing “inaccurate birthing practices” should require safety recommendations for viewers to avoid misinterpretations by the public. Researchers analysed 87 births shown in 48 episodes of BBC’s Call The Midwife, This Is Going To Hurt and Channel 4’s One Born Every Minute. They compared how the depiction of these births compared to modern guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (Nice). The births largely compared favourably to modern care guidance, the authors found. We saw too early cord clamping in most televised births but no programme informed viewers about the safety aspects Prof Susan Bewley But a third of the time depictions of midwives and doctors clamping the umbilical cord were shown inaccurately or dramatised, according to the paper which has been published in the journal JRSM Open. Researchers said that without a safety warning to inform viewers otherwise, the general public and healthcare professionals could think the clamping practices they see are correct. Nice guidance states that women should not have the umbilical the cord clamped earlier than one minute after the birth unless there is concern about cord integrity or the baby’s heartbeat. But the academics found that in 21 instances clamping appeared to happen immediately or too early. Susan Bewley, professor emeritus of obstetrics and women’s health at King’s College London, said: “Millions of viewers watch programmes like Call The Midwife every week to be entertained but the line between fact and fiction is blurred. “We are impressed that UK television shows have accurately depicted some changes in childbirth over the last century, but on the other hand they have also provided the public with a picture of poor-quality care when it comes to clamping during childbirth. “These inaccurate depictions could influence how people see real-world care. “We saw too early cord clamping in most televised births but no programme informed viewers about the safety aspects. “When showing outdated practices, broadcasters have a public health duty to inform viewers that this immediate medical intervention is no longer recommended. No broadcaster would show the sleeping positions associated with cot-death without comment.” Andrew Weeks, professor of international maternal health at the University of Liverpool, added: “Health professionals know that midwives and doctors should not interrupt the flow of blood to the newborn baby nor separate the mother and baby without a pressing reason, and yet this is what is being shown on popular television programmes as common practice. “Incorrect depictions like this, however routine, can lead to misinterpretations of correct practice by the public. “This illustrates the need for safety recommendations when TV dramas show birthing practices and procedures that are outdated and inaccurate.” A spokesperson for Call The Midwife said: “Call The Midwife is a drama, not a documentary, and is set half a century ago. “It is highly accurate to the period it depicts, and shows how childbirth has changed radically over the years.” The study was published as the charity Lullaby Trust, which raises awareness of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), highlighted infection prevention among newborns. It said that parents should avoid letting other people kiss their baby and should always ask people to wash their hands before touching a newborn. “Even infections that cause mild symptoms such as a common cold in adults and older children can be life-threatening for babies,” said charity chief executive Jenny Ward. Read More Halloween: 10 wicked ways to kit out your haunted house Black magic: Go back to black this season with the catwalk-inspired trend How to prep your home for when the clocks go back Menopause campaigner Mariella Frostrup: ‘I look forward to a future where women gradually stop feeling so ashamed’ More girls miss school and college due to their periods than colds, survey finds More girls miss school and college due to their periods than colds, survey finds
1970-01-01 08:00
