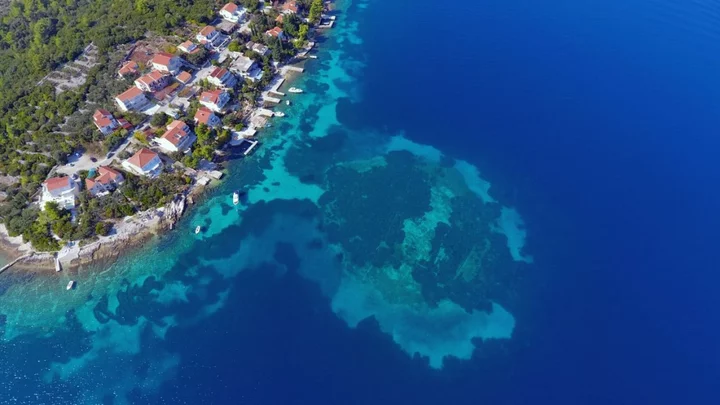

Scientists 'surprised' by 'strange underwater road' discovered in Europe
It’s not quite the lost city of Atlantis, but scientists have just uncovered a slice of history that had been swallowed up by the sea. Experts admitted that even they were surprised when divers unearthed a 7,000-year-old stone road that had lain buried under layers of sea mud. The ancient structure was discovered after archaeologist Igor Borzić, of the University of Zadar, spotted “strange structures” nearly 16 ft (5m) underwater in the Bay of Gradina, off the coast of Croatia. The submerged road once linked the island of Korčula to an artificial, prehistoric settlement that belonged to a maritime culture known as the Hvar. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The university released footage of the incredible finding over the weekend. It showed the passageway which consisted of stacked stones and measured some 12 ft (around 4m) across. Archaeologists believe people walked this road “almost 7,000 years ago”, with radiocarbon dating of wood near the site suggesting the settlement may have been built around 4,900 BC. “In underwater archaeological research of the submerged neolithic site of Soline on the island of Korčula, archaeologists found remains that surprised them,” the University of Zadar said in a Facebook statement. “Namely, beneath the layers of sea mud, they discovered a road that connected the sunken prehistoric settlement of the Hvar culture with the coast of the island of Korčula.” Borzić and his team also discovered another “almost identical” settlement on the other side of Korčula Island. Neolithic artefacts including a stone axe, cream blades and sacrificial fragments, were found at the site which lay at a depth of 4-5m. Understandably, the researchers were delighted and, as they continue to delve into their nation’s past, we wonder what else they’ll unearth. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Tesla offering discounts of over $1,300 on some U.S. Model 3 cars -website
By Hyunjoo Jin SAN FRANCISCO Tesla is offering discounts of more than $1,300 on some Model 3 cars
1970-01-01 08:00

U.S. FDA approves Krystal Biotech's skin disorder gene therapy
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration on Friday approved Krystal Biotech Inc's topical gene therapy for patients with
1970-01-01 08:00

Solar panel efficiency to increase 50% with first production of ‘miracle’ tandem cells
A South Korean firm has announced the world’s first production line for perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells, which promise an increase in efficiency of between 50-75 per cent compared to standard solar panels. The commercialisation of solar cells that use perovskite follows years of breakthroughs with the mineral, which has been hailed as a ‘miracle material’ for its potential to transform various industries, including renewable energy. Seoul-based Qcells said it will invest $100 million to roll out the next-generation solar cell technoloy, which until now has been limited to lab tests and academic research. The investment will fund a pilot production line at a factory in Jincheon, which is projected to be operational by late next year. “This investment in Jincheon will mark an important step in securing technological leadership,” said Qcells CEO Justin Lee. “With a global R&D network spanning from Korea, Germany and the US, Qcells will ramp up its efforts to produce high-efficiency advanced tandem cells.” Tandem solar cells are able to improve the efficiency of standard solar panels by splitting the light spectrum and optimising the harvesting of energy from each section into electricity. The current world record for solar cell efficiency is 32.5 per cent – meaning nearly a third of solar radiation is converted into eletrical energy – which was achieved with a perovskite-silicon tandem cell in December. By comparison, traditional silicon-based solar cells are currently only capable of reaching around 22 per cent efficiency. Qcells has so far succeeded in developing a tandem perovskite solar cell with a 29.3 per cent efficiency, which was achieved earlier this year in collaboration with German research centre Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin. The results were verified by the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) Read More Microsoft makes world first nuclear fusion energy deal Quantum computer discovers bizarre particle that remembers its past Nasa says Jeff Bezos will build moon lander to take astronauts to the Moon ChatGPT app launches for iPhone users amid scam frenzy Google to delete Gmail and Photos accounts in huge purge
1970-01-01 08:00
Scientists find that AI can read thoughts from monitoring your brain activity
Scientists have revealed they had found a way to combine the technology of brain scans and artificial intelligence to transcribe “the gist” of people’s thoughts. Alex Huth, an assistant professor of neuroscience and computing science at the University of Texas at Austin, and a co-author on the new study published in Nature Neuroscience, said that ‘this is a real leap forward.’ The study was led by Huth and Jerry Tang, a doctoral student in computer science. The main development from this study is that it’s non-invasive. This means that subjects do not require surgical implants. Instead, brain activity is measured using a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scanner. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter In the study, individuals listened to hours of podcasts in the scanner. Then, given the participant’s consent to have their thoughts decoded, they listened to a new story and the machine-generated corresponding texts from brain activity. It’s not a word-for-word transcript. For example, when an individual heard the phrase ‘I don’t have my driver’s licence yet’, the model decoded the individual’s thoughts to read as ‘she has not even started to learn to drive yet.’ Even when participants thought up their own stories, the machine was able to decode their thoughts still. Tang acknowledged that the advancements made in the study had the potential for negative aftermath. Tang said, ‘we take very seriously the concerns that it could be used for bad purposes and have worked to avoid that.’ They ran tests that highlighted that unless the machine had been trained on an individual’s particular brain activity, it could not decode its thoughts. An individual had to allow for the machine to train their brain activity over a long period of time inside a fMRI scanner for it to work. Researchers also found that it was easy to ‘sabotage’ the machine. Three participants were told to tell a different story in their mind, or count by seven, while listening to one of the podcasts. The study highlights even more development with artificial intelligence, after the popularity of OpenAI’s Chat GPT has sparked debate around the potential of AI. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

EU regulators' group sides with Big Tech against telcos' network fee push
By Foo Yun Chee BRUSSELS (Reuters) -The EU telecoms regulators' group BEREC on Friday criticised a push by telecoms providers
1970-01-01 08:00
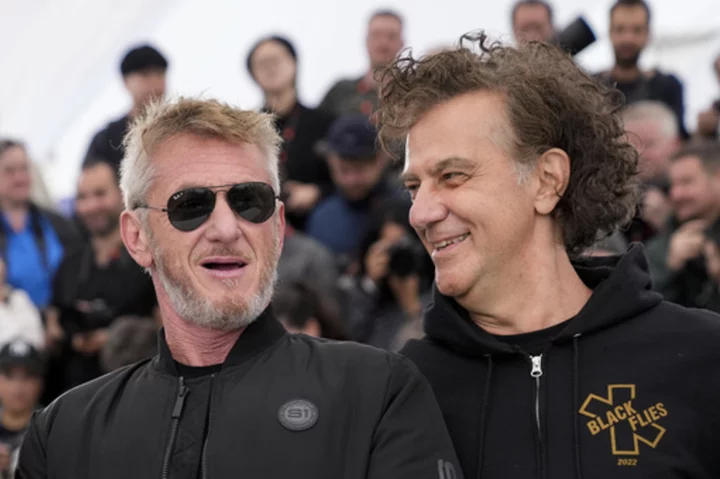

Sean Penn, backing WGA strike, says AI dispute is 'a human obscenity' at Cannes Film Festival
Sean Penn has strongly backed the current Hollywood screenwriters strike while speaking at the Cannes Film Festival on Friday, saying the dispute over artificial intelligence is “a human obscenity.”
1970-01-01 08:00

Twitter accuses Microsoft of refusing to pay for tweets and abusing its data access
Twitter is accusing Microsoft of abusing its data access privileges to its platform, in the latest sign of the social network's owner Elon Musk igniting a feud between the two tech companies.
1970-01-01 08:00

Exclusive-India's govt plans action against Google after antitrust breaches
By Aditya Kalra and Munsif Vengattil NEW DELHI India's government plans to take action against Alphabet Inc's Google
1970-01-01 08:00

Scientists discover that humans mastered fire centuries before history suggests
Humans in Europe may have mastered fire long before we previously thought. According to a study published in Scientific Reports, humans made the discovery around 245,000 years ago, up to 50,000 years earlier than scientist thought previously. Researchers studied samples from the Valdocarros II, a huge archaeological site found east of Madrid, Spain. Using chemical analysis, they found certain compounds that show things were burnt by fire in "organised" social events, rather than through accidents or wildfires. "We have found definitive evidence of things being burnt and those remains are organised into a pattern, suggesting it's humans who are making and controlling the fire. Either they were using the fire to cook or to defend themselves. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The spatial patterning in the fire tells us that they were encircling something, like a home or sleeping area, a living room or kitchen, or an enclosure for animals," Dr. Clayton Magill, study author and Assistant Professor at Heriot-Watt University in Scotland, said in a statement. Dr Magill added that this new work helps to fill in the gaps in our understanding of human-controlled fire and human development. "This is important because our species is defined by our use of fire," Dr Magill explained. "Being able to cook food to feed our big brains is one of the things that made us so successful in an evolutionary sense. Fire also brings protection and fosters communication and family connection. And we now have definitive, incontrovertible evidence that humans were starting and stopping fires in Europe about 50,000 years earlier than we suspected." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Nasa discover new planet that is entirely covered with volcanoes
Nasa scientists have found a planet they believe is covered by active volcanoes. In a study published in the journal Nature, scientists said they found the planet, which is the size of Earth about 90 light-years from Earth in the Crater constellation. They called it LP 791-18 d and one part is constantly scorched by sunlight, while the other is always in darkness. “The day side would probably be too hot for liquid water to exist on the surface. But the amount of volcanic activity we suspect occurs all over the planet could sustain an atmosphere, which may allow water to condense on the night side,” Björn Benneke, one of the astronomers who studied the planet, told NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The LP 791-18 system contains at least two other planets, called LP 791-18 b and c. The latter is two-and-a-half times larger than Earth and more than seven times its mass. It also affects the orbit of LP 791-18 d, making it travel along an elliptical path around the system’s sun. That path means LP 791-18 d is deformed every time it completes an orbit. “These deformations can create enough internal friction to substantially heat the planet’s interior and produce volcanic activity at its surface,” according to NASA. “A big question in astrobiology, the field that broadly studies the origins of life on Earth and beyond, is if tectonic or volcanic activity is necessary for life,” study co-author Jessie Christiansen said. “In addition to potentially providing an atmosphere, these processes could churn up materials that would otherwise sink down and get trapped in the crust, including those we think are important for life, like carbon.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Why Montana's TikTok ban may not work
Montana has become the first US state to ban TikTok on all devices, even personal ones, triggering renewed doubts about the short-form video app's future in the country.
1970-01-01 08:00
