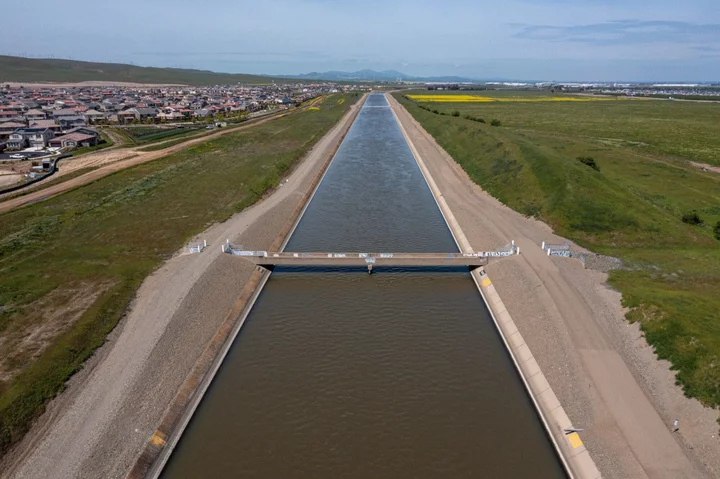

California Overestimates Water Supply by Ignoring Climate Change
California’s water agency has overestimated its supply because of a failure to account for climate change in its
2023-05-26 01:52

US Supreme Court rules against EPA in wetlands regulation challenge
By John Kruzel and Andrew Chung WASHINGTON (Reuters) -The U.S. Supreme Court on Thursday put another dent in the regulatory
2023-05-26 01:35
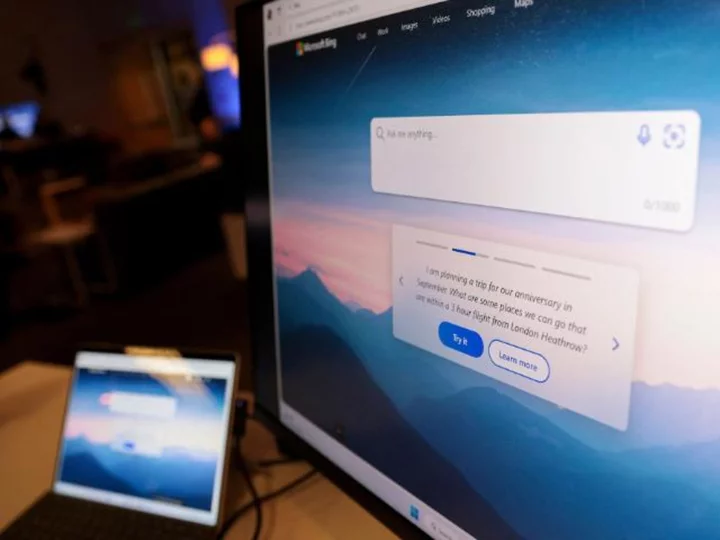
Microsoft leaps into the AI regulation debate, calling for a new US agency and executive order
Microsoft joined a sprawling global debate on the regulation of artificial intelligence Thursday, echoing calls for a new federal agency to control the technology's development and urging the Biden administration to approve new restrictions on how the US government uses AI tools.
2023-05-26 00:26

Westinghouse and Bechtel Solidify Project Team for AP1000® Nuclear Power Program in Poland
WARSAW, Poland--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 25, 2023--
2023-05-26 00:26

Kyle Bass Urges Investors to Develop Data Centers in a Play for AI
Kyle Bass, who has been predicting serious pain in the US office market, is taking a different view
2023-05-26 00:20

E Ink and MediaTek Expand Collaboration for Advanced eReader SoC Development
BILLERICA, Mass.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 25, 2023--
2023-05-25 23:31

Scientists develop powerful ‘pulses’ that can induce immediate ‘hibernation’ – and it could help us explore space
Scientists have developed new ultrasound technology that can induce immediate “hibernation”, they say. The system can be aimed at the head and bring on “torpor” a state similar to hibernation where mammals suppress their metabolism, reduce their body temperature and slow down other processes. The researchers behind the new system successfully brought it on in mice and rats, after pointing the ultrasound pulses at the animals’ heads. They suggest that it could work in humans – and might have important applications for long-distance space flight or medicine, they say. While further work is needed to understand how it might work on people, they suggest that it could be used when people have experienced acute emergencies or severe disease, for instance. If someone is in a car accident, for instance, they could essentially be put on ice until their organs are used for transplantation, for instance. It might also be useful in long journeys through space, where it would help reduce the amount of resources that people might stay alive if they are travelling to Mars or other distant locations. Mammals and birds keep high body temperatures and burn through a lot of energy. That characteristic is useful host of ways, but almost means that they require a lot of food and other resources. Some animals are able to limit the drawbacks of that situation by inducing torpor, which turns down many of those processes. It means that they use less energy, but are able to come back to living as normal after, without damage to their body. Humans are not able to do that. But if they were, it would be incredibly useful – which has led to the search for a noninvasive, safe and reliable way of inducing that state. The scientists found that directing ultrasound pulses at mice’s heads for around 10 seconds brought on the same conditions as torpor, with their heart rate slowing, their body temperature cooling and their metabolism slowing. They also built a special system that was able to measure that body temperature and send more of those pulses if a mouse appeared to be coming back to normal. Without that, however, the mice would wake back up again, returning to normal metabolism and body temperature. There are still a host of dangers, however. Experiments have shown that it is dangerous to bring animals back from those deep “torpid” states, and that they might not recover. If the mice were in cold environments, for instance, they did not spontaneously wake up. And any experiments in humans would be at risk of repeating those safety issues for people. The work is described in a new paper, ‘Induction of a torpor-like hypothermic and hypometabolic state in rodents by ultrasound’, published in Nature. Read More Apple lays bare danger of losing your health data What is Twitter Spaces and why did it go so wrong during DeSantis’s 2024 launch? Electric car range set to double with first production of breakthrough battery Apple lays bare danger of losing your health data What is Twitter Spaces and why did it go so wrong during DeSantis’s 2024 launch? Electric car range set to double with first production of breakthrough battery
2023-05-25 23:25

Weak Gaming GPU Sales Don't Matter for Nvidia as It Faces AI Gold Rush
Nvidia's GeForce RTX 4000 series is struggling to reignite demand for PC graphics cards, but
2023-05-25 23:13

Exclusive-AI rules 'cannot be bargained', EU's Breton says after OpenAI CEO threat
By Foo Yun Chee BRUSSELS Europe's artificial intelligence (AI) rules are not for negotiation, EU industry chief Thierry
2023-05-25 22:59
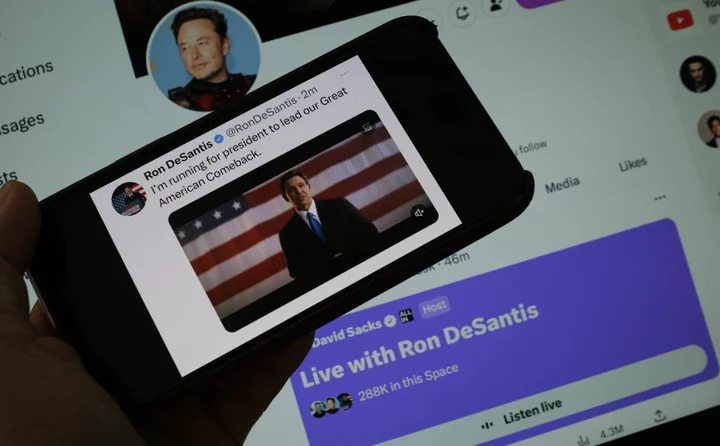
Twitter is removing view count metrics from videos
Ever since Elon Musk has taken over Twitter, it's become clear that he's obsessed with
2023-05-25 22:55
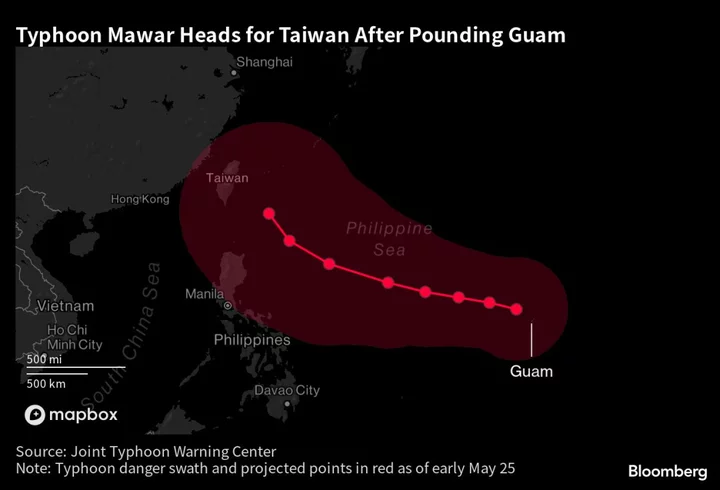
Guam Typhoon Highlights Threat to US Military’s Pacific Strategy
As Typhoon Mawar neared the coast of Guam early Wednesday, it also drew attention to an uncomfortable fact
2023-05-25 22:55

Safire Group Awarded Additional U.S. Air Force Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) Phase II Contract
KNOXVILLE, Tenn.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 25, 2023--
2023-05-25 22:31
You Might Like...

Electric car range set to double to 1,000km with first production of breakthrough battery

‘Battery Belt’ Factories Promise a Bright Future, But Workers Are Wary: Big Take Podcast
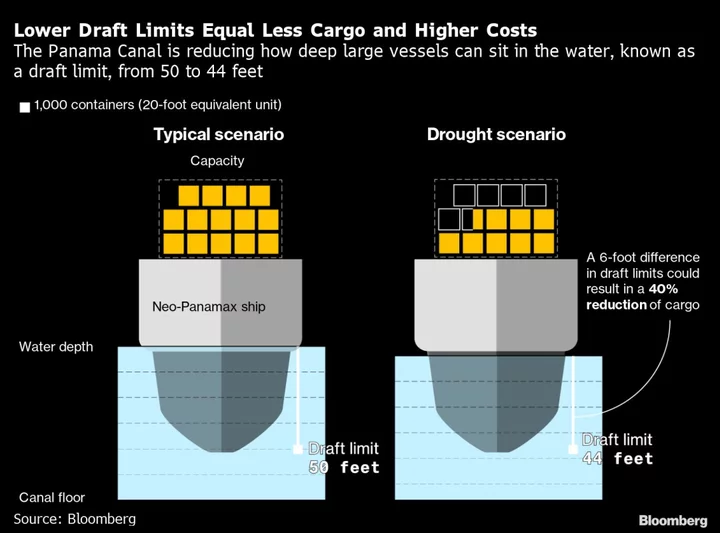
The Fed's Inflation Fight Faces a New Challenge: A Dry Panama Canal

South Africa Needs to Deal With ‘Energy Poverty,’ Minister Says

The Earth is being polluted by space junk, scientists discover

Canada Is Betting on Immigration for an Economic Boost: Big Take Podcast
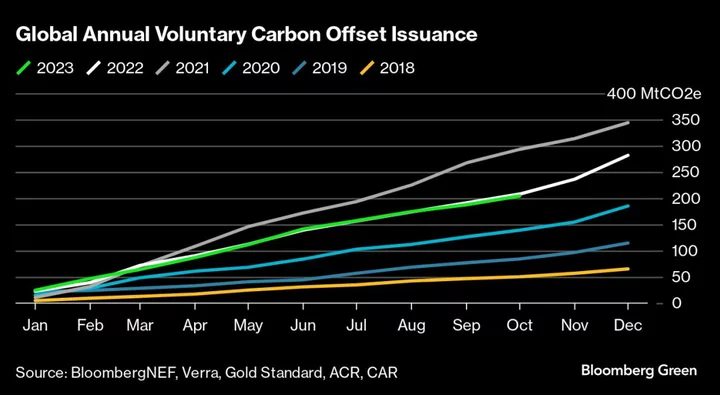
COP28 Holds Key to Global Carbon Market That Could Help Improve Offsets

UK Needs to Revive Rich Mining History to Counter China
