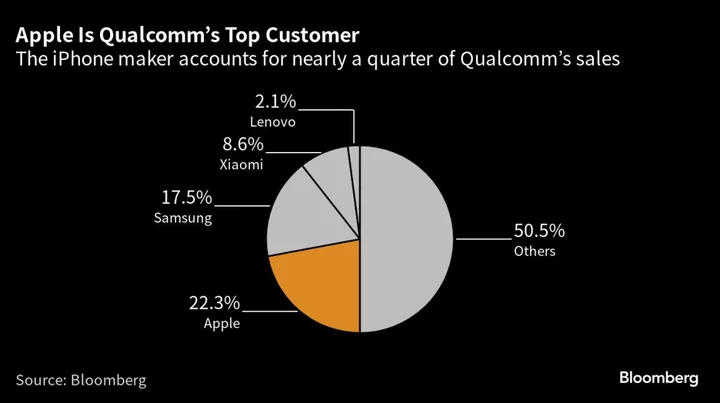
Apple Renews Qualcomm Deal in Sign Its Own Modem Chip Isn’t Ready
Apple Inc. is extending an agreement to get modem semiconductors from Qualcomm Inc. for three more years, a
2023-09-11 21:30

Suprema America and BioConnect Expand their Partnership to Deliver the Next Generation of Biometric Physical Security
DALLAS--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 11, 2023--
2023-09-11 20:57

SAIC to Modernize U.S. Space Force Ground Based Radar Maintenance and Sustainment Services
RESTON, Va.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 11, 2023--
2023-09-11 20:06

Artificial intelligence e discusses ways for humans to ride a 'coming wave' of new technology
If you have watched a telecast involving basketball superstar LeBron James during the past 20 years, you probably have heard an announcer declare: “You can’t stop him, you can only hope to contain him.”
2023-09-11 20:00

What China's new smartphone means for Wall Street
Stock prices of chipmakers have soared over the last year as AI became the story of 2023. But in recent weeks, there's been a notable drop in those shares as growing tensions between the US and China cloud their outlook.
2023-09-11 19:57

Black holes may lie even closer to us than we thought, new study finds
A new study has revealed that black holes could be lurking much closer to Earth than anticipated. A black hole in space is when "gravity pulls so much that even light can not get out," NASA explains. "The gravity is so strong because matter has been squeezed into a tiny space. This can happen when a star is dying." Due to no light being present, they are invisible. Only special tools can pick up on them. There are said to be around 10 million to 1 billion mass black holes in the Milky Way, according to Science Alert. However, astrologers only know of about 20 of them. Now, a recent study has revealed that they could be a lot closer to Earth than previously thought after investigating the Hyades cluster, "a group of stars located 150 light-years away". In a statement, astrophysicist Stefano Torniamenti of the University of Padua explained: "Our simulations can only simultaneously match the mass and size of the Hyades if some black holes are present at the centre of the cluster today (or until recently). The Hyades with hundreds of stars is said to be approximately 625 million years old. Due to its packed environment, "higher rates of collisions and mergers" are expected. At 153 light-years away, it is considered the closest star cluster to Earth. Researchers were able to observe two or three black holes in the Hyades, which are either still present or ejected less than 150 million years ago and hovering around the outskirts. "This observation helps us understand how the presence of black holes affects the evolution of star clusters and how star clusters in turn contribute to gravitational wave sources," Professor Mark Gieles of the University of Barcelona said. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-11 19:57

A look back at every iPhone ever
The iPhone is a device that redefined the term "cell phone." With about 1.2 billion active devices out in the world, Apple's trademark product created a revolution in the mobile phone industry, marking a shift away from the flip phones and keyboards of the past toward a future full of larger touch screens and powerful cameras.
2023-09-11 19:49

Volcano discovery could power electric cars for decades, scientists say
Scientists say they have discovered the largest lithium deposit in the world inside an extinct volcano in the United States, capable of meeting global battery demand for decades. Volcanologists and geologists reported evidence of the McDermitt caldera on the border of Nevada and Oregon containing up to 120 million tonnes of lithium, holding the potential to disrupt the price and supply dynamics of lithium globally. The ancient supervolcano exploded around 16 million years ago, forming the rare metal inside its volcanic rock. Lithium ion batteries are used to power everything from smartphones to electric vehicles, however the vast amounts of lithium required to produce them has led to a “lithium rush”, according to the researchers. Current supply forecasts suggest roughly 1 million metric tons of lithium will be needed to meet global demand by 2040 – an eight-fold increase from the total global production last year. Calculations from researchers estimate that the McDermitt caldera could contain up to 120 million metric tons of lithium, making it 12-times larger than the amount of lithium in the salt flats in Bolivia, which were previously considered the largest lithium deposit on Earth. “Developing a sustainable and diverse supply chain to meet lower-carbon energy and national security goals requires mining the highest-grade domestic lithium resources with the lowest waste:ore strip ratios to minimise both the volume of material extracted from the Earth,”the researchers noted in a study, published in Science Advances. “Volcano sedimentary lithium resources have the potential to meet this requirement, as they tend to be shallow, high-tonnage deposits with low waste:ore strip ratios.” Mining could begin as early as 2026, according to geologists at Lithium Americas Corporation, who made the discovery alongside GNS Science and Oregon State University. However, the site for a proposed mine on the Nevada side of the caldera has already drawn protests from environmental groups, as well as two area tribes who claim it would be built atop sacred land. Responding to the latest discovery, Tesla boss Elon Musk said the deposit will only be economically significant to the electric car industry if it can be refined in an efficient way. “Lithium ore is quite common throughout the world. The limiting factor is lithium refining,” Mr Musk posted on X, formerly known as Twitter, on Sunday. “Same goes for the cathode, which is primarily iron (medium range cars) or nickel (long range) and the anode, which is carbon. Refining matters more than ore.” Read More Battery breakthroughs are about to trigger a transport revolution Former Alibaba chair Daniel Zhang steps down as head of cloud division How Google reshaped the world – and is about to do it all over again Update your iPhone immediately
2023-09-11 19:16
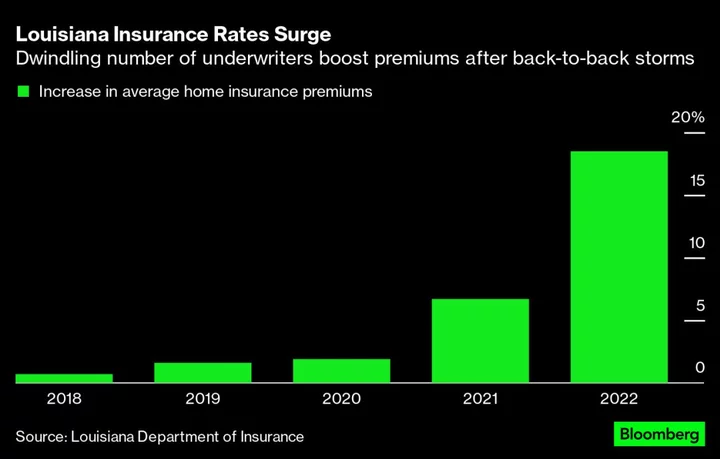
Climate Change Is Causing an Insurance Crisis in Louisiana
A little over a year ago, Peter Gardner, a Louisiana developer, completed rehabbing an apartment building with 144
2023-09-11 18:00

UK Geothermal Sites Near Financial Close After Auction Win
Two geothermal sites in south-west England are proceeding toward financial close after receiving government contracts in a renewables
2023-09-11 17:35

The best sites for geeky daters looking to make a connection
This content originally appeared on Mashable for a US audience and has been adapted for
2023-09-11 16:34

Crypto Exchange Coinbase to Disable Some Accounts of Indian Users
Sign up for the India Edition newsletter by Menaka Doshi – an insider's guide to the emerging economic
2023-09-11 15:48
You Might Like...

OpenAI Chooses London for Its First Corporate Office Outside US
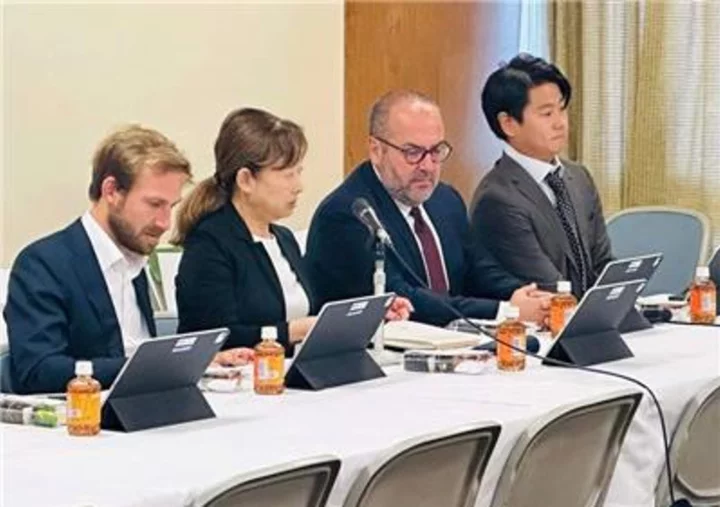

ADDING MULTIMEDIA Web3 Foundation Initiates Global Roundtable Discussions with Policy-makers, Starting in Japan
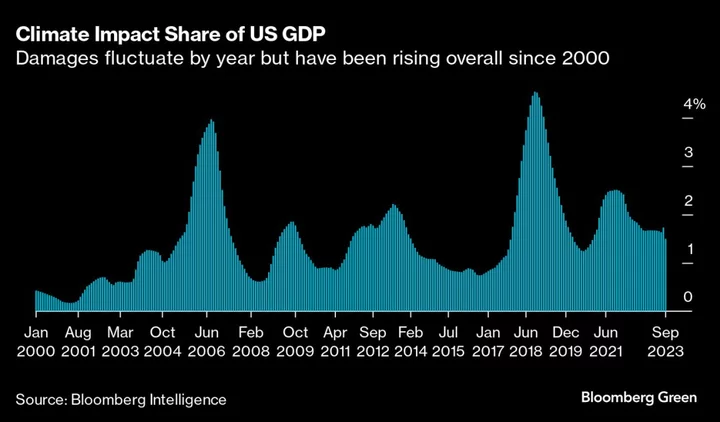
Nowhere Is Safe From Worsening Climate Change, New US Report Warns

Lawsuit says OpenAI violated US authors' copyrights to train AI chatbot

JPMorgan Expands $7 Billion ETF Platform With Funds Tied to PAB

From Climate to US-China Rivalry, Singapore Weighs How To Adapt

Innovative New Tool Empowers Unprecedented Health Plan Efficiency

TikTok details disinformation steps taken after EU demand
