
New technique represents major breakthrough in search for aliens, scientists say
A new technique is a dramatic breakthrough in the search for alien life, astronomers say. Researchers at the Breakthrough Listen project based at the University of California, Berkeley say they have developed a new way to be sure that any potential signal is really coming from space – and not from something more boring. Astronomers spend vast amounts of time looking for radio signals that might have come from alien civilisations as part of work on the search for extraterrestrial intelligence, or SETI. But they have in the past been fooled by very human technology, such as cellphones, microwaves and car engines, that can produce a blast of radio signals that look as if they have come from distant worlds. One way to check whether signals are really alien is to point the telescope elsewhere and then repeatedly return to the same spot, with the hope of seeing the signal again and ensuring that it is not a false alarm. But that is not foolproof – and only works if the signal sticks around. Some of the most promising radio signals might only be detectable once. The so-called “Wow!” signal, for instance – a radio signal detected in 1977 that was so shocking the astronomer who found it wrote the exclamation on a printout – has not been detected since, and astronomers still do not know whether it was an alien message or just a mistake. Now scientists have devised a new test that can be used to see whether a signal has really passed through interstellar space, which should help show that it is not from elsewhere on Earth. It works by looking for “scintillation” – the changes in amplitude of a signal as it is affected by the cold plasma of space. “The first ET detection may very well be a one-off, where we only see one signal. And if a signal doesn’t repeat, there’s not a lot that we can say about that. And obviously, the most likely explanation for it is radio frequency interference, as is the most likely explanation for the Wow! signal,” said Andrew Siemion, principal investigator for Breakthrough Listen and director of the Berkeley SETI Research Center, which operates the world’s longest running SETI program. “Having this new technique and the instrumentation capable of recording data at sufficient fidelity such that you could see the effect of the interstellar medium, or ISM, is incredibly powerful.” Dr Siemion called the breakthrough “one of the biggest advances in radio SETI in a long time” and said that it would be the first time researchers would be able to differentiate a real signal from a false alarm, even if it was only detected once. The technique can only be used for signals that have travelled 10,000 light years or more to Earth, researchers note. If it was closer to us, the scintillation effect cannot be seen because they are not travelling through enough of the interstellar medium, or ISM. The research is described in a new paper, ‘On Detecting Interstellar Scintillation in Narrowband Radio SETI’, published in The Astrophysical Journal. Read More Battery breakthroughs are about to trigger a transport revolution Huge asteroid nearly crashes into Earth – and is only spotted days later ChatGPT rival with ‘no ethical boundaries’ sold on dark web
1970-01-01 08:00

Microsoft, UK ask for two-month pause of appeal over Activision deal
By Sam Tobin LONDON Microsoft on Monday asked a London tribunal to pause its appeal against Britain's block
1970-01-01 08:00

U.S. chip lobby presses Biden to refrain from further China curbs
By Stephen Nellis and Karen Freifeld (Reuters) -The U.S.-based Semiconductor Industry Association trade group on Monday called on the Biden
1970-01-01 08:00
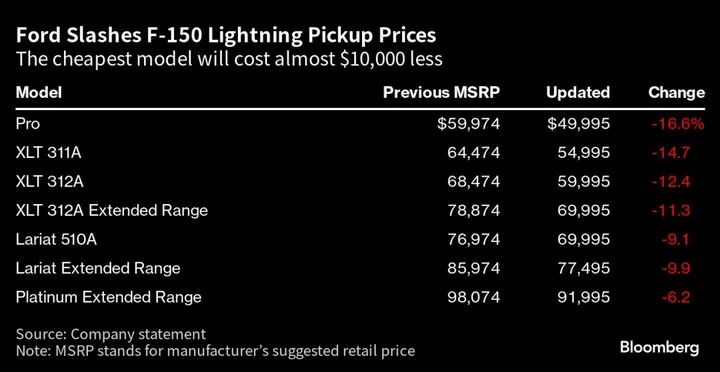
Ford Cuts Price on Electric Version of F-150 Truck by Up to 17%
Ford Motor Co. is slashing prices on the electric version of its best-selling F-150 pickup by as much
1970-01-01 08:00

ChatGPT rival with ‘no ethical boundaries’ sold on dark web
A ChatGPT-style AI tool with “no ethical boundaries or limitations” is offering hackers a way to perform attacks on a never-before-seen scale, researchers have warned. Cyber security firm SlashNext observed the generative artificial intelligence WormGPT being marketed on cybercrime forums on the dark web, describing it as a “sophisticated AI model” capable of producing human-like text that can be used in hacking campaigns. “This tool presents itself as a blackhat alternative to GPT models, designed specifically for malicious activities,” the company explained in a blog post. “WormGPT was allegedly trained on a diverse array of data sources, particularly concentrating on malware-related data.” The researchers conducted tests using WormGPT, instructing it to generate an email intended to pressure an unsuspecting account manager into paying a fraudulent invoice. Leading AI tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Bard have in-built protections to prevent people from misusing the technology for nefarious purposes, however WormGPT is allegedly designed to facilitate criminal activities. The experiment saw WormGPT produce an email that was “not only remarkably persuasive but also strategically cunning, showcasing its potential for sophisticated phishing attacks”, the researchers claimed. Screenshots uploaded to the hacking forum by WormGPT’s anonymous developer shows various services the AI bot can perform, including writing code for malware attacks and crafting emails for phishing attacks. WormGPT’s creator described it as “the biggest enemy of the well-known ChatGPT”, as it allows users to “do all sorts of illegal stuff”. A recent report from the law enforcement agency Europol warned that large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT could be exploited by cyber criminals to commit fraud, impersonation or social engineering attacks. “ChatGPT’s ability to draft highly authentic texts on the basis of a user prompt makes it an extremely useful tool for phishing purposes,” the report noted. “Where many basic phishing scams were previously more easily detectable due to obvious grammatical and spelling mistakes, it is now possible to impersonate an organisation or individual in a highly realistic manner even with only a basic grasp of the English language.” Europol warned that LLMs allow hackers to carry out cyber attacks “faster, much more authentically, and at significantly increased scale”. Read More Google’s AI chatbot Bard can now talk Elon Musk reveals plan to use AI to reveal mysteries of the universe Google has been ‘stealing everything ever created on the internet’ to train its AI Meet the AI human-like robots that can do our jobs
1970-01-01 08:00

With the rise of AI, social media platforms could face perfect storm of misinformation in 2024
Last month, a video posted to Twitter by Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis' presidential campaign used images that appeared to be generated by artificial intelligence showing former President Donald Trump hugging Dr. Anthony Fauci. The images, which appeared designed to criticize Trump for not firing the nation's top infectious disease specialist, were tricky to spot: they were shown alongside real images of the pair and with a text overlay saying, "real life Trump."
1970-01-01 08:00

Xbox and PlayStation sign major deal on the future of Call of Duty – as Activision deal gets closer
Microsoft will keep Call of Duty on PlayStation after it buys the series’ developer, according to a new deal signed with PlayStation. The Xbox and PlayStation makers have been engaged in a sometimes angry war in recent months, as Microsoft attempts to buy Activision Blizzard, the developer of games including Call of Duty. PlayStation’s objections centre around the fact that the deal would give Microsoft too much control over the gaming market, given the dominance of Call of Duty among players on consoles. Those objections have led to legal hearings, as well as opposition from regulators and competition authorities. At times, those legal objections have looked to derail the deal, which would be the biggest ever gaming acquisition if it is completed. But it now looks to be moving forward, after Microsoft announced that it had signed a “binding agreement” to make the games available on other consoles when the deal is complete. The deal could further ease regulators concerns about what would happen to the game as well as the broader console and gaming market if the deal goes ahead. It is the latest piece of good news for Microsoft, which won a legal case last week against objections from the US Federal Trade Commission, and looks to be moving towards closing the deal. “We are pleased to announce that Microsoft and PlayStation have signed a binding agreement to keep Call of Duty on PlayStation following the acquisition of Activision Blizzard. We look forward to a future where players globally have more choice to play their favorite games,” said Phil Spencer, Microsoft’s head of Xbox, in a tweet. And Microsoft President Brad Smith said in a tweet, “Even after we cross the finish line for this deal’s approval, we will remain focused on ensuring that Call of Duty remains available on more platforms and for more consumers than ever before.” The FTC had argued the deal would hurt consumers whether they played video games on consoles or had subscriptions because Microsoft would have an incentive to shut out rivals like Sony. To address the FTC’s concerns, Microsoft had earlier agreed to license “Call of Duty” to rivals, including a 10-year contract with Nintendo, contingent on the merger closing. Additional reporting by agencies Read More Battery breakthroughs are about to trigger a transport revolution ‘Hostile states using organised crime gangs as proxies in the UK’ Powerful solar flare to disrupt communications, Russians warn
1970-01-01 08:00

Microsoft and Activision Watch Hurdles to $69 Billion Deal Fall
Microsoft Corp. and Activision Blizzard Inc. — the video-game empire it’s seeking to take over in a $69
1970-01-01 08:00

Scientists are one step closer to creating a bonafide time machine
They may not be as stylish as a DeLorean or as sturdy as a blue police box, but wormholes in space could hold the key to real-life time travel – and a team of experts think they’ve figured out how. The trio of scientists delved deep into the laws of physics and discovered that it might be possible for humans to one day zip across galaxies in a matter of seconds, or journey through time itself. Now, this is all to do with the general theory of relativity and quantum physics, so don’t expect to get your head around it too easily. However, in their paper, Valeri P. Frolov and Andrei Zelnikov of Canada’s University of Alberta, and Pavel Krtouš of Prague’s Charles University proposed that a specific kind of wormhole would “inevitably” be “transformed into a time machine” if it was subject to particular conditions. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter For the uninitiated, wormholes can be described as spacetimes in which a “kind of tunnel exists connecting distant parts in the universe”. The main problem with them is… they don’t actually exist. At least not in any tangible way. As Drs Eric Christian and Louis Barbier put it in an explainer for NASA: “Wormholes are allowed to exist in the math of ‘General Relativity’, which is our best description of the Universe. “Assuming that general relativity is correct, there may be wormholes. But no one has any idea how they would be created, and there is no evidence for anything like a wormhole in the observed Universe.” Still, numerous experts in the field of gravitation and general relativity have spent years or even decades working on them, including Stephen Hawking in his time. For their paper, Frolov, Krtouš, and Zelnikov explored what is known as a ring wormhole, which was first described in 2016 by theoretical physicist Gary Gibbons, of Cambridge University, and Mikhail Volkov of the University of Tours. Unlike the spherical contortions of spacetime we might attribute to black holes, the ring wormhole proposed by Gibbons and Volkov connects sections of the universe (or, indeed, different universes) which are generally described as “flat”, as ScienceAlert notes. Ring-shaped masses could potentially create some pretty remarkable distortions in what would otherwise be flat spacetime if you consider how their electrical and magnetic fields might interact. And so Frolov, Krtouš, and Zelnikov decided to consider two types of such wormholes: “a wormhole connecting to flat spaces; and a wormhole connecting two distant domains in the same space”. For the latter, they concluded that if a “massive thin shell” surrounded one of the mouths of the ring wormhole, a “closed timelike curve” would form. This, as the name suggests, would mean that any travelling object (or ray of light) would come back to the exact same point whence it began. In other words, you could travel in space and time and return to your point of departure. The most exciting aspect of ring wormholes, as the authors point out is that: “For the ring wormhole an observer passing through it moves in a flat (or practically flat spacetime), while in the case of ‘standard’ (spherical) wormholes he/she should pass a domain filled with the matter violating the null energy condition.” Even without knowing what the “null energy condition” is, you can appreciate that the first option sounds a lot simpler. Now, before you start calling yourself Marty McFly or making a list of all the past mistakes you’d like to correct, we should stress that we’re a long way off seeing the creation of a bonafide, buckle-your-seatbelt time machine. But at least, thanks to the efforts of experts like Frolov, Krtouš, and Zelnikov, we’re at least one step closer to going back in the future. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

‘Hostile states using organised crime gangs as proxies in the UK’
Hostile states are using organised crime gangs to carry out illegal activity in the UK, the head of the National Crime Agency has warned. NCA director-general Graeme Biggar highlighted “the emerging links between serious and organised crime and hostile states” in a speech outlining the agency’s annual assessment of crime threats to Britain. Speaking in Westminster, central London, on Monday, he said: “North Korea has for some time used cybercrime to steal funds and more recently cryptocurrency. “The Russian state has long tolerated and occasionally tasked the cybercrime groups on its territory, and had links with its oligarchs and their enablers. “And over the last year we have seen hostile states beginning to use organised crime groups – not always of the same nationality – as proxies. “It is a development we and our colleagues in MI5 and CT (counter-terrorism) policing are watching closely.” Mr Biggar said the biggest group of offenders in the UK is those who pose a sexual threat to children, estimated to be between 680,000 and 830,000 people – around 10 times the prison population. He warned that the availability of abuse images online has a radicalising effect by normalising paedophiles’ behaviour, and that viewing images, whether real or AI-generated, increases the risk of someone going on to abuse a child themselves. There are around 59,000 people involved in serious organised crime in the UK, with around £12 billion generated by criminal activities each year, and around £100 billion of dirty cash from across the globe laundered through the UK. Key threats to the UK include: – Criminals exploiting migrants travelling to the UK in small boats. The number of arrivals doubled to more than 45,000 in 2022, with gangs using “bigger, flimsier, single-use boats” and packing more people on to each craft, Mr Biggar said. – Illegal drug use that fuels a raft of other crimes including violence, theft, use of guns and modern slavery. Nearly 120 tonnes of cocaine and 40 tonnes of heroin are consumed in the UK every year, and NCA analysis of waste water suggests cocaine use is increasing by 25% in some areas. The agency wants to stop the use of synthetic opioids like fentanyl getting a hold here as they have done in the US. – Online fraud, which accounts for more than 40% of all crime. Mr Biggar said: “We assess that 75% of fraud is partially or fully committed from overseas. Generative AI is also being used to make frauds more believable, through the use of ever better deep fake videos and Chat GPT to write more compelling phishing emails.” Mr Biggar said developments in technology such as increased use of end-to-end encryption are making the agency’s work harder. He finished his speech by saying: “Law enforcement, including the NCA, needs to do more to be at the leading edge of new technology: this will require collective vision and sustained investment. “And, secondly, we need more effective strategic partnership from technology companies. “This is about responsible behaviour about designing public safety into their products alongside privacy, so that we all reap the benefits from technology, rather than suffering their consequences.” Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Kim Kardashian, Rylan Clark and Dalai Lama among those joining new app Threads Mastercard helping banks predict scams before money leaves customers’ accounts Art historian helps build new Assassin’s Creed game after son’s suggestion
1970-01-01 08:00
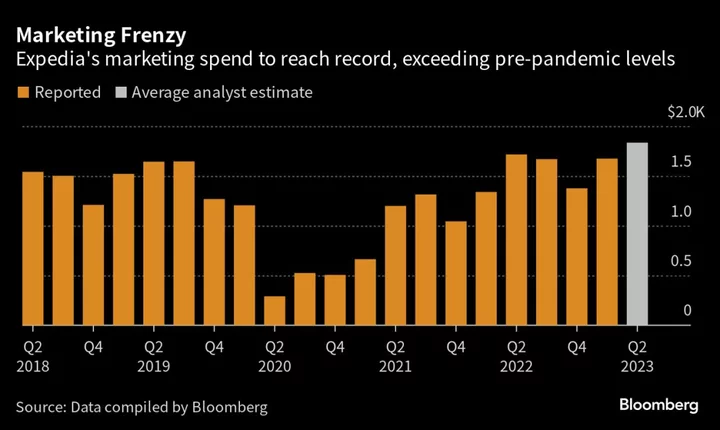
Expedia Launches Rewards Program Across Brands, Including Vrbo
Expedia Group Inc. is launching a long-awaited loyalty program across three of its flagship brands, capitalizing on a
1970-01-01 08:00

EU Commission sticks to US economist pick for senior antitrust job
By Foo Yun Chee BRUSSELS The European Commission stuck to its guns on Friday, saying it was not
1970-01-01 08:00
