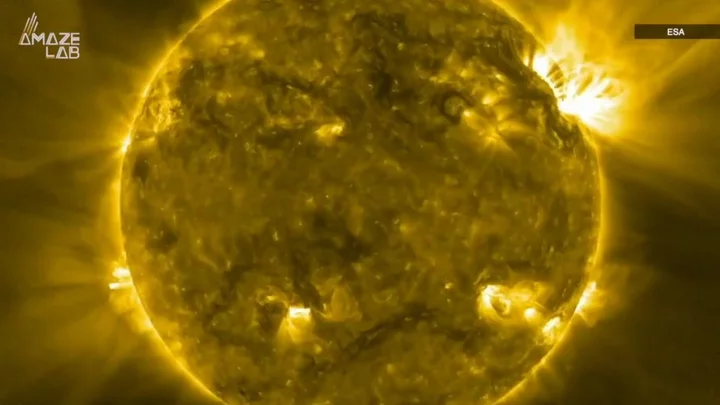

Tsunamis 3 times the size of the sun 'could disintegrate' Earth
Scientists have detected huge waves in outer space that measure three times the size of our sun. The waves are being formed on a star system called MACHO 80.7443.1718, found around 169,000 light-years from Earth in the Large Magellanic Cloud. The waves are formed in a similar way to waves on Earth. Just like ones on our planet are formed due to the gravitational pull of the moon, a nearby celestial object stretches the star and causes enormous waves in the system MACHO 80.7443.1718. Experts have studied the star’s unusual behaviour and published a paper in the journal Nature Astronomy. The experts stated that MACHO 80.7443.1718 contains a "heartbreak" star, which is a term they use to describe the way plasma is influenced by the pull of a nearby object to unleash incredible waves of energy. The sheer power of these waves is, itself, difficult to imagine. In fact, just one of them would end life on Earth in an instant. "Each crash of the star’s towering tidal waves releases enough energy to disintegrate our entire planet several hundred times over," MacLeod said. "This heartbreak star could just be the first of a growing class of astronomical objects," MacLeod added. "We’re already planning a search for more heartbreak stars, looking for the glowing atmospheres flung off by their breaking waves." The scale in general is far beyond human comprehension – at least ours, anyway. In fact, the waves of plasma measure around 2.5 million miles above the surface of the primary star – which itself has a radius of 10.4 million miles, around 24 times the size of the sun. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Man's legs turn purple in rare Covid complication
The effects of long Covid are still being uncovered by experts, and now doctors have been studying a rare complication that saw a man’s legs turn purple. A new research paper has been released which looks into the case of a 33-year-old man who had been infected with Covid 18 months earlier and experienced difficulties when standing up. His legs would turn purple when he did so, as well as tingling and itching, but things would return to normal when he lay down. The odd condition was diagnosed as POTS dysautonomia. This was determined after his pulse was found to rise to 127 beats per minute when standing, as well as feeling shaky and unsteady on his feet. The paper leads on from previous studies, which detected POTS in 20 people after they developed a Covid-19 infection. According to the new study published in The Lancet, there is "evidence is growing of a link between long Covid and POTS dysautonomia”. The paper’s co-author Dr Manoj Sivan said in a statement: "This was a striking case of acrocyanosis in a patient who had not experienced it before his Covid-19 infection. "Patients experiencing this may not be aware that it can be a symptom of long Covid and dysautonomia and may feel concerned about what they are seeing. Similarly, clinicians may not be aware of the link between acrocyanosis and long Covid." Dr Sivan added: "We need to ensure that there is more awareness of dysautonomia in long Covid so that clinicians have the tools they need to manage patients appropriately." Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

AI has created celebrity Mortal Kombat and Street Fighter games and they look amazing
2023 has so far been the year of artificial intelligence and although not all of its uses have been welcome it does appear to have come up with one good thing: celebrity fighting games. In the past few days, AI creations of two of the most popular beat-up franchises, Mortal Kombat and Street Fighter have emerged on social media. However, rather than feature classic characters like Ryu, Ken, Chun-Li, Scorpion, Sub-Zero and Raiden these iterations feature exaggerated versions of famous faces from the real world. The first of these that went viral was Celebrity Mortal Kombat which was shared by the actual creator of the original game Ed Boon but was created by the YouTube channel Interdimensional TV. The celebrity version features: Joe Biden, Beyonce, Elvis Presley, Pope Francis, Angela Merkel, Donald Trump, LeBron James, Mark Zuckerberg, Kanye West, Xi Jinping, Oprah Winfrey, Albert Einstein, Kim Jung-Un, Jackie Chan, Hillary Clinton, Vladimir Putin, Elon Musk, Jeff Bezos, Stephen Hawking, Mother Teresa, Snoop Dogg, Shaquille O'Neill, Rihanna, William Shakespeare, Marilyn Monroe, George Washington, Gordon Ramsay, Ruth Bader Ginsberg, Barack Obama, Tom Cruise, Keanu Reeves, Queen Elizabeth II, Marie Curie, Taylor Swift, Mahatma Gandhi, The Rock and J Robert Oppenheimer. If that wasn't enough a Celebrity Mortal Kombat II video has also been made with an updated roster that Boon also shared. This one stars Will Smith, Greta Thunberg, Winston Churchill, Freddie Mercury, David Bowie, Steve Irwin, Mike Tyson, Nicki Minaj, Jimi Hendrix, Steve Jobs, Lionel Messi, Richard Nixon, Narendra Modi, Lizzo, Mr Rogers, Emma Watson, Kim Kardashian, Ellen Degeneres, Sylvester Stallone, Cardi B, Hunter Biden, Arnold Schwarzenegger, Volodymyr Zelensky, Ice Cube, Usain Bolt, Mozart, Nicolas Cage, Katy Perry, Michael Jackson, Bruce Lee, Joe Rogan, Notorious B.I.G, PewDiePie, Leonardo DaVinci, Chris Pratt, Margaret Thatcher, Frida Khalo, Mitch McConnell, Tesla, Justin Trudeau, Manny Pacquiao, Josef Stalin, Morgan Freeman and Chuck Norris. However, if you are more of a Street Fighter player then fear not as your interests have also been catered for. Many of the same faces from the Mortal Kombat game reappear but there are a few new characters such as Peter Dinklage, Miley Cyrus, Chris Farley and Johnny Depp. Sadly it doesn't look like we'll get to play these games anytime soon but we'll be first in line at the arcade should they become available. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Instagram users are not happy with new likes feature
From Twitter being rebranded as X, to Meta who have rivalled this with their new Threads platform, there's been quite a few changes to social media this year. One of those recent changes also includes Instagram’s new-like animation which applies to those who updated the app. It means that when you like something on Instagram, the large heart will then appear in the area where you double-tapped on the photo and then the heart flies upwards off the screen. Of course, when it comes to social media updates, no one is a fan of change and Instagram users made this clear on X, formerly known as Twitter. Here is a compilation of reactions who all shared they weren't happy with the new like update, as one declared the feature "sucks," though this update did result in some amusing memes too: Unfortunately for those who updated the app, there is no way to change the like option back to the original but those who haven't updated Instagram can avoid the new feature if they opt out of auto-updates on Instagram. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
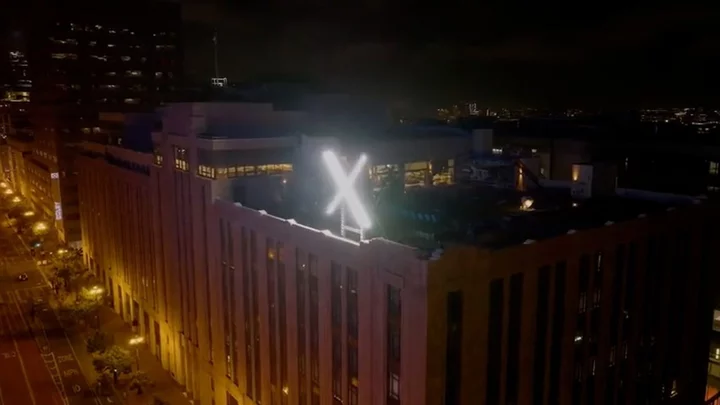

Elon Musk has updated the X logo again and everyone said the same thing
The logo of “X” (formerly known as Twitter) has changed again and everyone is saying the same thing. Since Elon Musk took over the social media platform Twitter, he has implemented some major changes, one of the biggest being a complete rebrand to “X” which left industry experts baffled. As part of the rebrand, the iconic logo of 17 years was changed from the famous sky blue and white bird logo to a black and white X that some have compared to resembling a porn site. Now, Musk has made another update to the default app icon logo, adding some white marks to the black background behind the X to give it a kind of worn grunge effect. But, the subtle change has been mercilessly mocked by X users and simply left everyone increasingly yearning to have the old bird logo back. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter “Impressive how they managed to make it look ever tackier,” one person argued. Another said: “Not the f**king grunge_overlay_04.png texture.” Someone else wrote: “Well it’s def not beating porn site allegations any time soon.” Among the criticism, others called for the app logo to be changed back to its original state. “They should update to this,” one person wrote. According to the number of likes the tweet has garnered, it would appear thousands of others agree. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
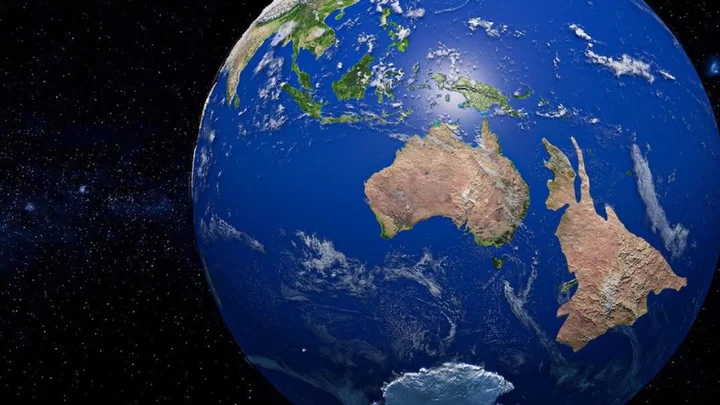

Scientists discover continent that had been missing for 375 years
Geoscientists discovered a continent that had been hiding in plain sight for almost 375 years. Historically, there's been speculation about whether a continent known as Zealandia or Te Riu-a-Māui in the Māori language exists. According to TN News, Zealandia is 1.89 million square miles in size. It was part of a supercontinent called Gondwana, which included most of Western Antarctica and Eastern Australia, over 500 million years ago. It was first said to be first discovered in 1642 by Dutch businessman and sailor Abel Tasman, who was desperate to uncover the "Great Southern Continent". Despite failing to find the new land, he met the local Māori, who were initially displeased by his arrival. However, they went on to provide valuable information about the surrounding land, including the existence of a large landmass to the east. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter It wasn't until 2017 that geologists discovered the continent had been hiding in plain sight all along. Scientists agreed on the existence of Zealandia, which started to "pull away" from Gondwana for reasons scientists are still trying to understand. Most of the newfound continent is underwater and has been used as an example by geologists at the Zealand Crown Research Institute GNS Science on how something "very obvious" can take a while to uncover. "[It's] a process which we don't completely understand yet, Zealandia started to be pulled away," Tulloch explained. His colleague Nick Mortimer, who led the study, joked that it was "kind of cool" before explaining: "If you think about it, every continent on the planet has different countries on it, [but] there are only three territories on Zealandia." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
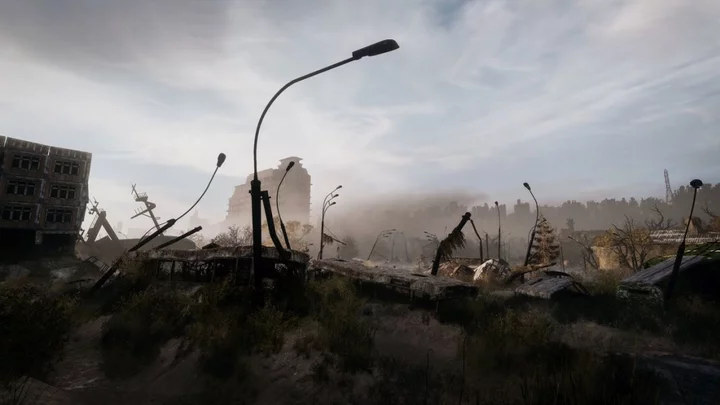

Experts have pinpointed exactly when society will collapse
A prediction about when society is most likely to collapse, made by scientists in the 1970s, has resurfaced – and it looks pretty bleak. Scientists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) used a computer to model patterns like population, natural resources and energy usage. The study, published by Club of Rome, picked out when these factors could hit “limits to growth”, which they said could lead to the downfall of modern life as we know it. They think we’ve got fewer than two decades left, with collapse due in 2040. Gulp. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter At the time, the report wasn’t given much credence. But a similar study was carried out in 2009, and came up with similar results. Published by American Scientist, the more recent study found that the model’s results were “almost exactly on course”. "It is important to recognise that its predictions have not been invalidated and in fact seem quite on target. We are not aware of any model made by economists that is as accurate over such a long time span," the study said. And to make matters worse, Dutch sustainability researcher Gaya Herrington concurred with the prediction in 2021. Speaking to The Guardian, Herrington said: “From a research perspective, I felt a data check of a decades-old model against empirical observations would be an interesting exercise.” Herrington found that data aligned with the predictions made back in 1972, which had a worse case scenario of economic growth coming to halt at the end of this decade, and collapse around 10 years later. Thankfully, there was a reason to be cheerful too. She added: “The key finding of my study is that we still have a choice to align with a scenario that does not end in collapse. "With innovation in business, along with new developments by governments and civil society, continuing to update the model provides another perspective on the challenges and opportunities we have to create a more sustainable world.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
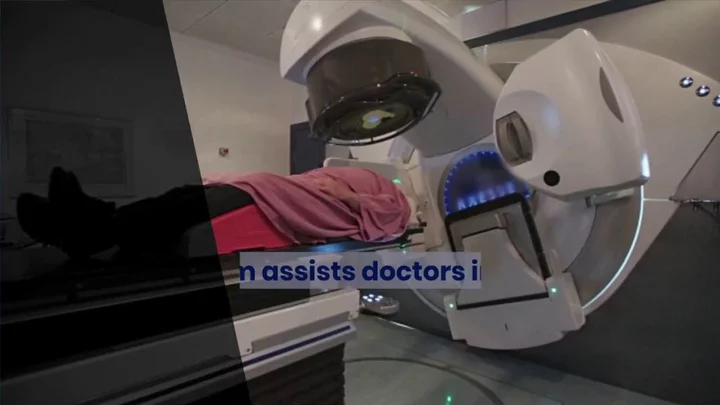

AI could soon be used to treat cancer in the NHS
Artificial intelligence could soon be used to perform radiotherapy to treat certain cancers for the first time. Draft guidance from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (Nice) has given approval to nine AI technologies for performing external beam radiotherapy in lung, prostate and colorectal cancers, which could save radiographers hundreds of thousands of hours and help relieve pressure on radiotherapy departments. Currently therapeutic radiographers outline healthy organs on digital images of a CT or MRI scan by hand so that the radiotherapy does not damage healthy cells by minimising the dose to normal tissue. Nice found that using AI to create the contours could free up between three and 80 minutes of radiographers’ time for each treatment plan, and that AI-generated contours were of a similar quality to manually drawn ones. Nice said that the contours would still be reviewed by a trained healthcare professional. It comes after a study found AI was safe to use in breast cancer screenings with evidence growing that it can be more effective in detecting cancers. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Meanwhile, Nice said it was also examining the evidence for using AI in stroke and chest scans. Dr Sarah Byron, the programme director for health technologies at Nice, said using AI could help reduce waiting lists. She added: “NHS colleagues working on the frontline in radiotherapy departments are under severe pressure with thousands of people waiting for scans. “The role imaging plays in radiotherapy treatment planning is quite pivotal, so recommending the use of AI technologies to help support treatment planning alongside clinical oversight by a trained healthcare professional could save both time and money. “We will continue to focus on what matters most and the recommendations made by our independent committee can help to bring waiting lists down for those needing radiotherapy treatment.” The health secretary, Steve Barclay, welcomed the announcement. He said: “It’s hugely encouraging to see the first positive recommendation for AI technologies from a Nice committee, as I’ve been clear the NHS must embrace innovation to keep fit for the future. “These tools have the potential to improve efficiency and save clinicians thousands of hours of time that can be spent on patient care. Smart use of tech is a key part of our NHS long-term workforce plan, and we’re establishing an expert group to work through what skills and training NHS staff may need to make best use of AI.” Charlotte Beardmore, the executive director of professional policy at the Society of Radiographers, welcomed the draft guidance but said it was not a replacement for staff and caution was needed. “It is critical there is evidence to underpin the safe application of AI in this clinical setting,” she said. Using AI would still require input by a therapeutic radiographer or another member of the oncology multi-professional team, she added. “Investment in the growth of the radiography workforce remains critical.” Science is pretty amazing. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
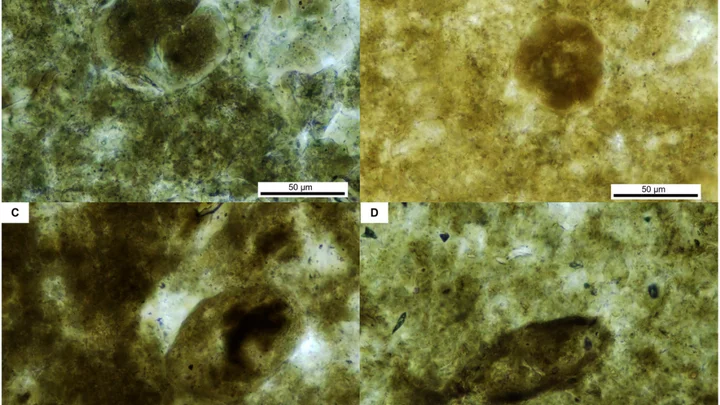
Scientists are cutting open parasitic eggs from 200 million years ago
A 200 million-year-old parasite has been discovered in fossilised poo, in the latest not-at-all-scary instance of scientists unearthing a species which blighted the Earth in ancient times. Researchers found that the earliest predators on the planet were infested with roundworm, also known as nematodes, among multiple other parasites. The fossilised poo, which is known to palaeontologists as coprolite, is thought to belong to a type of semi-aquatic phytosaur, which was a crocodile-like predator. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter It comes weeks after another team revived a prehistoric worm – the catchily named Panagrolaimus kolymaensis – which was found dormant in the Siberian permafrost in a state of “cryptobiosis”. The latest study saw researchers from Mahasarakham University, Thailand, analyse a three-inch-long portion of ancient poo and discover five types of parasitic remnants. The group sliced open the parasitic egg fossils with a diamond saw using a “standard thin section method,” their report said. The ultra-thin slices allowed the palaeontologists to look at cross-sections of the ancient infectious microbes under a microscope. One was identified as a nematode worm egg, while the others are thought to be either more eggs, protozoan cysts or spores from moss and ferns. While modern parasites are often an important part of ecosystems, it is usually more difficult to work out what their ancient equivalents did, because there are so few examples in the fossil record. The creatures often inhabited the soft tissues of their hosts, but are rarely preserved as fossils, making the latest discovery all-the-more significant. This fossilised late Triassic-era coprolite (the poo), was shielded from the elements in the Huai Hin Lat geological formation in Thailand, which is over 200 million years old. It was found by local villagers, according to the study's lead author, paleontologist Thanit Nonsrirach. “The peculiar appearance of these findings intrigued the villagers, who considered them potentially auspicious and capable of bestowing good luck if repurposed as talismans,” Nonsrirach told news outlet Inverse. “In 2010, our team received word of this discovery and embarked on a field expedition, guiding the villagers to the actual fossil site.” The discovery is the first record of parasites in a terrestrial vertebrate host from the late Triassic period in Asia, and provides a rare look at the life of an ancient creature that was infected by multiple species. This discovery also adds to the few known examples of nematode eggs preserved within the coprolites of Mesozoic animals. “Parasites of several species, including Ascaridida (roundworm) eggs were found in a coprolite, probably produced by a crocodile-like reptile and possibly a phytosaur,” said Nonsrirach, who works at Mahasarakham University's Palaeontological Research and Education Center. “This is therefore the first discovery of Ascaridida eggs and evidence of multi-infection in a host assignable to the Crurotarsi from the Late Triassic of Asia. “Coprolite is a significant palaeontological treasure trove, containing several undiscovered fossils and expanding our understanding of ancient ecosystems and food chains. “These findings are therefore a significant contribution to scientific understanding of the distribution and ecology of parasites of the distant past.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Scientists discover 3,000-year-old arrowhead made from a meteorite
An arrowhead believed to be 3,000 years old was made from the iron of a meteorite, according to scientists. The rare Bronze Age artefact was found near Lake Biel in Switzerland during a 19th-century excavation near a pile-dwelling station at a site in Mörigen (900-800 BC) before it was acquired by the Bern Historical Museum. In the new study published in the Journal of Archaeological Science, the 39-millimeter-long (1.5-inch-long) arrowhead was evaluated along with other Swiss archaeological finds to see if any were created from meteorites. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter This arrowhead in particular - which weighs 2.9 grams - was believed to be made from a meteorite that landed in Estonia. “Among just three large European iron meteorites with fitting chemical composition, the Kaalijarv meteorite (Estonia) is the most likely source,” the study said. It is thought this "large craterforming fall event" occurred in 1500BC during the Bronze Age and produced many small fragments. At this time, humans used the iron from meteorites, before they later learned how to smelt iron from oxide ores. "Archaeological objects made of meteoritic iron are extremely rare," the Bern Historical Museum said in a press release. Only 55 objects are known from the whole of Eurasia and Africa, and these come from 22 sites. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
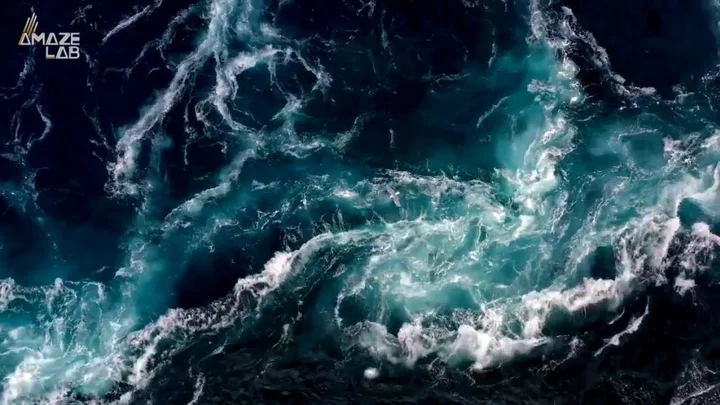

Never before seen ecosystem discovered thriving beneath ocean floor
Deep underground within the Pacific ocean, scientists have made a surprising discovery, which could significantly expand our understanding of marine life. Researchers found an entirely new ecosystem when turning over volcanic crust with the aid of an underwater robot, showing that even now, nature has many more secrets to unearth. The Schmidt Ocean Institute led an expedition with a team of international researchers to investigate a known site in the Pacific, according to Science Alert. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Subsurface fluids were found coursing beneath the ground, while scientists also found an ecosystem of worms, snails and chemosynthetic bacteria. The institute’s executive director, Jyotika Virmani, said: “This truly remarkable discovery of a new ecosystem, hidden beneath another ecosystem, provides fresh evidence that life exists in incredible places.” The new life was found beneath hydrothermal vents, which were first discovered in the 1970s spewing hot fluids loaded with minerals. They were in such a deep, dark location that scientists assumed there would be no life. Ecologist Monika Bright from the University of Vienna said: “Vent animals above and below the surface thrive together in unison, depending on vent fluid from below and oxygen in the seawater from above.” Scientists found tubeworms swimming through volcanic fluids, which makes it easier for them to get around and find new locations. The discovery came on the coast of central America, using a remote-controlled robot 2,500 metres below sea level. Wendy Schmidt, president of the Schmidt Ocean Institute, said: “The discovery of new creatures, landscapes, and now, an entirely new ecosystem underscores just how much we have yet to discover about our Ocean – and how important it is to protect what we don’t yet know or understand.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
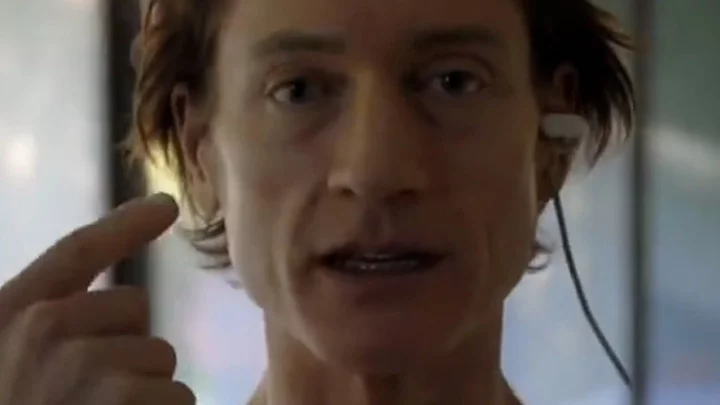

Man 'projected to live to 200' has to use machine to generate tears
The man who is 'ageing backwards' Bryan Johnson has revealed he now uses a machine to generate tears after his body stopped producing them. Johnson, who has the 'biological age of an 18-year-old' has gone viral for going to extremes to achieve peak health, however, it would seem everything isn't going so smoothly with his eyesight. "I have a dry eye condition which we found in our routine [doctor] visit", he tells the camera. He then films himself using the FDA-approved iTear100, which massages the side of his nose to stimulate tear ducts. Sign up to our new free Indy100 weekly newsletter
1970-01-01 08:00
