
Scientists find explanation for huge gravity hole in the Indian ocean
Scientists have found an explanation for a 'gravity hole' in the Indian Ocean. A gravity hole is an area where gravitational pull is low, causing the seafloor to sink. Deep beneath the ocean, there is one that is three million square kilometers in size and previously it has confused scientists. Now two researchers from the Indian Institute of Science, Debanjan Pal and Attreyee Ghosh, think they have solved the mystery. More than 1,000 kilometers (621 miles) beneath Earth's crust, they found cold, dense remnants of an ancient ocean plunged into a 'slab graveyard' beneath Africa some 30 million years ago, stirring up hot molten rock. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Pal and Ghosh retraced the formation of the massive geoid by modeling how tectonic plates skimmed over Earth's mantle for the past 140 million years. They ran simulations and compared the shape of the oceanic low those models predicted with observations of the dent itself. The models that reproduced the Indian Ocean geoid low in its current form all had one thing in common: plumes of hot, low-density magma wafting up beneath the low. These plumes, as well as a distinctive mantle structure, are what created the geoid low; if they rise high enough, Pal and Ghosh reckon. "In short, our results suggest that to match the [shape and amplitude of the] observed geoid low, plumes need to be buoyant enough to come up to mid-mantle depths," the pair wrote. The first of these plumes appeared about 20 million years ago, to the south of the Indian Ocean geoid low, and around 10 million years after the old Tethys Sea sank into the lower mantle. As the plumes spread beneath the lithosphere and inched towards the Indian peninsula, the low intensified. But more research needs to be done to work out what is really going on as not all scientists are convinced. Science is crazy. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
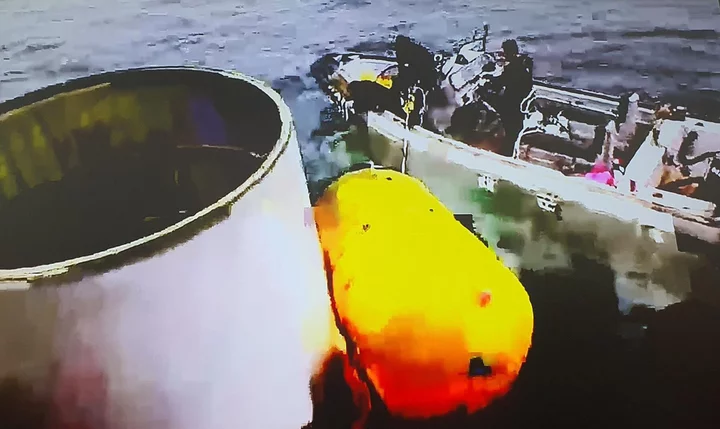

South Korea Salvages North’s Spy Satellite in Intelligence Win
South Korea salvaged a failed North Korean spy satellite from the sea, giving it a rare direct look
1970-01-01 08:00
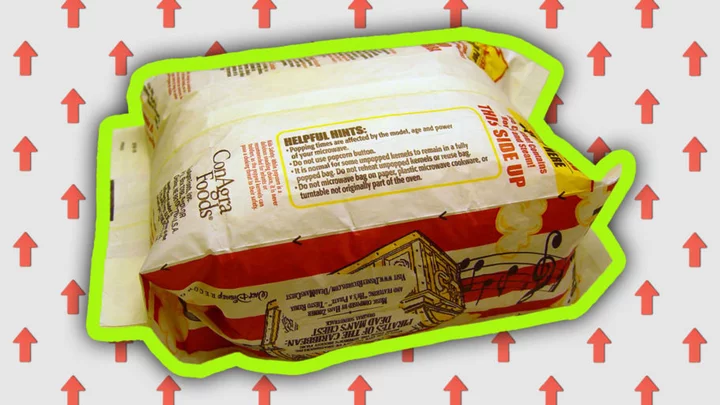

The Scientific Reason You Should Microwave Popcorn With “This Side Up”
Microwave popcorn bags are often covered in words—here’s why you should pay attention to “This Side Up.”
1970-01-01 08:00

Monday Was the Hottest Day Ever as Global Temperatures Rise
Global temperatures hit a record on Monday, underscoring the dangers of ever-increasing carbon emissions generated from burning fossil
1970-01-01 08:00

Time ran five times slower in the early universe, new study finds
New findings have revealed that time ran five times slower in the early universe, after scientists published new research into quasars. A quasar is a luminous active galactic nucleus and studying them has allowed scientists to measure time. The variation in brightness of quasars from the early universe has been measured to determine time dilation back to a billion years after the Big Bang. Experts have found that there was an era in which clocks moved five times slower than they do in the present day. The findings come as a relief to many cosmologists who have been perplexed by previous results that have come from studying quasars. The discovery that the universe is expanding led to the theorisation of “time dilation” – the idea that time moved slower the smaller the universe was. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Professor Geraint Lewis of the University of Sydney, the lead author of a new study, said in a statement: “Looking back to a time when the universe was just over a billion years old, we see time appearing to flow five times slower.” He continued, explaining: “If you were there, in this infant universe, one second would seem like one second – but from our position, more than 12 billion years into the future, that early time appears to drag.” To measure the extent of time dilation, scientists turned to quasars, as they are able to measure their change in brightness over a period they can estimate. The most distant quasar that is visible is 13 billion back in time and can still be seen despite its far distance. Their brightness varies due to turbulence and lumpiness in their accretion disks. Lewis explained the phenomenon as being “a bit like the stock market”. He said: “Over the last couple of decades, we’ve seen there is a statistical pattern to the variation, with timescales related to how bright a quasar is and the wavelength of its light.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
Scientists discover secret planet hiding in our solar system
There are eight planets in our solar system – plus poor old Pluto, which was demoted in 2006 – but what if there were more? Turns out that might be the case. Astronomers have calculated there is a 7 per cent chance that Earth has another neighbour hiding in the Oort cloud, a spherical region of ice chunks and rocks that is tens of thousands of times farther from the sun than we are. “It’s completely plausible for our solar system to have captured such an Oort cloud planet,” said Nathan Kaib, a co-author on the work and an astronomer at the Planetary Science Institute. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Hidden worlds like this are “a class of planets that should definitely exist but have received relatively little attention” until now, he said.. If a planet is hiding in the Oort cloud, it’s almost certainly an ice giant. Large planets like Jupiter and Saturn are generally born as twins. They have huge gravitational pulls of their own, however, and sometimes destabilise one another. That could have led to a planet to be nudged out of the solar system entirely – or exiled to its outer reaches, where the Oort cloud resides. “The survivor planets have eccentric orbits, which are like the scars from their violent pasts,” said lead author Sean Raymond, researcher at the University of Bordeaux’s Astrophysics Laboratory. That means that the Oort cloud planet could have a significantly elongated orbit, unlike the near-perfect circle Earth tracks around the sun. Trouble is, when things are that far away, they’re pretty difficult to spot. “It would be extremely hard to detect,” added Raymond. “If a Neptune-sized planet existed in our own Oort cloud, there’s a good chance that we wouldn’t have found it yet,” said Malena Rice, an astronomer at MIT not involved in this work. “Amazingly, it can sometimes be easier to spot planets hundreds of light-years away than those right in our own backyard.” Time to crack out the telescope. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
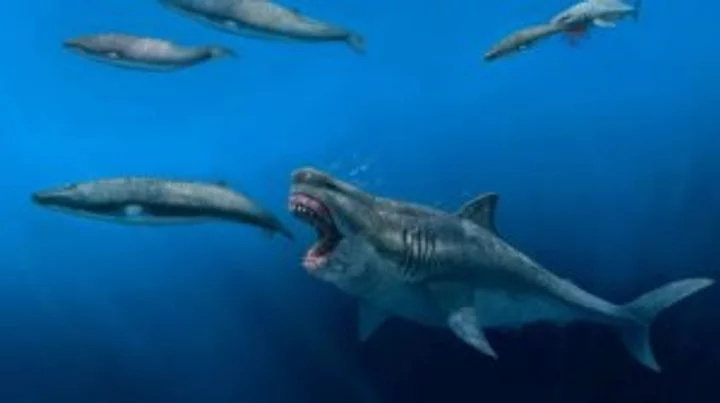

Scientists discover that megaladon's went extinct because of themselves
Scientists believe they have discovered the cause of the megalodon's extinction – and no, it’s not Jason Statham. Experts have been conducting research on fossils of teeth from the biggest species of shark the world has ever seen, which went extinct around 3.6 million years ago and measured at least 15 metres long. Research published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences explains that the animal was actually partially warm-blooded. Unlike most cold-blood sharks, the body temperature is thought to have been around 27 degrees. The temperature is higher than the sea temperatures around the time. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Study co author Robert Eagle, who is professor of marine science and geobiology at UCLA, said [via CNN]: “We found that O. megalodon had body temperatures significantly elevated compared to other sharks, consistent with it having a degree of internal heat production as modern warm-blooded (endothermic) animals do.” They were able to prove that the animals were warm-blooded by analysing how carbon-13 and oxygen-18 isotopes were closely bonded together in the fossilised teeth. Senior study author Kenshu Shimada is a paleobiologist at DePaul University in Chicago, who said: “A large body promotes efficiency in prey capture with wider spatial coverage, but it requires a lot of energy to maintain. “We know that Megalodon had gigantic cutting teeth used for feeding on marine mammals, such as cetaceans and pinnipeds, based on the fossil record. The new study is consistent with the idea that the evolution of warm-bloodedness was a gateway for the gigantism in Megalodon to keep up with the high metabolic demand.” The fact it was warm-blooded means that regulating body temperature could have been the cause of its eventual demise. The Earth was cooling when the animal went extinct, which could have been a critical factor. “The fact that Megalodon disappeared suggests the likely vulnerability of being warm-blooded because warm-bloodedness requires constant food intake to sustain high metabolism,” Shimada said. “Possibly, there was a shift in the marine ecosystem due to the climatic cooling,” causing the sea level to drop, altering the habitats of the populations of the types of food megalodon fed on such as marine mammals and leading to its extinction. “One of the big implications for this work is that it highlights the vulnerability of large apex predators, such the modern great white shark, to climate change given similarities in their biology with megalodon,” said lead study author Michael Griffiths, professor of environmental science, geochemist and paleoclimatologist at William Paterson University. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

The world's shortest IQ test will reveal how average your intelligence is in 3 questions
IQ tests offer a formula that allows you to compare yourself to other people and see how average (or above average) your intelligence is. The Cognitive Reflection Test (CRT) is dubbed the world’s shortest IQ test because it consists of just three questions. It assesses your ability to identify that a simple problem can actually be harder than it first appears. The quicker you do this, the more intelligent you appear to be. Here are the three questions: 1. A bat and a ball cost £1.10 in total. The bat costs £1.00 more than the ball. How much does the ball cost? 2. If it takes five machines five minutes to make five widgets, how long would it take 100 machines to make 100 widgets? 3. In a lake, there is a patch of lily pads. Every day, the patch doubles in size. If it takes 48 days for the patch to cover the entire lake, how long would it take for the patch to cover half of the lake? Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Here is what a lot of people guess: 1. 10 pence 2. 100 minutes 3. 24 days These answers would be wrong. When you're ready, scroll down for the correct answers, and how you get to them: 1. The ball would actually cost 5 pence or 0.05 pounds If the ball costs X, and the bat costs £1 more, then it will be: X+£1 Therefore Bat+ball=X + (X+1) =1.1 Thus 2X+1=1.1, and 2X=0.1 X= 0.05 2. It would take 5 minutes to make 100 widgets. Five machines can make five widgets in five minutes; therefore one machine will make one widget in five minutes too. Therefore if we have 100 machines all making widgets, they can make 100 widgets in five minutes. 3. It would take 47 days for the patch to cover half of the lake If the patch doubles in size each day going forward, it would halve in size going backwards. So on day 47, the lake is half full. In a survey of almost 3,500 people, 33 per cent got all three wrong, and 83 per cent missed at least one. While this IQ test has its shortcomings – its brevity, and lack of variation in verbal and non-verbal reasoning - only 48 per cent of MIT students sampled were able to answer all three correctly. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

UK Insurance Group Pushes Members to Act on Biodiversity Loss
A British insurance group is pushing its members, which include Allianz SE, Aviva Plc and Chubb Ltd., to
1970-01-01 08:00
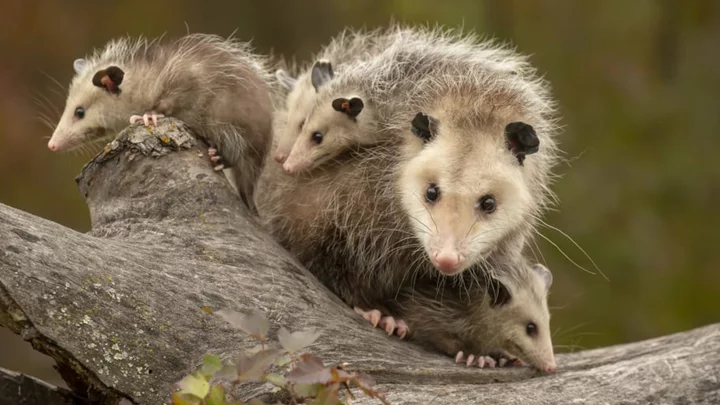

13 Facts About Opossums
Opossums have a bad reputation, but they’re smarter and more beneficial to people than other woodland denizens. Discover more about these unique marsupials here.
1970-01-01 08:00

17 of the funniest memes about Elon Musk's Twitter reading limit
As per Elon Musk's latest announcement, Twitter has started limiting the number of tweets a person can read. The tech mogul, who took over the platform in October in a $44 billion (£35 billion) sale, revealed on Sunday (2 July) that verified accounts can read up to 6,000 posts a day. Meanwhile, unverified users are limited to 600 a day, with newer Twitter accounts restricted to reading 300. "Rate limits increasing soon to 8,000 for verified, 800 for unverified & 400 for new unverified," he added later. The Tesla and SpaceX CEO said Twitter had imposed the "temporary limit" to "address extreme levels of data scraping & system manipulation." The decision sparked a furious backlash from many users, with one writing: "Sooo what’s everyone’s Instagram? Where we movin’ to cause this Twitter limit is dumb AF." Another added: "Seriously fed up with twitter now. This ‘rate limit’ thing is ridiculous. You can’t read a thread or see replies. What is the point? Why is Elon doing this… and why didn’t he warn people weeks ago if he was going to change rules?" Musk did not say when the limits will increase, or how long the restrictions will be in place for. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Inevitably, many more Twitter users hit back at the move in the most Twitter way possible: Memes. To add salt to the wound, thousands of people complained of problems accessing the site on Saturday (1 July). #Twitterdown and RIP Twitter began trending as frustrated users were faced with a message saying "Rate limit exceeded. Please wait a few moments then try again." Last week, people trying to access Twitter were told they would need to log in to an account to view tweets, in what Musk called a "temporary emergency measure." It comes after another outage in February, when many users were not able to tweet, follow accounts or access their direct messages as the platform was plagued by widespread technical problems. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
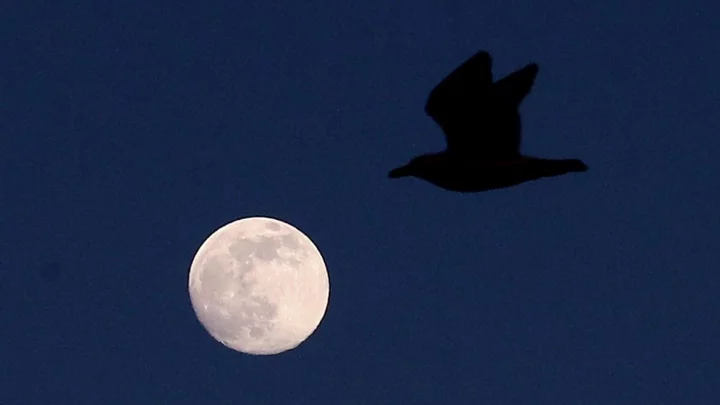

A 'supermoon' is on its way - here's how to take great photos of it
Try as you might, the moon is famously difficult to photograph. Smartphone images inevitably turn out blurred, or with the light all wrong. With Monday’s full moon set to be a supermoon, then, how can people try to ensure that they actually get a decent shot of it? A supermoon is an occasional coincidence that happens when the moon is at its closest point to the Earth in its orbit. When this happens, the Moon is usually brighter and appears larger in the sky than at other times. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The best time to catch it is just after sunset, when the Moon is just on the rise. The colour of the sky, and sometimes the clouds, should make it easier to get the right exposure, because the difference between the sky and the Moon’s colour is not so extreme. If you have a newer smartphone, you may also have settings which let you alter the focal length, exposure, ISO (the sensitivity of the camera) and shutter speed. “Make sure not to use flash, and switch on HDR (high dynamic range), if your phone has it. HDR, simply put, means that there will be a high contrast between the darkest and lightest parts of an image,” Mark Lord, founder and owner of Mark Lord Photography, told IFLScience. “This typically makes images more striking. Many modern smartphones feature HDR. Using flash, meanwhile, has ruined many a night sky capture.” Meanwhile, think about the focus too. Tempting as it may be to zoom in on the moon and try to get as much of it as you can is usually not going to work. “Even newer smartphones lack the capacity for zoom. Trying to zoom in on an object, particularly one as far away as the moon, may compromise the resolution and quality of an image” Lord added. “Instead, I recommend creating a more interesting shot by taking a landscape-style photo, adding depth and variety by making use of objects and landmarks in the foreground. A full moon captured through tree branches, for example, can make for a very spooky and atmospheric image.” So it’s time to get ready, and get snapping. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
