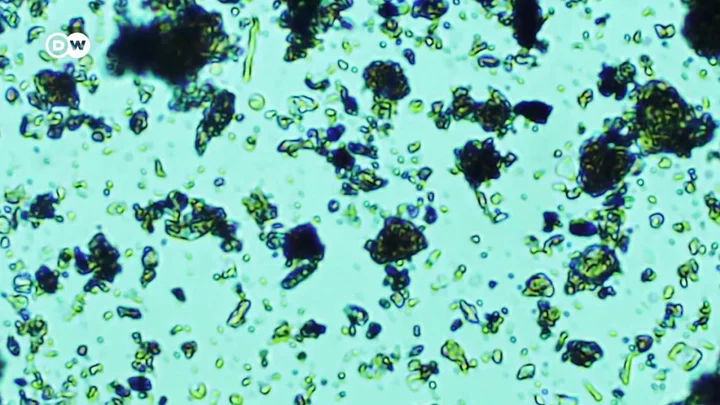
A key part of our bodies continues to live on years after we die
A key part of the human body survives even when we pass away, it has been revealed. Writing in the Conversation, Jennifer DeBruyn, Professor of Environmental Microbiology, University of Tennessee explained that microbes living in your gut which help you digest food, produce essential vitamins and protect you from infection, live on and help recycle dead bodies long after they pass. She explained: "When you die, your heart stops circulating the blood that has carried oxygen throughout your body. Cells deprived of oxygen start digesting themselves in a process called autolysis. "Enzymes in those cells – which normally digest carbohydrates, proteins and fats for energy or growth in a controlled way – start to work on the membranes, proteins, DNA and other components that make up the cells. "The products of this cellular breakdown make excellent food for your symbiotic bacteria, and without your immune system to keep them in check and a steady supply of food from your digestive system, they turn to this new source of nutrition." The human body is pretty amazing. It comes after researchers discovered a strange reoccurring mathematical pattern within human cells. Our bodies are made up of a massive variety of individual cells with countless different functions, from neurons in our nervous system to the oxygen carriers that all work in harmony to keep us alive. Experts from scientific research institutions in Germany, Canada, Spain, and the US have worked together on a study to determine just how many cells of each type there are in the human body and the results are staggering. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
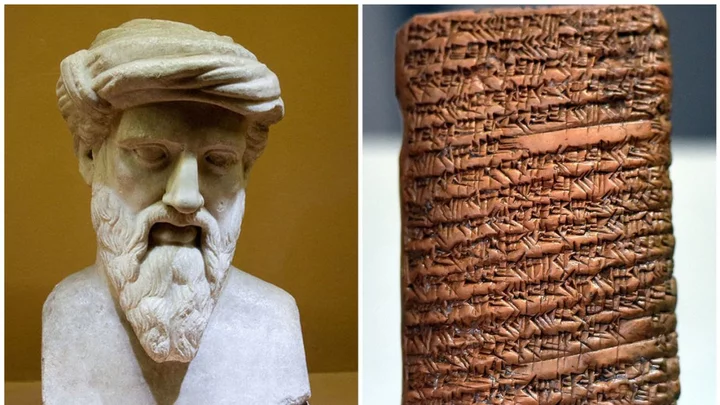

Pythagoras' theorem found on tablet that is 1,000 years older than Pythagoras himself
For many of us, the mere words “Pythagoras’s theorem” are enough to revive pencil-smudged exercise books and desperate attempts to copy classmates’ work. And yet, it turns out the name that has struck dread in countless school kids over the centuries is about as accurate as this writer’s attempts at geometry. Because although it is assumed that the legendary Greek philosopher Pythagoras himself was to thank for the equation a2 + b2 = c2, it turns out it was being used some 1,000 years before his time. Archaeologists have found the equation on a Babylonian tablet which was used for teaching back in 1770 BCE – centuries before Pythagoras’s birth in around 570 BC, as IFL Science notes. Another earlier tablet, from between 1800 and 1600 BC, even features a square with labelled triangles inside. Translations of the markings, which followed the base 60 counting system used by ancient Babylonians, prove that these mathematicians were familiar with Pythagorean theorem (although, obviously, they didn’t call it that) as well as other advanced mathematical principles. In a paper dedicated to the discovery, data scientist Bruce Ratner wrote: "The conclusion is inescapable. The Babylonians knew the relation between the length of the diagonal of a square and its side: d=square root of 2. "This was probably the first number known to be irrational. However, this in turn means that they were familiar with the Pythagorean Theorem – or, at the very least, with its special case for the diagonal of a square [...] more than a thousand years before the great sage for whom it was named." And yet, one key problem remains unsolved: why did the equation become equated with the famous Greek? Well, most likely because Pythagoras wanted it to be. In his paper, Ratner points out that although the Ionian icon is widely considered the first bonafide mathematician, little is known about his specific mathematical achievements. Unlike his successors, he didn’t write any books that we know of, so there’s no written evidence of his work. However, we do have proof that he founded a semi-religious school called the Semicircle of Pythagoras, which followed a strict code of secrecy. As Ratner explained: “Pythagorean knowledge was passed on from one generation to the next by word of mouth, as writing material was scarce. Moreover, out of respect for their leader, many of the discoveries made by the Pythagoreans were attributed to Pythagoras himself. “Consequently, of Pythagoras’ actual work nothing is known. On the other hand, his school practiced collectivism, making it hard to distinguish between the work of Pythagoras and that of his followers. “Therefore, the true discovery of a particular Pythagorean result may never be known.” Still, he stressed, even though Pythagoras wasn’t the brains behind the most famous formula in maths, he does deserve a little credit for putting it on the map. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
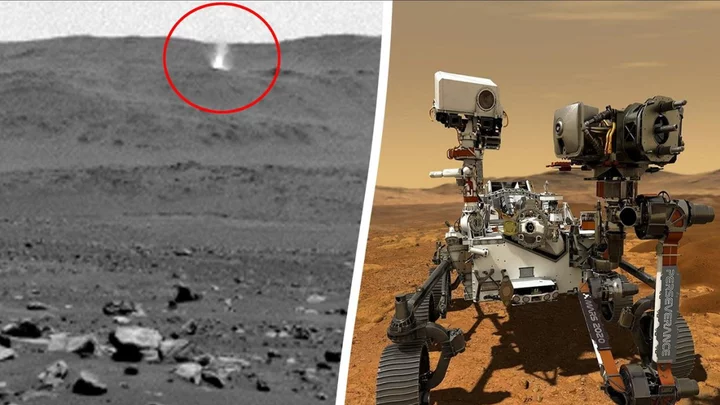

NASA captures 'dust devil' on the surface of Mars
A NASA rover has captured incredible footage of a “dust devil” sweeping across the surface of Mars. To many on Earth, dust devils are known to form vertical columns of particles and hot air when the weather is particularly warm. But, astronomers have now observed a dust devil forming on Mars and it was absolutely huge, reaching an astounding 1.2 miles high. Images of the phenomenon were captured by NASA's Perseverance rover, which made its way to the Red Planet on 30 July 2020 and landed in February 2021. The machine’s cameras captured the plume of air and particles moving from east to west, travelling at a speed of around 12 miles per hour at Thorofare Ridge, on the western rim of the planet’s Jezero Crater, on 30 August 2023. The rover was located around 2.5 miles from the passing dust whirlwind when it captured the incredible scene in a series of photographs. NASA used the image data received from Perseverance to create a moving image made up of 21 frames taken four seconds apart, sped up 20 times. A NASA blog post about the phenomenon explained: “Using data from the imagery, mission scientists determined that the dust devil was about 2.5 miles (4 kilometres) away, at a location nicknamed ‘Thorofare Ridge,’ and moving east to west at a clip of about 12 mph (19 kph). “They calculated its width to be about 200 feet (60 meters). While only the bottom 387 feet (118 meters) of the swirling vortex are visible in the camera frame, scientists used the dust devil's shadow to estimate its full height at about 1.2 miles (2 kilometres).” It comes after alien enthusiasts were given a new reason to get excited about potential life on Mars, after scientists found cracked mud on the Red Planet. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Physics Nobel Prize rewards science on a 'tiny timescale'
This year's Nobel Prize in Physics rewards research into electrons in "flashes of light".
1970-01-01 08:00
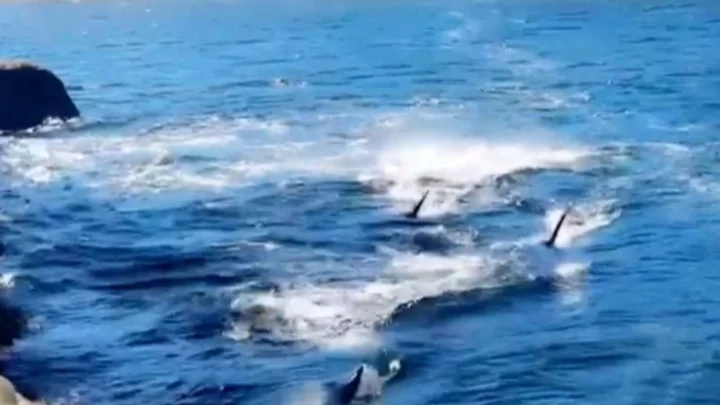

Experts investigate baffling case of orca that swallowed 7 sea otters whole
Experts have been left baffled after the body of a female orca (Orcinus orca) was found on a beach and inside there were seven sea otters that had been swallowed whole. The dead animal washed up on the Commander Islands (Komandorski Islands) on the Bering Sea coast in 2020 - far from its typical area, according to the study published in Aquatic Mammals. But there has been further confusion due to otters not being associated as part of an orca's normal diet, with the species preferring seals, sea lions, dolphins, and whales. Six of the seven otters were inside the orca's stomach while the other one was lodged in the orca's throat, raising a possible answer to how the mammal died. Dr Olga Filatova, a cetacean researcher at Moscow State University described what they had found as "very unusual" and noted that otters are not associated with an orca's - aka a killer whale's - diet. “...killer whales normally do not eat sea otters - there were some observations of them harassing and killing sea otters, but very few proofs of actual consumption," she said. What's more, the fact that the otters were swallowed whole is also different from how orcas typically consume their food as they normally rip it apart. Therefore, this particular orca swallowing seven otters whole has raised some eyebrows. Some possible theories Dr. Filatova has come up with as to understand what happened include the idea that the orca was "very hungry, or sick, or crazy". Meanwhile, this bizarre case could possibly be the answer to the recorded decline in sea otters in the area. “Investigating the stomachs of stranded killer whales is crucial to directly confirm feeding on particular species," Dr Filatova and her colleagues concluded. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Typhoon Koinu on Track to Hit Taiwan, Approach Hong Kong
Severe Typhoon Koinu will pass over the southern tip of Taiwan in coming days before heading toward Hong
1970-01-01 08:00

Scientists have discovered a disturbing link between milk tea and depression
Bad news for milk tea drinkers, as the beverage - which comes in different forms such as bubble tea - has some disturbing links to depression, according to a new study. Milk tea is widely consumed worldwide, but it has become particularly popular among young people in China over recent years. While many of us buy the drink as a sweet treat or pick-me-up, researchers from Tsinghua University and the Central University of Finance and Economics in China investigated whether milk tea addiction is a thing. After 5,281 university students in Beijing were surveyed as part of the research published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, they found that milk tea addiction does exist and also spotted connections between this issue with anxiety and depression. Researchers noted the "tremendous growth" the beverage has had with youth as well as their findings from the study. "Our findings highlighted that milk tea consumption might lead to addiction, and it is associated with depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation," they wrote in the paper. Nearly half of the students surveyed said they had at least one cup of milk tea on a weekly basis, while a scale of addiction was used to understand the symptoms such as cravings, immoderation and how this affects daily life. Given that milk tea includes both caffeine and extra sugar, the effects of these ingredients cause worry - with low moods and social isolation as examples. "The results indicate that milk tea consumption might lead to addiction symptoms, including frequency, dependence/craving, intention to stop, unable to stop, tolerance, and guilty feelings," the paper read. Milk tea addiction has been compared to social media and drugs in terms of how damaging it can be, particularly when used to try and regulate emotions. However, a large study would be needed over a longer period of time to gain further understanding of this. To conclude, researchers want further regulation and safeguarding against both the physical and mental symptoms possibly connected to drinking milk tea, for example addiction, depression and obesity. "Current findings can assist policymakers in developing regulations such as restricting advertising, providing psycho-education, establishing food hygiene standards for such a prosperous youth-dominant consumption industry while protecting their mental health," they stated. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
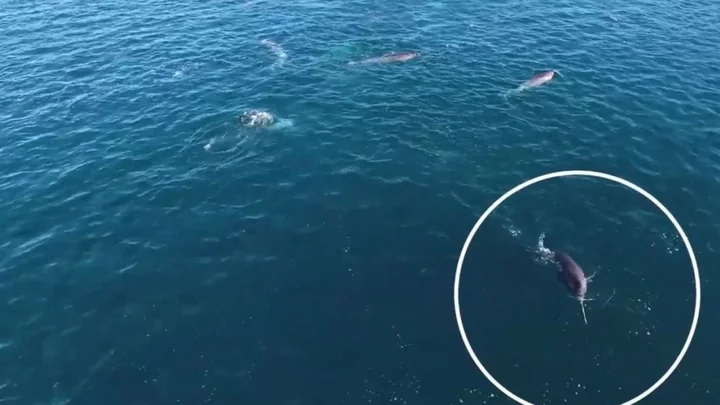

There's a sinister reason why you never see narwhals in aquariums
Narwhals are among the most elusive creatures in the ocean, with their long, spiralling tusks giving them an almost mythological quality. And whilst many people would pay good money to see these unicorns of the sea in the flesh, they are notably absent from the world’s aquariums. The reason for this is both dark and mysterious, since there have only been two attempts to keep the toothed whales in captivity. Both of these ended in tragedy and the general acceptance that narwhals simply don’t belong in our sealife centres. The legendary porpoises, which are related to belugas and orcas, are found in Arctic coastal waters and rivers. They have two teeth and, in males, the more prominent of these grows into the swordlike tusk which can be up to 10 feet long, according to National Geographic. Back in 1969, Coney Island’s New York Aquarium becoming the first-ever centre to put a narwhal on display. According to IFL Science, the aquarium became home to a young calf called Umiak, whose name referred to the canoe used to hunt the species in the High Arctic. It was captured by members of the Inuit community who said that it followed their canoe back to camp after they killed its mother for meat. Umiak was put in a tank alongside a female “white whale” (most likely a beluga), who acted as its stepmother. And although staff reportedly fed vast quantities of milk mixed with chopped clams to keep it happy, they weren’t able to keep it healthy. Less than a year after Umiak arrived at the centre, the orphaned narwhal died of pneumonia, as reported by The New York Times at the time. Still, the animal’s swift and tragic demise didn’t stop Canada’s Vancouver Aquarium from attempting the same feat in 1970. The aquarium had been gearing up to host a narwhal since 1968, when its director, Murray Newman, hoped that bringing narwhals to the city could generate interest in the species and help with its conservation, IFL Science reports. After two unsuccessful attempts to capture one of the whales themselves, Newman and his team were forced to buy a young male from a community of Inuit hunters based in Grise Fiord on Canada’s Ellesmere Island. The animal was reportedly called Keela Luguk – a phonetic spelling of the word “qilalugaq”, which means “narwhal” in some Inuktitut dialects. Within a week of Keela Luguk’s arrival at Vancouver Aquarium in August 1970, the centre had caught two female narwhals and three calves, which were then added to his tank. However, in less than a month, the three calves had died. And by November, the two females were also gone. As public outrage mounted, the mayor of Vancouver himself called for Keela Luguk to be returned to the wild. But Newman would not succumb to their pressure and, eventually, on 26 December that same year, the young whale was reported to have died too. It’s not known exactly why the narwhals fared so dismally in captivity, particularly given that the species’s closest relative, the beluga, can survive a number of years, or even decades, in aquarium facilities. However, the porpoises are known to be exceptionally sensitive animals, with studies finding that they are so affected by human-made noises that even the sound of a ship sailing near their habitat is enough to radically impact their behaviour. Fortunately, aquariums seem to have got the memo, and narwhals have largely been left to continue their lives as fabled enigmas of the sea. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
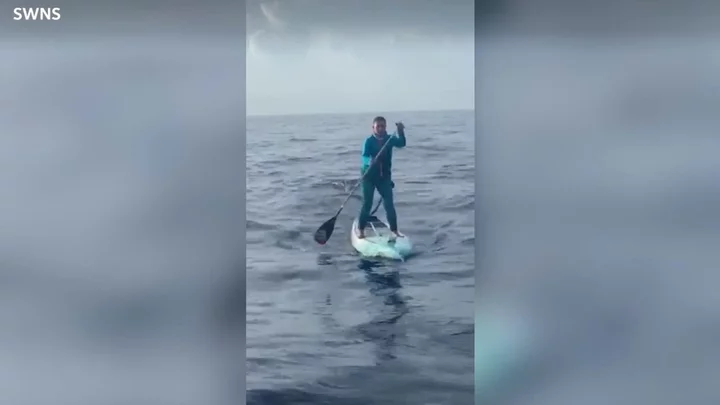

Groundbreaking footage shows how hammerhead sharks get their hammers
Hammerhead sharks are named that for a fairly obvious reason, but now groundbreaking footage has emerged which shows exactly how their unique head shape occurs. The strange-looking hammerhead shark has a very broad nose and spaced-out eyes that lend to its name and make it one of the most bizarre-looking sharks out there. Scientists studying the creature have until now had no idea how their hammers form, but now researchers have gotten a glimpse thanks to new footage. The species’ embryonic development is notoriously hard to study as they don’t lay eggs, so experts instead have been helped by the bonnethead sharks (Sphyrna tiburo), the smallest hammerhead species which is commonly found in estuaries and waters in the Gulf of Mexico and the Western North Atlantic Ocean. In a study published in Developmental Dynamics, researchers looked at embryos that had been preserved from bonnetheads that had been caught in previous studies to ensure that no additional sharks were affected. They studied embryos of the sharks at different stages of their development and witnessed as the shark's head started to form its unique shape. Hammerhead Transformation www.youtube.com The team found that the bonnetheads develop their head early on in their development, but the hammer doesn’t begin to form until around halfway through their gestation when the cartilage that forms the hammer begins to expand from the nasal area. The lead author, Steven Byrum, explained: “It’s the perfect qualities of the bonnethead that allowed us [to] do it with this species. “This was a unique opportunity we may not be able to get for very much longer with bonnetheads and may not be able to get in any other species of hammerhead.”
1970-01-01 08:00

Divers discover Megalodon teeth in flooded cave in Mexico
Divers in Mexico have discovered Megalodon teeth in a flooded inland cave and the findings have confirmed scientific beliefs. Megalodons were absolutely gigantic prehistoric sharks that reached sizes of up to 50 feet long. They dominated the oceans before going extinct around 3.6 million years ago. Scientists are interested in studying fossils of the huge sea creature, with the animal's teeth proving the most abundant type of fossil to be found today. Teeth fossils were found in Mexico by speleologist (cave specialist) and photographer Kay Nicte Vilchis Zapata and fellow speleologist Erick Sosa Rodriguez while diving in a newly discovered sinkhole in Cholul in 2019. The cenote is 400 meters long and 28 meters deep and located inside were fifteen teeth fossils from various shark species. They also discovered human remains and a vertebrae fossil that potentially belongs to an ancient species. A total of 13 of the 15 teeth fossils belonged to three different species of shark – one being the megalodon (Carcharocles megalodon), while the other two species were the mackerel shark (Isurus oxyrinchus) and the sawshark (Pristiophoridae). Zapata told local media at the time: “We were looking at the wall and suddenly I saw a little something, I went closer and I saw that it was a tooth, that was the first and apparently it belonged to a sawshark.” Experts believe the geological timescale of the megalodon teeth lies anywhere between 2.5 million to 5 million years old. Speleologist Sosa Rodriguez said: “It is just proof of what scientists have already studied and written about; what kind of wildlife lived here millions of years ago when this was part of the sea.” Scientists have suggested that the megalodon’s warm body temperature may have been the reason for its extinction. There is some thought that the megalodon was able to maintain a body temperature around 7 degrees centigrade warmer than the water around it, but ultimately this may have been its downfall. Randy Flores, a UCLA doctoral student and fellow of the Centre for Diverse Leadership in Science, explained: “Maintaining an energy level that would allow for megalodon’s elevated body temperature would require a voracious appetite that may not have been sustainable in a time of changing marine ecosystem balances when it may have even had to compete against newcomers such as the great white shark.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
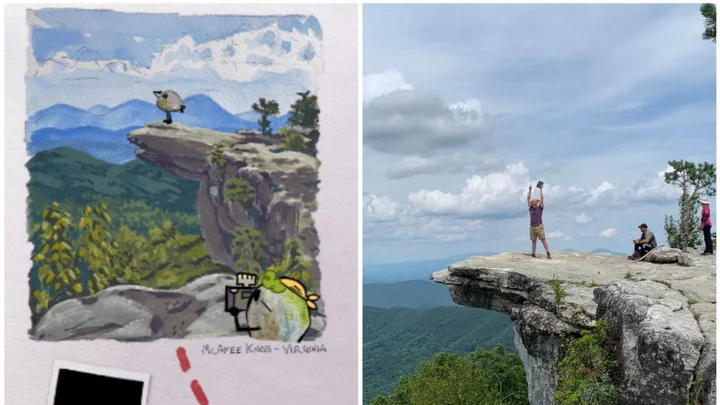

What's the Appalachian Trail? The iconic footpath featured in today's Google Doodle
As many of us face the drudgery of a Monday morning commute and a day holed up at work, it’s almost painful to think of beautiful, far-off lands and breathtaking views. And yet, this is what Google is inviting us to do with today’s interactive Doodle. Head to the search engine’s homepage and you’ll find a slideshow in the style of an illustrated scrapbook, teaching readers all about the Appalachian Trail. The iconic trail is the longest hiking-only footpath in the world, spanning more than 14 US states and 2,190 miles, as it meanders across dense forests, rushing rivers, and soaring mountains. And if you're wondering why the tech company has decided to pay tribute to the famous landmark today, it's because on 2 October 1968, America’s National Trails System Act established the Appalachian Trail as one of the country’s first National Scenic Trails. Hiking the full length of the path can take between five and seven months to complete and requires careful planning. And yet, as Google’s slideshow points out, around 3,000 people attempt this staggering feat each year, with a total of three million people visiting the trail annually. The route has served walking enthusiasts for nearly 100 years, having been completed in 1937. It was first proposed by conservationist Benton MacKaye in 1921, with his original plan calling for a stretch of several self-sustaining agricultural camps along the way, Google notes in its blurb for the Doodle. Then 10 years later, a hiker named Earl Shaffer became the first person to make it from one end to the other. Since then, more than 14,000 people have joined him in completing the trek. Perhaps inevitably for such a legendary trail, it has engendered a number of unique traditions. These include being given a “trail name” by fellow hikers and eating two litres of ice cream at the route’s mid-point. However, the trail’s oldest and most important tradition is to leave it just as you found it so that everyone can enjoy the same natural beauty. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Scientists now say finding alien life in the universe is 'only a matter of time'
Scientists are optimistic about the possibility of finding life on other planets. Nasa's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) found a possible sign of a gas that, on Earth, is produced by simple marine organisms. It was detected this month in the atmosphere of a planet named K2-18b, which is 120 light years away. The planet is in what astronomers call ''the Goldilocks zone' - the right distance away from its star for the surface temperature to be neither too hot nor too cold, but just right for there to be liquid water, which is essential to support life. The team expects to know in a year's time whether the hints are confirmed or have gone away. "We live in an infinite Universe, with infinite stars and planets. And it's been obvious to many of us that we can't be the only intelligent life out there," Prof Catherine Heymans, Scotland's Astronomer Royal told the BBC. "We now have the technology and the capability to answer the question of whether we are alone in the cosmos." Prof Nikku Madhusudhan of the Institute of Astronomy at Cambridge University, who led the study, told the BBC that if the hints are confirmed "it would radically change the way we think about the search for life". "If we find signs of life on the very first planet we study, it will raise the possibility that life is common in the Universe." He predicted that within five years there will be "a major transformation" in our understanding of life in the Universe. If his team don't find life signs on K2-18b, they have 10 more Goldilocks planets on their list to study - and possibly many more after that. Even finding nothing would "provide important insights into the possibility of life on such planets", he said. Meanwhile there are other separate projects all looking for signs of life in the universe. Pretty exciting. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
