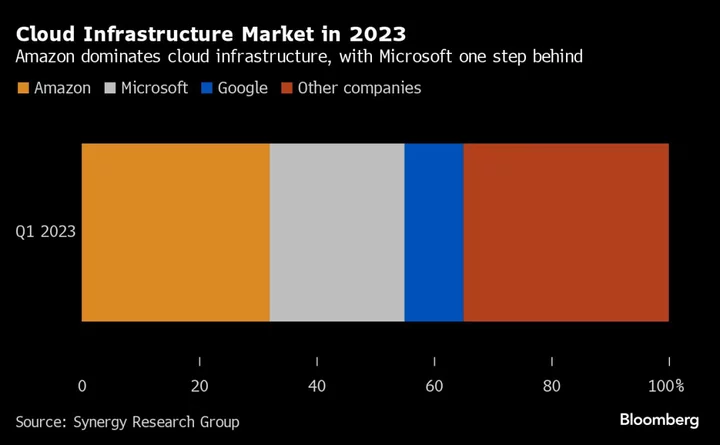
How Amazon Is Going After Microsoft's Cloud Computing Ambitions
Amazon is the driving force behind a trio of advocacy groups working to thwart Microsoft's growing ambition to
1970-01-01 08:00

HelloFresh Falls Most Since IPO After Warning on Profit
HelloFresh SE fell a record 25% on Thursday, erasing €886 million ($964 million) of market value, after the
1970-01-01 08:00

Fed Latest: Barr Issues Warning on Hedge Funds’ Basis Trades
The Federal Reserve’s top banking regulator on Thursday joined a chorus of US officials expressing concern about highly
1970-01-01 08:00
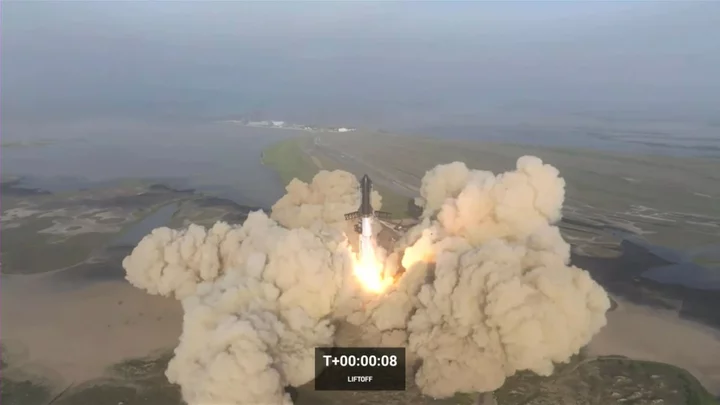

SpaceX Starship: World’s biggest rocket to launch again after first attempt ended in spectacular explosion
SpaceX is about to launch the world’s biggest and tallest rocket once again. Elon Musk’s private space company has got its final approval from US federal regulators to launch Starship on Friday morning local central time. The first launch of the rocket initially appeared to go well, with the rocket launching up into the sky and preparing for its journey around Earth. But minutes later the spacecraft began to tumble and soon after that it blew up in a vast explosion. Since then, SpaceX has been working to comply with regulators including aviation authorities as well as those tasked with protecting the environment and wildlife around its base in Texas. The Federal Aviation Administration issued its license Wednesday, noting that SpaceX has met safety, environmental and other requirements to launch again. Elon Musk's rocket company said it was targeting Friday morning. After the self-destruct system blew up the rocket over the Gulf of Mexico, SpaceX made dozens of improvements to the nearly 400-foot (121-meter) rocket and to the launch pad, which ended up with a large crater beneath it. SpaceX has a $3 billion NASA contract to land astronauts on the lunar surface as early as 2025, using the spacecraft. A month ago, the FAA completed its safety review of the upcoming Starship launch. It needed more time to wrap up its environmental review. No one was injured in the first attempt, but the pad was heavily damaged as the rocket's 33 main engines ignited at liftoff. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service later reported that concrete chunks, steel sheets and other objects were hurled thousands of feet (hundreds of meters) from the pad. It also said a plume of pulverized concrete sent material several miles (up to 10 kilometers) away. Wildlife and environmental groups sued the FAA over what they considered to be the FAA’s failure to fully consider the environmental impacts of the Starship program near Boca Chica Beach. Plans call for the test flight to last 1 /1/2 hours and fall short of a full orbit of Earth. The spacecraft would go eastward, passing over the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific oceans before ditching near Hawaii. Nothing of value will be on board. Additional reporting by agencies Read More The world’s most powerful rocket should launch imminently, Elon Musk says Robot hand with bones, ligaments and tendons 3D printed in world first Users of iPhones can now check bank balance from Wallet app
1970-01-01 08:00

Biggest-ever simulation of the universe could finally explain how we got here
It’s one of the biggest questions humans have asked themselves since the dawn of time, but we might be closer than ever to understanding how the universe developed the way it did and we all came to be here. Computer simulations are happening all the time in the modern world, but a new study is attempting to simulate the entire universe in an effort to understand conditions in the far reaches of the past. Full-hydro Large-scale structure simulations with All-sky Mapping for the Interpretation of Next Generation Observations (or FLAMINGO for short), are being run out of the UK. The simulations are taking place at the DiRAC facility and they’re being launched with the ultimate aim of tracking how everything evolved to the stage they’re at now within the universe. The sheer scale of it is almost impossible to grasp, but the biggest of the simulations features a staggering 300 billion particles and has the mass of a small galaxy. One of the most significant parts of the research comes in the third and final paper showcasing the research and focuses on a factor known as sigma 8 tension. This tension is based on calculations of the cosmic microwave background, which is the microwave radiation that came just after the Big Bang. Out of their research, the experts involved have learned that normal matter and neutrinos are both required when it comes to predicting things accurately through the simulations. "Although the dark matter dominates gravity, the contribution of ordinary matter can no longer be neglected, since that contribution could be similar to the deviations between the models and the observations,” research leader and astronomer Joop Schaye of Leiden University said. Simulations that include normal matter as well as dark matter are far more complex, given how complicated dark matter’s interactions with the universe are. Despite this, scientists have already begun to analyse the very formations of the universe across dark matter, normal matter and neutrinos. "The effect of galactic winds was calibrated using machine learning, by comparing the predictions of lots of different simulations of relatively small volumes with the observed masses of galaxies and the distribution of gas in clusters of galaxies," said astronomer Roi Kugel of Leiden University. The research for the three papers, published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, was undertaken partly thanks to a new code, as astronomer Matthieu Schaller of Leiden University explains. "To make this simulation possible, we developed a new code, SWIFT, which efficiently distributes the computational work over 30 thousand CPUs.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
1970-01-01 08:00

Glencore Bets on US Love of Coal With New Fossil Fuel Giant
Glencore Plc is preparing to unleash a new coal supermajor on the New York market that would –
1970-01-01 08:00
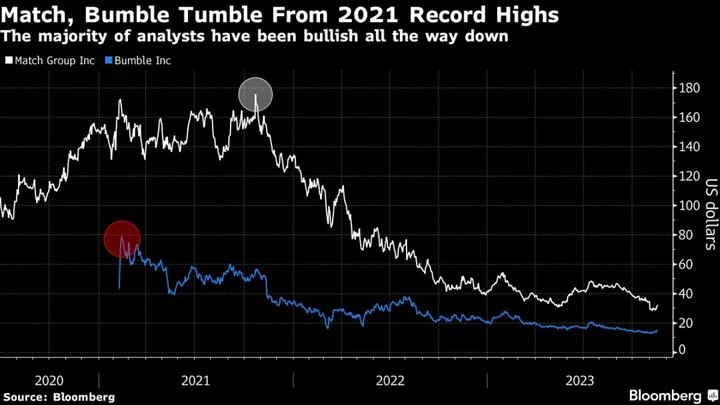
Match and Bumble’s 80% Stock Plunges Test Analyst Commitment
Online dating stocks have mostly been ghosted by this year’s scorching technology rally. Many on Wall Street continue
1970-01-01 08:00

Ramaswamy’s Crypto Policy Calls for Deregulation and Gutting the SEC
Vivek Ramaswamy vows to rescind most federal cryptocurrency regulations and drastically reduce headcount at the Securities and Exchange
1970-01-01 08:00

BlackRock woos investors for ethereum trust to further crypto push
Asset management giant BlackRock on Thursday began courting public investors for an ethereum trust, doubling down on its
1970-01-01 08:00

Water discovered to be leaking from Earth's crust into the planet's core
There is much we still don’t know about the inside of our planet – but scientists recently discovered water is slowly leaking down there from the surface. It’s not a simple journey. The liquid is dripping down descending tectonic plates, before eventually reaching the core after a 2,900 kilometre journey. And while the process is slow, it has over billions of years formed a new surface between the molten metal of the outer core and the outer mantle of the Earth. In a new study, scientists at Arizona State University have said the water is triggering a chemical reaction, creating the new layer, which is “few hundred kilometres thick”. (That’s “thin” when it comes to the inner layers of the Earth.) “For years, it has been believed that material exchange between Earth's core and mantle is small. Yet, our recent high-pressure experiments reveal a different story. “We found that when water reaches the core-mantle boundary, it reacts with silicon in the core, forming silica," co-author Dr Dan Shim wrote. “This discovery, along with our previous observation of diamonds forming from water reacting with carbon in iron liquid under extreme pressure, points to a far more dynamic core-mantle interaction, suggesting substantial material exchange.” So what does it mean for all of us up on the surface? The ASU release said: “This finding advances our understanding of Earth's internal processes, suggesting a more extensive global water cycle than previously recognised. “The altered ‘film’ of the core has profound implications for the geochemical cycles that connect the surface-water cycle with the deep metallic core.” How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Walmart Lifts Profit Outlook, Stays Cautious on US Consumers
Walmart Inc. modestly raised its annual profit forecast but struck a cautious tone about the outlook for US
1970-01-01 08:00

Top Dubai Crypto Official to Step Down After Less Than Year
The head of Dubai’s crypto regulator is poised to depart after less than a year on the job,
1970-01-01 08:00
