
University professor claims that 'aliens 100 per cent live among us'
A university professor who worked on US government programmes relating to UFOs has said he believes that "aliens are 100 per cent living among us". Dr Garry Nolan of Stanford University School of Medicine spoke about “advanced forms of intelligence” during a recent conference called The Pentagon, Extraterrestrial Intelligence and Crashed UFOs. He said: "I think it's an advanced form of intelligence that using some kind of intermediaries. It's not that they walk among us wearing a skin suit. You're going to put something there that I think of as an intelligence test." Nolan went on to say: "They're showing up and saying who amongst you are intelligent enough to realize what it is you're looking at. 'Can you see what's in front of you for what it really is? Can you see the anomalous data point?" Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter He then spoke his own experiences of people reverse engineering ‘downed crafts', while adding that he believes aliens will not come to Earth to harm humans. "100%" Aliens Have Already Arrived -Dr. Garry Nolan | SALT iConnections New York www.youtube.com "A tiny piece of knowledge from that could revolutionize what we're doing,” Nolan stated. "I'm not worried about them coming and raiding us or taking our women and children. That's not my concern. My concern is how do we use it,” he went on to say. Meanwhile, it was recently claimed that Logan Paul could be the most important figure in the UFO-hunting community. Documentary filmmaker James Fox has spoken about a piece of footage that was rumoured to have been uncovered by UFO specialist Chuck Clark around 30 years ago. The footage is thought to have been recorded by two men in the Nevada desert and has been the focus of much speculation in the community of UFO hunters. While the clip has never been widely shared and has become the stuff of urban legend, Fox has revealed that Paul could be the key to the video being shared with the public in the future. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
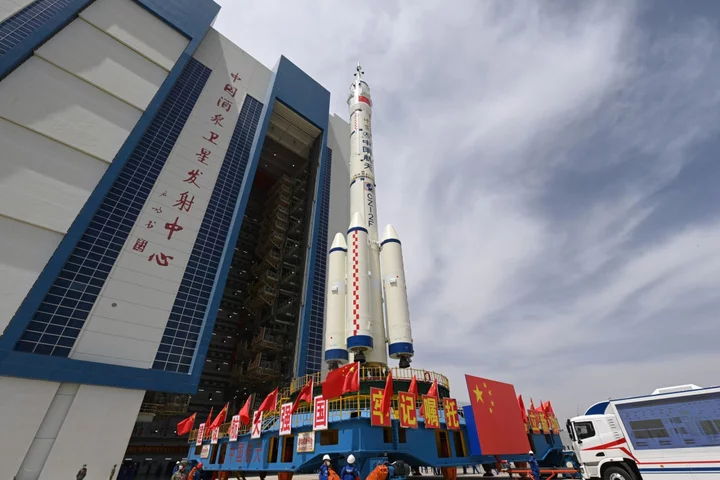

Xi Charm Offensive Turns to Space as ‘Divine Craft’ Launches
China’s Shenzhou 16 mission blasted off from deep in the Gobi Desert, showcasing the space program’s rapid progress
1970-01-01 08:00
Biden-McCarthy Debt Limit Deal Puts Government Services on a Diet
The debt-limit deal would rein in spending on some federal government services but barely dents the roughly $20
1970-01-01 08:00

Taylor Swift fans are getting amnesia at her concerts due to a rare phenomenon
Taylor Swift fans have shared feelings of forgetfulness after seeing the pop-star performing on her highly anticipated Eras Tour. Speaking to Time, Jenna Tocatlian, 25, spoke about her experience seeing Swift at Gillette Stadium in Massachusetts. Speaking about one of Swift’s nightly surprise songs At the concert that Tocatlian attended the song was 'Better Man', but she said: ‘If I didn’t have the 5-minute video that my friend kindly took of me jamming to it, I probably would have told every that it didn’t happen.’ She added that as she waited to leave the stadium, during an hour-long wait, she found it difficult to grasp the reality of a night she had waited so long to experience. ‘It’s hard to put together what you actually witness,’ she told Time. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter It seems Tocatlian isn’t the only one experiencing ‘post-concert amnesia’. Taking to social media, many users have shared their inability to recall the events of the show, from small details to even significant parts of the concert. Some described having feelings of guilt after waiting so long to attend the show and leaving without explicit memories. Ewan McNay, an associate professor in the psychology department at the State University of New York in Albany, told Time that the experience may be a result of too much excitement. He explained that ‘this is not a concert-specific phenomenon - it can happen any time you’re in a highly emotional state.’ This is because as a result of feelings of excitement, the body’s stress levels increase, which in turn causes neurons associated with memory to start firing indiscriminately. McNay shared that this makes forming new memories ‘really hard.’ The biological explanation for this occurrence is due to the body seeing excitement as a state of stress. The body then starts pumping out the brain’s favourite molecule for memory: glucose. Because the body thinks it’s stressed, it doesn’t want to waste energy on memory formation. Your vagal nerves, which regulate internal organ functions, also become stimulated as a result of the perceived stress. All this causes the part of your brain responsible for emotional processing - known as your amygdala - to release a neurotransmitter called norepinephrine. This helps to categorise memories as having high emotional content, increasing the likelihood that they’ll be stored vividly in your mind. However, McNay goes on to explain that too much of this chemical release can actually invest the process, especially if caffeine or alcohol are included. Which leads to your brain struggling to create and store new memories. For those who want to try and have a better memory of an important event, whether it’s seeing Taylor Swift, or getting married, McNay shared some helpful techniques. He says to try and achieve a ‘semi-meditative state’ and relaxing. He also adds that physical responses such as screaming at a concert tells the body that you must be scared. If you stand still in a more relaxed state, your brain will know not to get too excited, and aid the formation of new memories. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
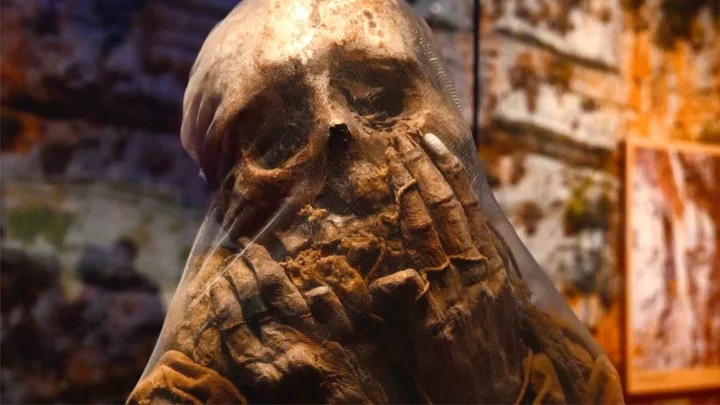

Scientists have discovered the 'largest mummy workshop' ever
Archeologists in Egypt have discovered what they have called "the largest and most complete" mummification workshop ever at a site near Cairo. As reported by The Telegraph, the site dates back to the 4th century and the 30th Dynasty in the early Ptolemaic era and is near the oldest stone pyramid in Egypt, Djoser's Step. Mostafa Waziri, the secretary general of Egypt’s supreme council of Antiquities is quoted as saying: "Two stone beds for human embalming were found in a number of rooms. The beds were approximately two metres long and one metre wide. They were made of stone blocks and covered with a layer of mortar that sloped down to a gutter. "The mummification beds were used to prepare the body by extracting the human organs, which were placed in canopic jars that were discovered." Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The mud brick site, which was only used for humans, reportedly contains two embalming beds, body organ tools, linen rolls and canopic jars. In a separate workshop, which was dedicated to mummifying just animals, bronze tools were found as well as five limestone beds. Other artifacts that were found were intact wooden and stone statues, funerary objects as well as inscriptions on the tomb walls about various activities including hunting. Perhaps the most interesting element of the find were two tombs believed to belong to high-ranking officials and priests that had been carved into stone. Experts at the site predict that the two tombs are 4,400 and 3,400-year-old respectively. This comes after scientists in Germany found the remains of a lost city dubbed 'the Atlantis of the North Sea' which was swept away by waves more than 600 years ago. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
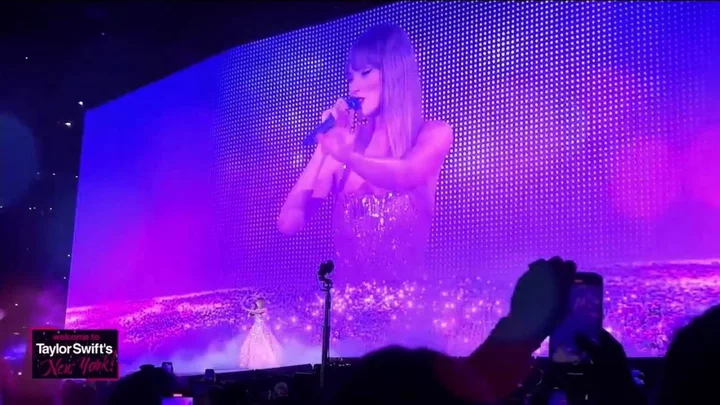

Taylor Swift fans are forgetting parts of the singer's concerts thanks to rare phenomenon
Taylor Swift fans have shared feelings of forgetfulness after seeing the pop-star performing on her highly anticipated Eras Tour. Speaking to Time, Jenna Tocatlian, 25, spoke about her experience seeing Swift at Gillette Stadium in Massachusetts. Speaking about one of Swift’s nightly surprise songs At the concert that Tocatlian attended the song was 'Better Man', but she said: ‘If I didn’t have the 5-minute video that my friend kindly took of me jamming to it, I probably would have told every that it didn’t happen.’ She added that as she waited to leave the stadium, during an hour-long wait, she found it difficult to grasp the reality of a night she had waited so long to experience. ‘It’s hard to put together what you actually witness,’ she told Time. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter It seems Tocatlian isn’t the only one experiencing ‘post-concert amnesia’. Taking to social media, many users have shared their inability to recall the events of the show, from small details to even significant parts of the concert. Some described having feelings of guilt after waiting so long to attend the show and leaving without explicit memories. Ewan McNay, an associate professor in the psychology department at the State University of New York in Albany, told Time that the experience may be a result of too much excitement. He explained that ‘this is not a concert-specific phenomenon - it can happen any time you’re in a highly emotional state.’ This is because as a result of feelings of excitement, the body’s stress levels increase, which in turn causes neurons associated with memory to start firing indiscriminately. McNay shared that this makes forming new memories ‘really hard.’ The biological explanation for this occurrence is due to the body seeing excitement as a state of stress. The body then starts pumping out the brain’s favourite molecule for memory: glucose. Because the body thinks it’s stressed, it doesn’t want to waste energy on memory formation. Your vagal nerves, which regulate internal organ functions, also become stimulated as a result of the perceived stress. All this causes the part of your brain responsible for emotional processing - known as your amygdala - to release a neurotransmitter called norepinephrine. This helps to categorise memories as having high emotional content, increasing the likelihood that they’ll be stored vividly in your mind. However, McNay goes on to explain that too much of this chemical release can actually invest the process, especially if caffeine or alcohol are included. Which leads to your brain struggling to create and store new memories. For those who want to try and have a better memory of an important event, whether it’s seeing Taylor Swift, or getting married, McNay shared some helpful techniques. He says to try and achieve a ‘semi-meditative state’ and relaxing. He also adds that physical responses such as screaming at a concert tells the body that you must be scared. If you stand still in a more relaxed state, your brain will know not to get too excited, and aid the formation of new memories. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
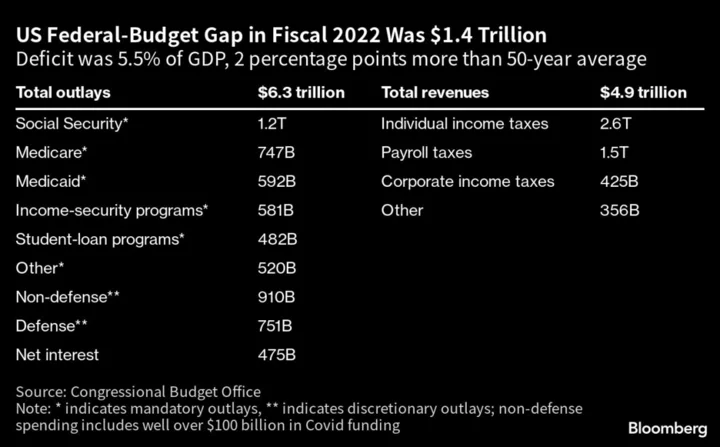
'Bizarre' footage captures moment an octopus wakes up from a 'nightmare'
Rare footage of an octopus having a 'nightmare' has been captured and it is fascinating scientists who study the creatures. The footage comes courtesy of The Rockefeller University in New York where an octopus named 'Costello' was studied for 24 hours a day in a laboratory. In papers published by bioRxiv, they found that on at least four occasions the octopus woke up abruptly and began flailing its tentacles, changing colour, shooting black ink into the water and displaying "antipredator and predatory behaviors." The experts put this behaviour down to temporary stress which they believe was likely caused by a bad dream or even a memory from a previous traumatic moment. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Speaking to LiveScience, Eric Angel Ramos, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Vermont said: "It was really bizarre because it looked like he was in pain; it looked like he might have been suffering, for a moment. And then he just got up like nothing had happened, and he resumed his day as normal." Compilation of the four abnormal sleep-associated episodes documented in a male Octopus insularis. www.youtube.com One thing the scientists did note is that when Costello arrived in the lab he appeared to be recovering from several severe injuries having lost the majority of two of his tentacles following an attack. When suggesting that Costello could have been dreaming about the attack the scientists noted: "can result in long-term behavioral and neural hypersensitivity." There has also been suggestions from Robyn Crook an associate professor of biology at San Francisco State University, who was not involved in the study, that Costello's behaviour could be down to something called senescence, which is when an octopus' body begins to break down before their death. Ramos concluded that he could not "exclude that senescence could be one of the drivers of this." This is not the first time footage of this nature has been captured. Back in 2019, PBS shared incredible footage of an octopus changing colour while it appeared to be dreaming. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Japan Calls on North Korea to Abandon ‘Satellite’ Launch
Japan called for North Korea to refrain from a planned rocket launch it described as a “serious provocation”
1970-01-01 08:00
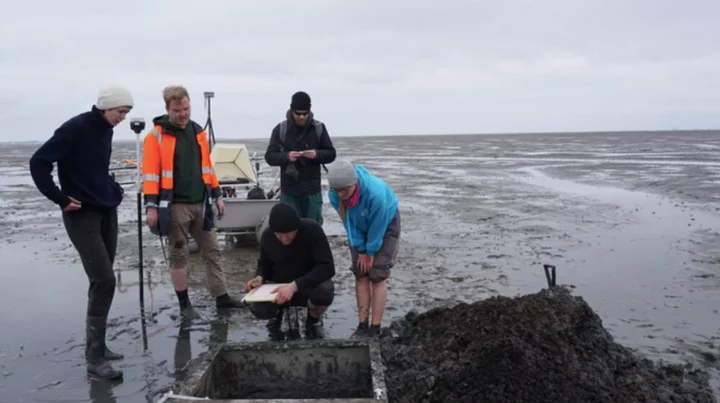

Europe's 'City of Atlantis' discovered after being lost for 600 years
The remains of a church from a sunken town known as the 'Atlantis of the North Sea' has been discovered beneath the mud on Germany's coast. The church is believed to be part of a site called 'Rungholt' located in the Wadden Sea. The town, which was previously thought to be a local legend, has not been seen since 1362 after it was submerged beneath the waves during an intense storm. However, new research has shown that the town really did exist and that they had built reinforcements around the settlement to protect them from the severe elements. The research was carried out on the area by archeologists from Kiel University, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, the Center for Baltic and Scandinavian Archaeology, and the State Archaeology Department Schleswig-Holstein. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Searching the Wadden Sea which is the longest stretch of intertidal sand and mud flats on Earth, the team, using geophysical imaging technology found man-made mounds that had been constructed to protect the town against the tides. Amongst this structure were the foundations of a building which the team determined had to be a church which may have been the location of the town centre. In a statement, Dr. Dennis Wilken, a geophysicist at Kiel University of Kiel University said: "Settlement remains hidden under the mudflats are first localized and mapped over a wide area using various geophysical methods such as magnetic gradiometry, electromagnetic induction, and seismics." Dr. Hanna Hadler from the Institute of Geography at Mainz University added: "Based on this prospection, we selectively take sediment cores that not only allow us to make statements about spatial and temporal relationships of settlement structures, but also about landscape development." Dr. Ruth Blankenfeldt, an archaeologist at ZBSA also suggested that the "special feature of the find lies in the significance of the church as the centre of a settlement structure, which in its size must be interpreted as a parish with superordinate function." The storm that washed away Rungholt has gone down in history as one of the largest to ever hit the region, affecting not just Germany but also the Netherlands, Denmark and the UK. The storm happened on January 1362 and has since been referred to as "the great drowning of men." According to historical reports, Rungholt was once a busy trading port for fishermen but was also populated by taverns, brothels and churches. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00

Scientists might have discovered a simple way to stop the ageing process
The feeling of hunger could be a simple way to stop the ageing process, according to a new study. Researchers at the University of Michigan tricked fruit flies into feeling hungry which resulted in the insects living longer – even when they eat their calorie intake. The study - published in Science - suggests that the perception of insatiable hunger alone can generate the anti-aging effects of intermittent fasting. (And since it’s the perception rather than actual hunger, it means the bugs don’t actually have to starve). Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter "We've sort of divorced [the life extending effects of diet restriction] from all of the nutritional manipulations of the diet that researchers had worked on for many years to say they're not required," physiologist Scott Pletcher said, as per Michigan Medicine. "The perception of not enough food is sufficient." You may have heard the term intermittent fasting before, as it is a popular diet fad that consists of going for extended periods of time without eating, followed by a period of eating normally, according to Bupa. Despite its popularity, evidence supporting its benefits is limited in terms of research on humans. Perhaps you’re thinking… why fruit flies? Well, the insects actually share 75 percent of the same disease-related genes as us, while also sharing similar qualities to mammals in terms of their metabolisms and brains, according to Science Alert. In the research, branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) essential nutrients that appear to trigger feelings of fullness in flies when consumed, were used. The fruit flies maintained their hunger through getting fed snacks low in BCAA and their hunger was noticed through how much the insects ate from a buffet of food hours after eating the snack. More food was consumed by flies who earlier ate a low-BCAA snack, and they choose protein over carbs, focusing on what their hungry bodies needed. From learning this, the team directly activated the neurons in fruit flies that trigger hunger responses, they found these hunger-stimulated flies also lived longer. "Demonstration of the sufficiency of hunger to extend life span reveals that motivational states alone can be deterministic drivers of ageing," Pletcher and colleagues wrote in the findings. Along with fruit flies, rodents have also been part of the study and both seems to suggest calorie restriction can extend life and is good for our health too. Though of course, more extensive research is required to see whether or not this is also the case with humans. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
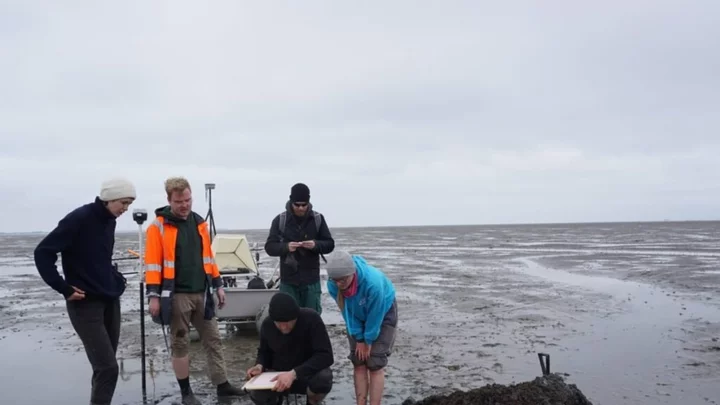

Remains of the 'Atlantis of the North Sea' discovered in Germany
The remains of a church from a sunken town known as the 'Atlantis of the North Sea' has been discovered beneath the mud on Germany's coast. The church is believed to be part of a site called 'Rungholt' located in the Wadden Sea. The town, which was previously thought to be a local legend, has not been seen since 1362 after it was submerged beneath the waves during an intense storm. However, new research has shown that the town really did exist and that they had built reinforcements around the settlement to protect them from the severe elements. The research was carried out on the area by archeologists from Kiel University, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, the Center for Baltic and Scandinavian Archaeology, and the State Archaeology Department Schleswig-Holstein. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Searching the Wadden Sea which is the longest stretch of intertidal sand and mud flats on Earth, the team, using geophysical imaging technology found man-made mounds that had been constructed to protect the town against the tides. Amongst this structure were the foundations of a building which the team determined had to be a church which may have been the location of the town centre. In a statement, Dr. Dennis Wilken, a geophysicist at Kiel University of Kiel University said: "Settlement remains hidden under the mudflats are first localized and mapped over a wide area using various geophysical methods such as magnetic gradiometry, electromagnetic induction, and seismics." Dr. Hanna Hadler from the Institute of Geography at Mainz University added: "Based on this prospection, we selectively take sediment cores that not only allow us to make statements about spatial and temporal relationships of settlement structures, but also about landscape development." Dr. Ruth Blankenfeldt, an archaeologist at ZBSA also suggested that the "special feature of the find lies in the significance of the church as the centre of a settlement structure, which in its size must be interpreted as a parish with superordinate function." The storm that washed away Rungholt has gone down in history as one of the largest to ever hit the region, affecting not just Germany but also the Netherlands, Denmark and the UK. The storm happened on January 1362 and has since been referred to as "the great drowning of men." According to historical reports, Rungholt was once a busy trading port for fishermen but was also populated by taverns, brothels and churches. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
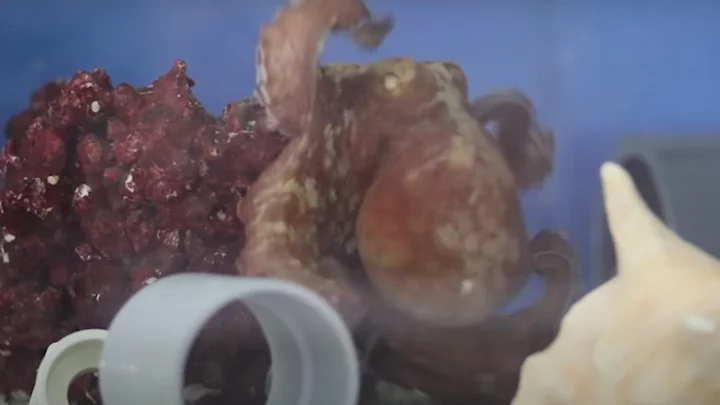
Pineapple 'needles' revelation has people questioning whether they'll eat the fruit again
A revelation about pineapples only made noticeable thanks to a TikTok account and a microscope, has people reevaluating whether they are allergic to the fruit or not. You may have noticed that whenever you've eaten a chunk of the delicious citrus fruit, you are sometimes greeted with an odd tingling sensation in your mouth. Well, if you've ever been curious about what that actually is then the TikTok account SF Microscopy is here to help. The account analyses all sorts of things under a microscope and exposes all the fascinating and dare we say worrying things that lie within everyday objects that the naked eye cannot see. One of the biggest videos on the account, with 35 million views, is about a pineapple. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter In the caption, the person behind the account writes: "One of my favorite fruits is pineapple, but every time I eat them, my mouth tingles. I read that the fruit contains raphides! Kiwis, grapes, taro, and yams also have large amounts of these crystals. These needles serve as a defensive function against insect herbivores to deter them from eating the plant’s fruits and protect the seeds. The needles work with other chemical substances, like bromelain in the pineapple, to amplify the effects." If that sounds a bit farfetched then take a look at the video for yourself and you might find that its even more alarming than you might have imagined. @sf_microscopy One of my favorite fruits is pineapple, but every time I eat them, my mouth tingles. I read that the fruit contains raphides! Kiwis, grapes, taro, and yams also have large amounts of these crystals. These needles serve as a defensive function against insect herbivors to deter them from eating the plant’s fruits and protect the seeds. The needles work with other chemcial substances, like bromelain in the pineapple, to amplify the effects. #microscope #microbiology #underthemicroscope #microscopy #microcosmos #nature #pineapple #crystals #fyp #fypage #fypシ The fact that these needles are real has people second-guessing the feeling they experience when they eat pineapples. One person wrote: "My mouth be sore as hell after going crazy on them pineapples & kiwis." Another added: "So ummmm…I’m not allergic to pineapple????" A third said: "Makes sense that when i accidentally inhaled pineapple juice i just about died." While a fourth person said: "It’s gonna stop me i dont feel like being stabbed." Will you stop eating pineapples now that you know this? I think this writer might be willing to live in blissful, delicious ignorance. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
1970-01-01 08:00
