
New telescope reveals stunning images of the universe as it has never been seen before
The Euclid space telescope has revealed its first full-colour images, showing the universe as it has never been seen before. The five images, taken by the European Space Agency’s newly launched flying observatory, show the shining lights of distant galaxies. Scientists hope they will also prove useful in better understanding those galaxies, which includes some of the most massive structures in the known universe. Many of the galaxies have never been seen before. And much of the information in them could help explain mysteries such as dark energy and the expansion of the universe. The images released on Tuesday include one of the Perseus cluster of galaxies which shows 1,000 galaxies belonging to the cluster, and more than 100,000 additional galaxies further away in the background. Many of these faint galaxies were previously unseen, and some of them are so far that their light has taken 10 billion years to reach us. Another image captures the spiral galaxy IC 342, nicknamed the Hidden Galaxy, because it is difficult to observe as it lies behind the busy disc of our Milky Way, and so dust, gas and stars obscure our view. One of the new pictures is of globular cluster NGC 6397 - the second-closest globular cluster to Earth, located about 7,800 light-years away. Globular clusters are collections of hundreds of thousands of stars held together by gravity. These faint stars tell us about the history of the Milky Way and where dark matter is located. To create a 3D map of the universe, Euclid will observe the light from galaxies out to 10 billion light-years. The first irregular dwarf galaxy that Euclid observed is called NGC 6822 and is located just 1.6 million light-years from Earth. And the fifth image shows a panoramic and detailed view of the Horsehead Nebula, also known as Barnard 33 and part of the constellation Orion. Scientists hope to find many dim and previously unseen Jupiter-mass planets in their celestial infancy, as well as young brown dwarfs and baby stars, in this new observation. Professor Carole Mundell, ESA director of science, said: “Dark matter pulls galaxies together and causes them to spin more rapidly than visible matter alone can account for; dark energy is driving the accelerated expansion of the universe. “Euclid will for the first time allow cosmologists to study these competing dark mysteries together. “Euclid will make a leap in our understanding of the cosmos as a whole, and these exquisite Euclid images show that the mission is ready to help answer one of the greatest mysteries of modern physics.” Rene Laureijs, the ESA’s Euclid project scientist, said: “We have never seen astronomical images like this before, containing so much detail. “They are even more beautiful and sharp than we could have hoped for, showing us many previously unseen features in well-known areas of the nearby universe. “Now we are ready to observe billions of galaxies, and study their evolution over cosmic time.” Euclid was launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral in Florida on July 1. Named after the ancient Greek mathematician Euclid, the two-tonne probe made its way towards an area in space known as the second Lagrange point, where the gravitational forces of Earth and the sun are roughly equal - creating a stable location for the spacecraft. The UK has contributed £37 million towards the £850 million mission, with scientists playing key roles in designing and building the probe and leading on one of the two scientific instruments on board. Dr Caroline Harper, head of space science at the UK Space Agency, said: “These first colour images showcase Euclid‘s enormous potential, giving us incredibly sharp images of galaxies and stars, and helping us understand more about the impacts of dark matter and dark energy on the universe. “The UK has played an important role in the mission, leading on the development of the visible imager (VIS) instrument and on key elements of the data processing pipeline, funded by the UK Space Agency. “And this is just the start - UK researchers will be using Euclid data for many years to come to make significant new scientific discoveries about the composition and evolution of the cosmos.” Additional reporting by Press Association Read More Euclid space telescope releases first full-colour images of cosmos First full-colour images of universe captured by Euclid telescope revealed Watch again: ESA reveals first full-colour images of ‘dark universe’ from Euclid Tim Peake: Possibility of all-UK space mission a ‘very exciting development’ Strange purple light phenomenon ‘Steve’ spotted across UK skies Nasa sending VR headset up to ISS to treat astronaut’s mental health
2023-11-08 03:00
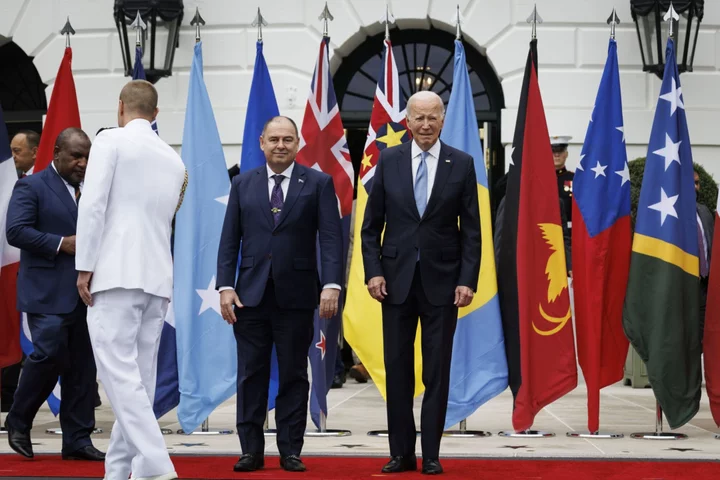

US, China Vie for Influence at Upcoming Pacific Forum, With Climate Change in Focus
The world’s two largest powers will descend on the small Pacific nation of the Cook Islands this week
2023-11-08 02:00

Former Meta employee tells Senate company failed to protect teens safety
By Katie Paul NEW YORK A former Meta employee is testifying before a U.S. Senate subcommittee on Tuesday,
2023-11-08 01:54

'Sophisticated' prosthetic hand found on medieval skeleton
If you thought prosthetic hands were too advanced for people living hundreds of years ago, think again. Archaeologists have found the remains of a man who died in Medieval Germany, who had prosthetics in place of several fingers. The grave was found by pipeline workers in Freising, a town near Munich. The Bavarian State Office for Monument Preservation said: “Even for experienced archaeologists, this was a particularly special find: a skeleton in which parts of the fingers of its left hand are missing.” The archaeologists removed the metal from the man’s skeleton to restore and analyse it. They came to the conclusion that he had lost his fingers at some point in his life. Walter Irlinger, deputy of the general conservator at BSOMP, said: “The hollow prosthetic on the left hand replaced four fingers. The index, middle, ring and pinky fingers are individually formed out of sheet metal and are immobile. The prosthetic fingers lie slightly curved, parallel to one another.” The prosthetic also had scraps of fabric and leather, suggesting that the fingers had a leather cover, and were tied to the hand using straps. There was also a gauze-like material inside the fingers, which may have acted as a cushion for the man’s skin from contact with the metal. That period of German history included the Thirty Years’ War, which ended in 1648, which would have increased the need for amputations and prosthetics. One of the most famous amputees from the time was Götz von Berlichingen – or “Götz of the Iron Hand”. He was a German knight who lost his right hand from a cannon injury at the siege of Landshut in 1504. “In the past, prosthetics looked very much like what they were replacing,” said Jacky Finch, a researcher in the KNH Center for Biomedical Egyptology at the University of Manchester. “Nowadays, implants are placed in the sensory system to control nerve action, rather than devices attached to the body by straps or artificially powered.” The BSOMP statement continued: “Doctors at that time were already thinking about how they could make life easier for amputees. “In central Europe, there are currently around 50 similar prostheses from the late middle ages to early modern age that are known.” How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-08 01:36
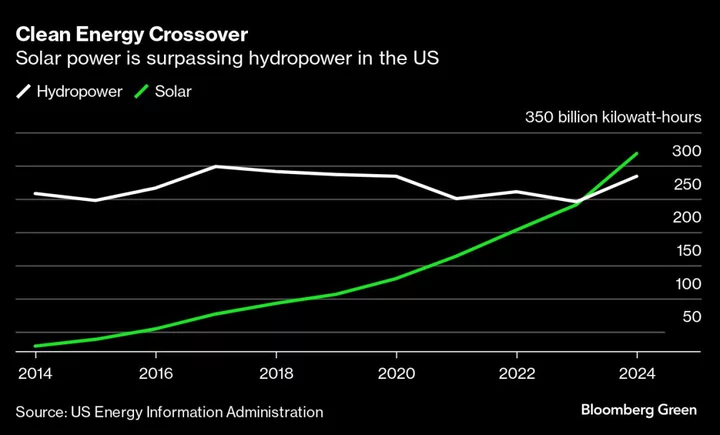
US Solar Generation to Surpass Hydropower in 2024 for First Time
The US is on track to generate more electricity from sunshine next year than from hydropower for the
2023-11-08 00:48

Mystery ‘eye burn’ outbreak linked to NFT event
Several attendees at an NFT festival in Hong Kong have been hospitalised after they reported experiencing vision issues, eye-burning sensations and sunburned skin after the event, which was allegedly lit with UV lighting. ApeFest 2023 was held from Friday to Sunday for members of the Bored Ape Yacht Club and their guests. To be a member, people must own an NFT within the collection of digital ape artworks. The Bored Ape Yacht Club artworks, created by blockchain company Yuga Labs, gained notoriety for becoming an exclusive online club that includes celebrities who have bought a Bored Ape NFT, such as Madonna, Justin Beiber, Serena Williams and many more, according to Decrypt. The NFTs, which, like cryptocurrency, sit on a blockchain; the person who owns the image has sole intellectual property rights and can choose to sell to another owner. Many crypto and NFT owners and fans went to the event, but some came away from the experience with bizarre symptoms. Attendees took to X (formerly Twitter) to ask other fest-goers if they had similar symptoms. One user wrote: “Anyone else’s eyes burning from last night? Woke up at 3am with extreme pain and ended up in the ER.” To which another person, under the username @CryptoJune777, replied: “I woke up at 04:00 and couldn’t see anymore. Had so much pain and my whole skin is burned. Needed to go to the hospital.” @CryptoJune77 also added that a doctor said that it could have been the UV lighting coming from the stage that burned their skin and damaged their eyes. Many other people replied to the tweets, saying they had experienced the same issue, with some also adding that they had to go to hospital. Another user, Adrian ZduÅ„czyk, said he had to pay $3000HKD ($383USD) for his hospital expenses after he was diagnosed with “photokeratitis over both eyes” due to unprotected exposure to UV radiation. “So many of my friends are still unaware they must seek medical help to make sure they end up with no damage, as well,” the user wrote. “Please go get your eyes checked immediately. We’ve most likely been exposed to experience similar to Mt Everest climbers - snow blindness.” UV radiation can cause photokeratitis, which is essentially like sunburning your eye, which can produce symptoms such as blurriness, tearing, redness and, in rare cases, temporary vision loss or colour changes, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Photokertitis is often associated with snow blindness, as climbers, snowboarders, or skiers can experience it when the sun reflects off ice and snow. After the sunburn allegations started circulating on social media, the Bored Ape Yacht Club issued a statement on X. “Apes, we are aware of the eye-related issues that affected some of the attendees of ApeFest and have been proactively reaching out to individuals since yesterday to try and find the potential root causes,” they said in their post. “Based on our estimates, we believe that much less than 1% of those attending and working the event had these symptoms.” “While nearly everyone has indicated their symptoms have improved, we encourage anybody who feels them to seek medical attention just in case,” the club added. The owner of the Bored Ape Yacht Club project, Yuga Labs, told The Verge that it is aware of the situation and is taking the reports seriously. “We are actively reaching out and in touch with those affected to better understand the root cause,” said a spokesperson for the company. “Based on our estimates, the 15 people we’ve been in direct communication with so far represent less than one per cent of the approximately 2,250 event attendees and staff at our Saturday night event.” The Independent has contacted Yuga Labs for further comment. Read More Guidance set to urge parents not to buy smartphones for primary school children ChatGPT update allows anyone to make their own personalised AI assistant Elon Musk weighs in on the scooped bagel debate Guidance set to urge parents not to buy smartphones for primary school children ChatGPT update allows anyone to make their own personalised AI assistant Elon Musk weighs in on the scooped bagel debate
2023-11-08 00:40

Canada Seen Missing 2030 Climate Target Due to Government Delays
Canada is on track to miss its 2030 climate target largely due to delays in rolling out key
2023-11-08 00:29
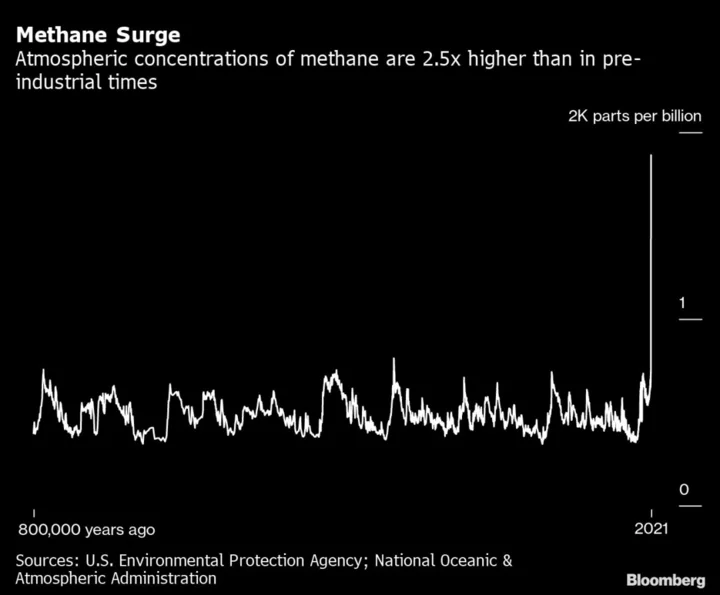
China, World’s Top Methane Emitter, Issues Plan to Cut Pollution
China, the world’s largest emitter of methane, said it will boost monitoring, reporting and data transparency to reduce
2023-11-07 23:16

GlobalFoundries projects profit above estimates in positive sign for chip market
Contract chipmaker GlobalFoundries forecast fourth-quarter profit above analysts' estimates on Tuesday, providing the latest sign that a supply
2023-11-07 21:53
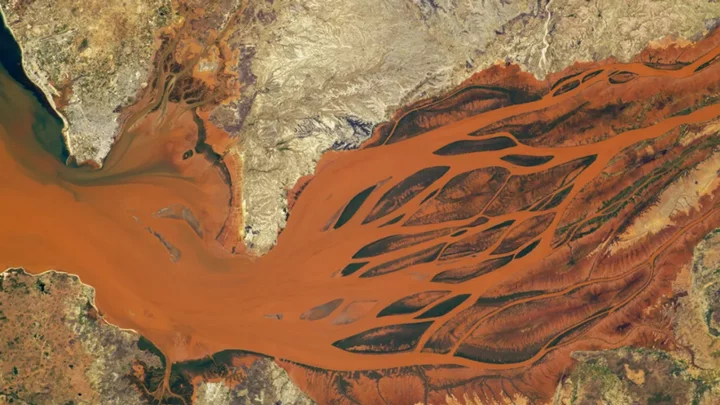

Astronauts capture the 'blood of Earth' in stunning photo
The Earth is home to truly stunning natural features, but sometimes you need a new perspective to appreciate it all over again. Thankfully, the experts at NASA are on hand to remind us just how incredible our planet is with the release of new photos showing the “blood of Earth”. The incredible images seem to show it bleeding, with dramatic red liquid appearing to cascade over the surface. However, it’s nothing at all to do with blood – which is probably just as well. Instead, the first picture shows the Laguna Colorada in the Bolivian Andes in South America from space. Remarkably, the image was taken by an astronaut onboard the International Space Station (ISS) using just a Nikon digital camera. The fact that it was taken more than 400 kilometres away from Earth on a handheld device is pretty staggering, and it offers a look at a natural phenomenon which we’d never otherwise get to see. The first picture shows the impact of red algae flourishing in the shallow water of the laguna, while the second shows the Betsiboka River Delta in Madagascar. This time, the red colour comes as a result of the iron-rich sediment. It’s pretty awe-inspiring stuff, and it’s not the first time that red “blood” has been seen running from our planet, either. Antarctica’s Blood Falls is a bizarre geographical feature in the McMurdo Dry Valleys region of the continent, and it’s one of the strangest natural phenomena you're likely to see. It features a flow of water the colour of blood that can be seen seeping out from a glacier into the ocean. The mystery behind it has fascinated members of the scientific community for decades, but a solution has now been found. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-11-07 20:15

Apple Shrunk the iPhone’s Carbon Footprint. There’s a Way to Shrink It Even Further
Apple has announced a dizzying array of products this year, though none more central to its business than
2023-11-07 20:00

European "photonics" chip companies call for $4.5 billion in EU funding
AMSTERDAM Executives from a group of Europe's largest "photonic" computer chip companies have called on the European Union
2023-11-07 19:55
You Might Like...

DeSantis campaign accused of using fake AI images of Trump hugging Fauci in ad
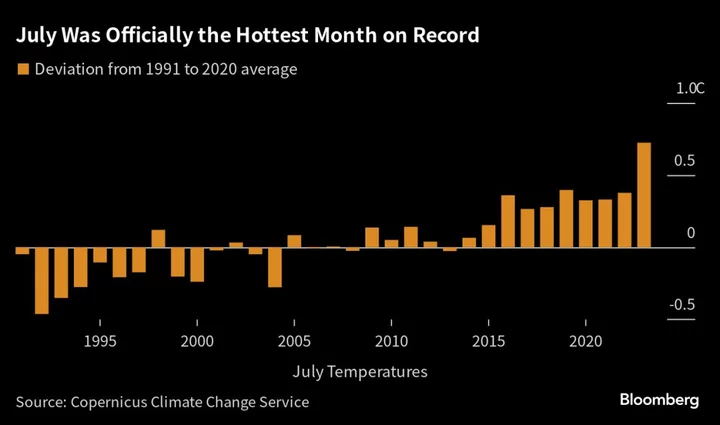
July Was the Hottest Month on Record

WhatsApp unveils new feature to protect ‘your most intimate conversations’

Navigator CO2 Cancels US Corn Belt Carbon Pipeline Plan

Spotify reports strong user growth, raises prices
Chinese artists boycott big social media platform over AI-generated images

These Stocks Are Moving the Most Today: Salesforce, Snowflake, Pure Storage, Tesla, Nutanix, and More

What to watch this weekend: ‘Succession’ finale, John Wick, Matchbox Twenty, 'American Born Chinese'
