
Scientists unveil 'missing' law of nature in landmark discovery
A group of scientists and philosophers claim to have identified a “missing law of nature”, in a discovery which has huge implications for our understanding of how, basically, everything works. Most of us are familiar with the names – if not the intricacies – of many of the physical laws which govern the world and beyond, such as gravity and thermodynamics. And yet, no established physical law has been able to describe the behaviours of countless complex systems that exist across the universe – until now. In a paper published in the PNAS journal on 16 October, a multidisciplinary team from some of the US’s top institutes and universities, unveiled a new law claiming to do just that. In a nutshell, their law states that evolution is not limited to life on Earth, it also occurs in other massively complex systems – from planets to atoms. This means that these systems naturally “evolve” to states of greater diversity, and complexity. In other words, the researchers found evolution to be a common feature of the natural world's complex systems which, according to the Carnegie Institution for Science, comprise the following characteristics: “They are formed from many different components, such as atoms, molecules, or cells, that can be arranged and rearranged repeatedly “Are subject to natural processes that cause countless different configurations to be formed.” Only a small fraction of these configurations survive via a process of natural selection called “selection for function”. According to the researchers, regardless of whether the system is living or nonliving, when a new configuration works and function improves, evolution occurs. The authors' new law – which they have christened "the Law of Increasing Functional Information" – states that the system will evolve "if many different configurations of the system undergo selection for one or more functions." "An important component of this proposed natural law is the idea of 'selection for function,'" the study’s lead author, astrobiologist Dr Michael L. Wong, explained. The team’s research builds on Charles Darwin’s theory of natural selection, which suggests the function exists to ensure the “survival of the fittest”. For their work, Dr Wong and his team expanded on this perspective, pointing to the existence of three types of this selection for function in nature. The first, most basic type, they claim, is stability – the stable arrangements of atoms or molecules which are selected to continue. Second, are dynamic systems which are selected for their ongoing supplies of energy. And the third, and most intriguing, function is "novelty" – the tendency of evolving systems to explore new configurations which can lead to surprising new behaviours or characteristics. Novelties are, ironically, nothing new. Indeed, life’s evolutionary history is rich with examples: photosynthesis evolved when single cells learned to harness light energy; multicellular life evolved when cells learned to cooperate; and species evolved thanks to advantageous new behaviours such as walking and thinking. The same type of evolution happens in the mineral kingdom, as the Carnegie Institution for Science notes in a release published by Phys.org. Indeed, Earth's minerals, which began with about 20 at the dawn of our solar system, now number almost 6,000 known today. This is thanks to the ever more complex physical, chemical, and biological processes which have occurred over the past 4.5 billion years. The paper also notes that just two major elements – hydrogen and helium – formed the first stars shortly after the big bang. Those earliest stars then used this hydrogen and helium to create around 20 heavier chemical elements, which was built upon by the next generation of stars. "Charles Darwin eloquently articulated the way plants and animals evolve by natural selection, with many variations and traits of individuals and many different configurations," co-author and research lead Robert M. Hazen explained. "We contend that Darwinian theory is just a very special, very important case within a far larger natural phenomenon. “The notion that selection for function drives evolution applies equally to stars, atoms, minerals, and many other conceptually equivalent situations where many configurations are subjected to selective pressure." The new law has a number of exciting implications, including a deeper understanding of how the Universe itself came to exist. It could also help explain how life differs from other complex evolving systems, and could help aid the search for life elsewhere. Furthermore, at a time when increasingly autonomous AI systems are of increasing concern, it’s very handy to have a law that characterises how both natural and symbolic systems evolve. It also offers insights into how we could artificially influence the rate of evolution of some systems which, again, could prove invaluable. The key point to remember, as Dr Wong put it, is that whilst life is the “most striking example of evolution”, it’s not the only one. Evolution, it transpires, is everywhere. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
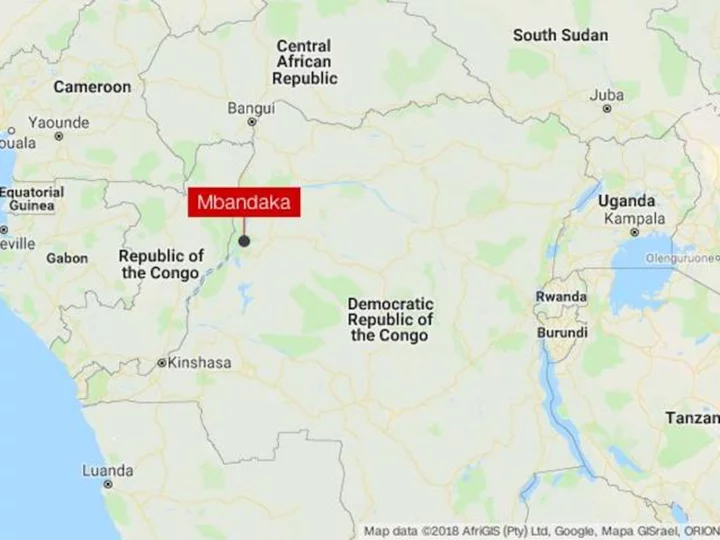
Congo boat tragedy death toll climbs to 52, dozens still missing
The bodies of at least 52 people have been recovered from the Congo River after their boat capsized late last week, a provincial minister said on Monday, warning that the death toll could rise further with many still missing.
1970-01-01 08:00

3 Braves club options to decline for 2024, 1 to pick up
The Atlanta Braves have several club options to decide on. Here are three the team should opt out of, and one player Atlanta should keep around.
1970-01-01 08:00

Johnny Marr stopped drinking after kind Noel Gallagher gesture
Johnny Marr decided it was best to stop drinking after he agreed to replace a guitar he gifted Noel Gallagher whilst hungover.
1970-01-01 08:00

Russia fines Zoom $1.18 million for operating without local office -RIA
MOSCOW A Russian court on Tuesday fined Zoom Video Communications 115 million roubles ($1.18 million) for operating without
1970-01-01 08:00

Chelsea handed £80m boost in potential Stamford Bridge rebuild
Chelsea have been handed a big boost in their plans to redevelop Stamford Bridge after successfully acquiring the majority of a piece of neighbouring land from a local veterans charity.
1970-01-01 08:00

J&J lifts profit outlook on strong demand for top-seller Stelara
(Reuters) -Johnson & Johnson on Tuesday raised its 2023 profit forecast, helped by resilient demand for its blockbuster anti-inflammatory drug
1970-01-01 08:00

Choice Hotels offers to buy Wyndham for $7.8 billion
(Reuters) -Choice Hotels on Tuesday proposed to acquire Wyndham Hotels and Resorts for about $7.8 billion in a cash and
1970-01-01 08:00
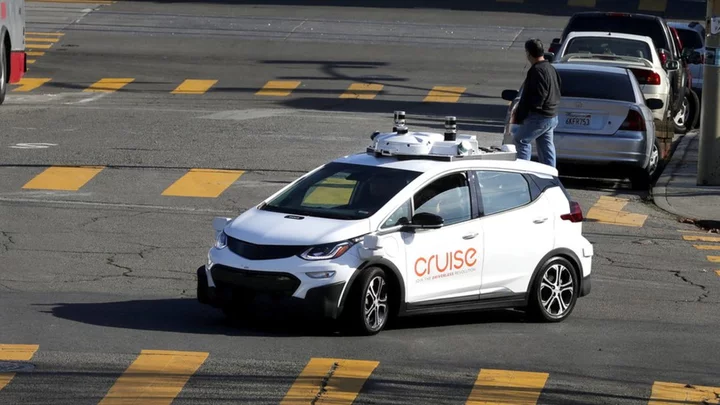

Cruise self-driving cars investigated after two accidents
The US safety regulator is looking into GM's Cruise self-driving cars after reports of pedestrian injuries.
1970-01-01 08:00
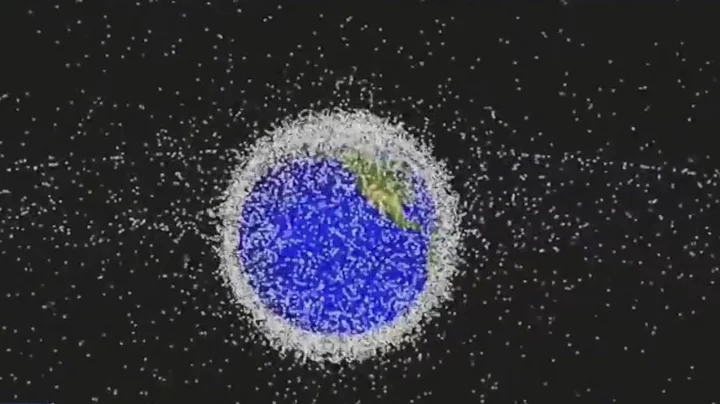

The Earth is being polluted by space junk, scientists discover
Minuscule traces of metal from space junk that's designed to be disposable are invisibly polluting the Earth's atmosphere, a new study has found. In recent times, spacecrafts launched into space have been designed so that they fall out of orbit and fall back down to Earth after their intended use. So instead of the materials crashing on land, they can burn up in the upper atmosphere. Although the debris of rockets and satellites burn up when re-entering the planet's atmosphere, the consequences of metal vapour being left behind currently remain unknown. But given the amount of space exploration taking place, the amount of metal vapour is expected to rise in the years to come. Physicist Daniel Murphy of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has led a team of researchers to investigate what effects this metal vapour could have as well as its impact over time and this study was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, as per Science Alert. He listed "iron, silicon, and magnesium from the natural meteoric source" as the current refractory material in stratospheric particular. Murphy has warned how this composition could be affected by the metal vapour from space junk. "However, the amount of material from the reentry of upper-stage rockets and satellites is projected to increase dramatically in the next 10 to 30 years," he wrote. "As a result, the amount of aluminum in stratospheric sulfuric acid particles is expected to become comparable to or even exceed the amount of meteoric iron, with unknown consequences for inclusions and ice nucleation." To find out if metal vapour remained, Murphy and his team took and analyzed 500,000 stratospheric aerosol droplet samples to see if they had traces of spacecraft metals. Aerosols contain sulfuric acid droplets made from the oxidation of the carbonyl sulfide gas and in the atmosphere, this can appear naturally or as a pollutant. Metal and silicon traces can be found in these droplets too, acquired from meteors which vaporize upon atmospheric entry. Around 20 metals were discovered from this research, and while some metals had similar ratios to the vaporizing meteors, other metals such as lithium, aluminium, copper, and lead exceeded the anticipated amounts. Particles from vaporized spacecraft were found in 10 per cent of stratospheric aerosols over a certain size while other common spacecraft metals such as niobium and hafnium were also present. Consequently, these traces of spacecraft particles could affect how water freezes into ice in the stratosphere, and stratospheric aerosol particles could change in size. Due to more space exploration planned in an "era of rapid growth" for the industry, the researchers predict "the percentage of stratospheric sulfuric acid particles that contain aluminum and other metals from satellite reentry will be comparable to the roughly 50 per cent that now contain meteoric metals." Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Rema's Calm Down falls off Billboard Hot 100 after setting new record
Nigerian music star Rema's song Calm Down falls off the Billboard Hot 100 chart after 57 weeks.
1970-01-01 08:00
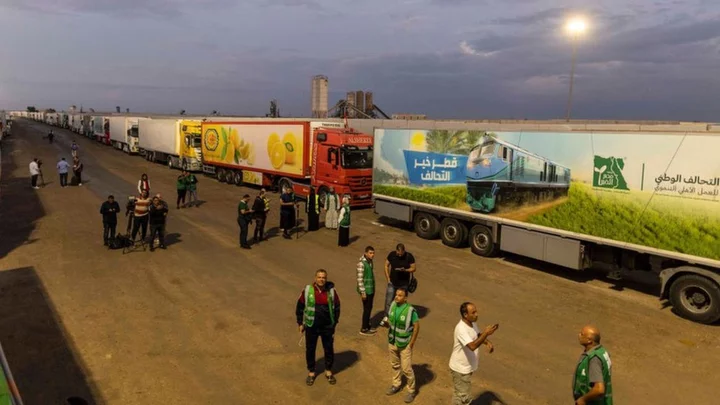

Why Egypt remains reluctant to open Rafah crossing to Gaza
Hundreds of lorries carrying aid are parked up on the Egyptian side of the Rafah crossing.
1970-01-01 08:00
